444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2750
The Asia-Pacific cotton seed market represents one of the most dynamic agricultural segments in the global economy, driven by increasing demand for high-quality cotton production and advanced agricultural technologies. This region encompasses major cotton-producing nations including China, India, Pakistan, and Australia, which collectively contribute to a substantial portion of global cotton cultivation. The market is experiencing robust growth, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.2% through the forecast period, reflecting the region’s commitment to agricultural modernization and sustainable farming practices.
Regional dynamics in the Asia-Pacific cotton seed market are characterized by diverse climatic conditions, varying agricultural policies, and different levels of technological adoption. Countries like India and China dominate production volumes, while nations such as Australia lead in technological innovation and seed quality standards. The market benefits from favorable government initiatives promoting cotton cultivation, increasing mechanization of farming practices, and growing awareness about genetically modified cotton varieties that offer enhanced pest resistance and improved yields.
Market participants are increasingly focusing on developing hybrid and genetically modified cotton seeds that can withstand regional challenges such as bollworm infestations, drought conditions, and soil salinity issues. The adoption rate of Bt cotton varieties has reached approximately 78% in major producing regions, demonstrating the market’s shift toward technologically advanced solutions. This transformation is supported by extensive research and development activities, strategic partnerships between seed companies and agricultural research institutions, and comprehensive farmer education programs.
The Asia-Pacific cotton seed market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem encompassing the production, distribution, and commercialization of cotton seeds across the Asia-Pacific region, including both conventional and genetically modified varieties designed for optimal cotton fiber production.
Cotton seeds serve as the fundamental input for cotton cultivation, determining crucial factors such as fiber quality, yield potential, disease resistance, and environmental adaptability. The market encompasses various seed types including hybrid varieties, genetically modified organisms (GMOs), and conventional open-pollinated varieties, each designed to meet specific regional requirements and farming conditions. These seeds undergo rigorous testing and certification processes to ensure compliance with local agricultural standards and international quality benchmarks.
Market scope extends beyond mere seed production to include comprehensive support services such as technical advisory, crop protection solutions, and post-harvest management guidance. The industry involves multiple stakeholders including seed manufacturers, agricultural research institutions, government regulatory bodies, distribution networks, and end-user farmers. This interconnected ecosystem ensures the delivery of high-quality cotton seeds that can maximize productivity while maintaining environmental sustainability and economic viability for farming communities across the region.
Strategic market analysis reveals that the Asia-Pacific cotton seed market is positioned for substantial expansion, driven by increasing cotton demand from the textile industry and growing adoption of advanced agricultural technologies. The market demonstrates strong fundamentals with China and India maintaining their positions as dominant players, collectively accounting for approximately 68% of regional production. This growth trajectory is supported by favorable demographic trends, rising disposable incomes, and expanding textile manufacturing capabilities across the region.
Key growth drivers include the widespread adoption of genetically modified cotton varieties, government support for agricultural modernization, and increasing awareness about sustainable farming practices. The market benefits from technological innovations such as precision agriculture, digital farming solutions, and advanced breeding techniques that enhance seed performance and crop yields. Additionally, the growing emphasis on organic cotton production is creating new opportunities for specialized seed varieties that meet organic certification requirements.
Market challenges encompass regulatory complexities surrounding GMO approvals, climate change impacts on agricultural productivity, and fluctuating cotton prices that affect farmer investment decisions. However, these challenges are being addressed through collaborative efforts between industry stakeholders, research institutions, and government agencies. The market outlook remains positive, with emerging opportunities in precision agriculture, biotechnology applications, and sustainable farming solutions expected to drive continued growth and innovation in the coming years.

Market intelligence indicates several critical insights that shape the Asia-Pacific cotton seed landscape. The following key insights provide a comprehensive understanding of market dynamics:
Primary market drivers propelling the Asia-Pacific cotton seed market include the expanding textile industry, which continues to experience robust growth driven by increasing consumer demand for cotton-based products. The region’s position as a global textile manufacturing hub creates sustained demand for high-quality cotton fiber, directly translating into increased cotton seed requirements. Government initiatives supporting agricultural modernization and crop diversification further accelerate market growth by providing financial incentives, technical support, and infrastructure development for cotton cultivation.
