444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2750
Market Overview: The Asia-Pacific Open Banking market stands at the forefront of financial innovation, reshaping traditional banking landscapes and fostering enhanced connectivity across the region. Open Banking, driven by technological advancements and regulatory initiatives, is transforming how financial services are delivered and consumed. This comprehensive article delves into the intricacies of the Asia-Pacific Open Banking market, exploring key trends, market drivers, challenges, and the vast opportunities it presents.
Meaning: Open Banking refers to a financial model that allows third-party financial service providers to access and utilize consumer banking data through Application Programming Interfaces (APIs). By enabling the secure exchange of data between banks and authorized third-party providers, Open Banking aims to enhance competition, drive innovation, and empower consumers with more personalized and efficient financial services.
Executive Summary: The Asia-Pacific Open Banking market has experienced remarkable growth, propelled by a confluence of factors including regulatory mandates, technological advancements, and shifting consumer expectations. As financial ecosystems embrace openness, the market offers a dynamic landscape of opportunities for banks, FinTechs, and other stakeholders. Understanding the key market insights is essential for navigating this evolving landscape successfully.

Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights:
Market Drivers:
Market Restraints:
Market Opportunities:
Market Dynamics: The Asia-Pacific Open Banking market operates within a dynamic environment shaped by technological evolution, regulatory changes, and evolving consumer expectations. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for financial institutions seeking to harness the full potential of Open Banking and stay competitive in the evolving financial landscape.
Regional Analysis:
Competitive Landscape:
Leading Companies in the Asia-Pacific Open Banking Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
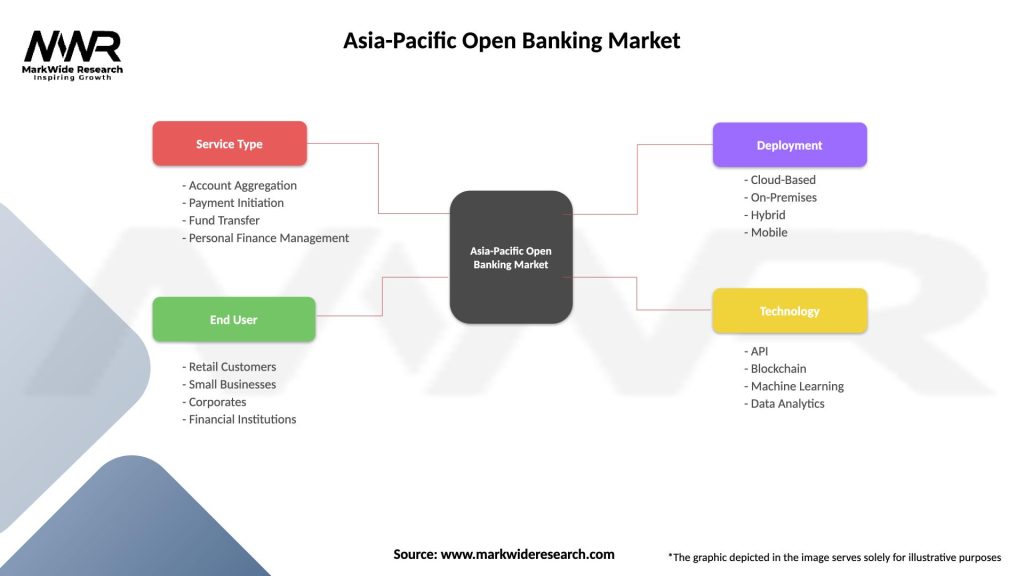
Segmentation: The Asia-Pacific Open Banking market can be segmented based on various factors, including:
Segmentation allows for a more nuanced understanding of the diverse market dynamics across different service types, end-users, and countries.
Category-wise Insights:
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders:
SWOT Analysis: A SWOT analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the Asia-Pacific Open Banking market’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats:
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Understanding these factors through a SWOT analysis empowers industry participants to capitalize on strengths, address weaknesses, seize opportunities, and mitigate potential threats.
Market Key Trends:
Covid-19 Impact: The Covid-19 pandemic has accelerated the digital transformation of the financial services sector, including the adoption of Open Banking. Some key impacts of Covid-19 on the Asia-Pacific Open Banking market include:
Key Industry Developments:
Analyst Suggestions:
Future Outlook: The future outlook for the Asia-Pacific Open Banking market is poised for significant growth and transformation, driven by a convergence of factors including regulatory reforms, technological advancements, and shifting consumer expectations. As governments in the region increasingly embrace open banking frameworks and digitalization initiatives, the market presents vast opportunities for financial institutions, fintech startups, and technology providers. Key trends such as the proliferation of APIs (Application Programming Interfaces), the rise of digital payment solutions, and the emergence of collaborative ecosystems will shape the trajectory of the market. Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence, blockchain, and machine learning technologies will drive innovation in product offerings and customer experiences. By leveraging these trends and fostering strategic partnerships, stakeholders in the Asia-Pacific Open Banking market can unlock new revenue streams, improve operational efficiency, and enhance financial inclusion across the region.
Conclusion: The Asia-Pacific Open Banking market represents a transformative force reshaping the financial services landscape. Regulatory support, technological advancements, and a growing appetite for innovation are propelling the adoption of Open Banking across the region. As financial institutions, FinTechs, and technology players collaborate to unlock the full potential of Open Banking, the market is poised for continued growth and evolution.
What is Open Banking?
Open Banking refers to a financial services model that allows third-party developers to build applications and services around financial institutions. It enables secure access to consumer banking data, fostering innovation and competition in the financial sector.
What are the key players in the Asia-Pacific Open Banking Market?
Key players in the Asia-Pacific Open Banking Market include companies like Ant Financial, DBS Bank, and Commonwealth Bank of Australia, which are actively developing open banking solutions and partnerships to enhance customer experiences, among others.
What are the main drivers of the Asia-Pacific Open Banking Market?
The main drivers of the Asia-Pacific Open Banking Market include the increasing demand for personalized financial services, advancements in technology such as APIs, and regulatory support promoting transparency and competition in the banking sector.
What challenges does the Asia-Pacific Open Banking Market face?
Challenges in the Asia-Pacific Open Banking Market include concerns over data security and privacy, the need for standardization across different jurisdictions, and resistance from traditional banks wary of sharing customer data.
What opportunities exist in the Asia-Pacific Open Banking Market?
Opportunities in the Asia-Pacific Open Banking Market include the potential for fintech startups to innovate new financial products, the ability for banks to enhance customer engagement through personalized services, and the expansion of cross-border banking solutions.
What trends are shaping the Asia-Pacific Open Banking Market?
Trends shaping the Asia-Pacific Open Banking Market include the rise of digital wallets, increased collaboration between banks and fintechs, and the growing emphasis on customer-centric services that leverage data analytics for better decision-making.
Asia-Pacific Open Banking Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Service Type | Account Aggregation, Payment Initiation, Fund Transfer, Personal Finance Management |
| End User | Retail Customers, Small Businesses, Corporates, Financial Institutions |
| Deployment | Cloud-Based, On-Premises, Hybrid, Mobile |
| Technology | API, Blockchain, Machine Learning, Data Analytics |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Asia-Pacific Open Banking Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at