Technological advancement serves as a crucial driver, with biotechnology innovations enabling the development of superior cotton varieties that offer enhanced pest resistance, improved fiber quality, and higher yields. The adoption of precision agriculture technologies allows farmers to optimize seed selection, planting patterns, and crop management practices, resulting in improved productivity and profitability. Additionally, the growing awareness about sustainable farming practices is driving demand for cotton seeds that require reduced pesticide applications and water consumption.
Economic factors including rising disposable incomes, urbanization trends, and expanding middle-class populations across the region contribute to increased cotton consumption in domestic markets. The development of integrated supply chains connecting seed producers directly with cotton growers enhances market efficiency and reduces distribution costs. Furthermore, international trade agreements and export opportunities create additional demand for high-quality cotton production, encouraging farmers to invest in premium cotton seed varieties that meet global quality standards.
Regulatory challenges represent significant restraints in the Asia-Pacific cotton seed market, particularly regarding the approval and commercialization of genetically modified varieties. Complex regulatory frameworks and lengthy approval processes can delay the introduction of innovative cotton seed technologies, limiting market growth potential. Environmental concerns related to GMO cultivation and potential impacts on biodiversity create additional regulatory hurdles and public resistance in certain regions.
Economic constraints affecting smallholder farmers include limited access to credit facilities, high seed costs, and inadequate insurance coverage against crop failures. These factors restrict the adoption of premium cotton seed varieties and advanced farming technologies, particularly among resource-constrained farming communities. Market volatility in cotton prices creates uncertainty for farmers, affecting their willingness to invest in expensive hybrid or genetically modified seeds.
Technical limitations encompass challenges related to seed storage, distribution infrastructure, and quality maintenance throughout the supply chain. Inadequate cold storage facilities and transportation networks in rural areas can compromise seed viability and performance. Additionally, knowledge gaps among farmers regarding proper seed handling, planting techniques, and crop management practices can limit the effectiveness of advanced cotton seed varieties, reducing their market acceptance and adoption rates.
Emerging opportunities in the Asia-Pacific cotton seed market are substantial, driven by technological innovations and evolving agricultural practices. The development of climate-smart cotton varieties presents significant potential, as these seeds can address growing concerns about climate change impacts on agriculture. Opportunities exist for creating cotton seeds that are specifically adapted to changing weather patterns, water scarcity, and extreme temperature conditions prevalent in various parts of the region.
Digital agriculture integration offers transformative opportunities for market expansion, including the development of smart seed technologies embedded with sensors and data collection capabilities. These innovations enable real-time monitoring of crop performance, soil conditions, and environmental factors, providing valuable insights for optimizing cotton production. The growing adoption of precision farming techniques creates demand for specialized cotton seeds that can maximize the benefits of technology-driven agriculture.
Organic cotton production represents a rapidly growing market segment, with increasing consumer awareness about sustainable and environmentally friendly textiles. This trend creates opportunities for developing certified organic cotton seed varieties that meet stringent organic farming standards while maintaining competitive yields and fiber quality. Additionally, the expansion of e-commerce platforms and digital distribution channels provides new avenues for reaching farmers directly, reducing distribution costs and improving market accessibility.
Market dynamics in the Asia-Pacific cotton seed sector are characterized by complex interactions between supply and demand factors, technological innovations, and regulatory environments. The market exhibits cyclical patterns influenced by cotton price fluctuations, weather conditions, and global textile demand trends. These dynamics create both challenges and opportunities for market participants, requiring adaptive strategies and flexible business models.
Competitive dynamics are intensifying as international seed companies expand their presence in the region while local players strengthen their market positions through strategic partnerships and product innovations. The market is witnessing increased consolidation activities, with larger companies acquiring smaller regional players to enhance their distribution networks and local market knowledge. Innovation cycles are accelerating, with new cotton seed varieties being introduced more frequently to address evolving farmer needs and market requirements.
Supply chain dynamics are evolving toward greater integration and efficiency, with companies investing in direct distribution networks and digital platforms to improve farmer engagement. The market is experiencing a shift from traditional dealer-based distribution to more direct relationships between seed companies and farmers. According to MarkWide Research analysis, approximately 42% of cotton farmers now prefer direct purchasing relationships with seed manufacturers, indicating a fundamental change in market dynamics and customer preferences.
Comprehensive research methodology employed for analyzing the Asia-Pacific cotton seed market incorporates both primary and secondary research approaches to ensure data accuracy and market insights reliability. The methodology encompasses extensive field surveys, expert interviews, and stakeholder consultations across major cotton-producing regions including China, India, Pakistan, Australia, and emerging markets.
Primary research activities include structured interviews with seed manufacturers, agricultural researchers, government officials, and cotton farmers to gather firsthand insights about market trends, challenges, and opportunities. Field visits to cotton cultivation areas provide direct observations of farming practices, seed performance, and adoption patterns. Secondary research involves analysis of government agricultural statistics, industry reports, academic publications, and company financial statements to validate primary findings and identify market patterns.
Data validation processes ensure information accuracy through cross-referencing multiple sources, statistical analysis, and expert review panels. The research methodology incorporates quantitative analysis of market trends, growth patterns, and competitive positioning alongside qualitative assessment of market dynamics, regulatory impacts, and technological developments. This comprehensive approach provides a robust foundation for market analysis and strategic recommendations.
China maintains its position as the largest cotton seed market in the Asia-Pacific region, accounting for approximately 35% of regional consumption. The Chinese market is characterized by strong government support for cotton production, advanced agricultural technologies, and substantial investments in biotechnology research. Bt cotton adoption has reached saturation levels, with focus shifting toward developing varieties with enhanced fiber quality and environmental adaptability.
India represents the second-largest market, contributing around 28% of regional demand, with diverse agro-climatic conditions supporting various cotton seed varieties. The Indian market benefits from a large farming population, government subsidies, and increasing adoption of hybrid cotton varieties. Pakistan follows as a significant market player, with cotton cultivation being a major economic activity and substantial potential for market expansion through improved seed technologies and farming practices.
Australia leads in terms of technological innovation and seed quality standards, despite representing a smaller market share by volume. The Australian cotton seed market is characterized by high-tech farming practices, premium seed varieties, and strong research and development capabilities. Emerging markets including Vietnam, Bangladesh, and Myanmar show promising growth potential, driven by expanding textile industries and government initiatives to promote cotton cultivation as an alternative crop for economic diversification.
Market leadership in the Asia-Pacific cotton seed sector is distributed among several key players, each with distinct competitive advantages and market positioning strategies. The competitive landscape is characterized by intense rivalry, continuous innovation, and strategic partnerships aimed at expanding market reach and enhancing product portfolios.
Competitive strategies include investments in research and development, strategic acquisitions, partnerships with agricultural research institutions, and expansion of distribution networks. Companies are increasingly focusing on developing region-specific cotton varieties that address local challenges such as pest resistance, drought tolerance, and soil adaptability.
Market segmentation of the Asia-Pacific cotton seed market reveals distinct categories based on various criteria including seed type, technology, application, and distribution channels. This segmentation provides insights into market dynamics and growth opportunities across different segments.
By Seed Type:
By Technology:
By Application:
Hybrid cotton seeds represent the largest category, accounting for approximately 52% of market share due to their superior performance characteristics and consistent yield advantages. These varieties offer improved fiber quality, enhanced disease resistance, and better adaptability to diverse growing conditions. Farmer preference for hybrid seeds continues to grow as agricultural extension services promote their benefits and demonstrate their economic advantages through field demonstrations and training programs.
Genetically modified cotton seeds constitute a rapidly expanding category, with Bt cotton varieties leading adoption rates across major producing regions. This category benefits from reduced pesticide requirements, lower production costs, and improved crop safety for farmers. The development of second-generation GM varieties with stacked traits is creating new growth opportunities and addressing evolving pest resistance challenges.
Conventional cotton seeds maintain their relevance in specific market segments, particularly in regions with regulatory restrictions on GM crops and among farmers practicing organic agriculture. This category serves niche markets requiring non-GM varieties and provides cost-effective options for price-sensitive farming communities. Open-pollinated varieties continue to play an important role in subsistence farming systems and seed saving practices, though their market share is gradually declining in favor of improved varieties.
Seed manufacturers benefit from the expanding Asia-Pacific cotton seed market through increased revenue opportunities, economies of scale in production, and enhanced market penetration across diverse regional markets. The growing demand for advanced cotton varieties enables companies to invest in research and development activities, leading to innovative product development and competitive differentiation. Strategic partnerships with local distributors and agricultural institutions provide market access and customer relationship advantages.
Cotton farmers gain significant advantages from improved cotton seed varieties including higher yields, reduced production costs, and enhanced crop quality. Advanced seed technologies enable farmers to achieve productivity improvements of 15-25% compared to traditional varieties, directly impacting their economic returns. Additionally, pest-resistant varieties reduce pesticide applications, improving farm safety and environmental sustainability while lowering input costs.
Textile industry stakeholders benefit from consistent supply of high-quality cotton fiber, enabling better product quality and manufacturing efficiency. The availability of specialized cotton varieties with specific fiber characteristics supports the development of premium textile products and enhances competitiveness in global markets. Government agencies benefit from increased agricultural productivity, rural economic development, and enhanced food security through diversified farming systems and improved farmer incomes.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Biotechnology advancement represents the most significant trend shaping the Asia-Pacific cotton seed market, with companies investing heavily in developing next-generation GM varieties with multiple stacked traits. These innovations address complex agricultural challenges including pest resistance, herbicide tolerance, and improved fiber quality characteristics. Gene editing technologies such as CRISPR are emerging as powerful tools for precise crop improvement, enabling faster development of superior cotton varieties.
Sustainability focus is driving market transformation toward environmentally responsible cotton production practices. This trend encompasses the development of cotton seeds requiring reduced water consumption, lower pesticide applications, and improved soil health maintenance. Circular agriculture concepts are gaining traction, with emphasis on developing cotton varieties that support regenerative farming practices and carbon sequestration.
Digital integration is revolutionizing cotton seed marketing and distribution through e-commerce platforms, mobile applications, and digital advisory services. Precision agriculture technologies are enabling farmers to optimize seed selection, planting decisions, and crop management practices based on real-time data and predictive analytics. According to MWR research, digital platform adoption among cotton farmers has increased by 38% over the past two years, indicating rapid technological transformation in agricultural practices.
Recent industry developments highlight the dynamic nature of the Asia-Pacific cotton seed market, with significant investments in research and development, strategic partnerships, and technological innovations. Major seed companies are establishing regional research centers and breeding programs to develop location-specific cotton varieties that address local agricultural challenges and market requirements.
Regulatory developments include streamlined approval processes for GM cotton varieties in several countries, facilitating faster market introduction of innovative seed technologies. Government initiatives supporting cotton cultivation through subsidies, technical assistance, and infrastructure development are creating favorable market conditions for industry growth and farmer adoption of advanced seed varieties.
Technology partnerships between seed companies and agricultural technology providers are accelerating the development of integrated solutions combining superior genetics with precision farming tools. These collaborations are creating comprehensive value propositions for farmers, including seed technologies, crop protection products, and digital advisory services. Acquisition activities continue to reshape the competitive landscape, with companies seeking to expand their geographic presence and enhance their product portfolios through strategic transactions.
Strategic recommendations for market participants include prioritizing investments in climate-smart cotton seed development to address growing environmental challenges and changing weather patterns. Companies should focus on developing varieties with enhanced drought tolerance, heat resistance, and adaptability to diverse soil conditions prevalent across the Asia-Pacific region. Research collaboration with agricultural universities and government research institutions can accelerate innovation while reducing development costs and risks.
Market expansion strategies should emphasize building strong relationships with farming communities through comprehensive extension services, technical support, and farmer education programs. Companies should invest in local distribution networks and digital platforms to improve market accessibility and customer engagement. Product differentiation through specialized cotton varieties targeting specific market segments such as organic cotton, premium fiber quality, and niche applications can create competitive advantages and premium pricing opportunities.
Operational excellence initiatives should focus on supply chain optimization, quality assurance systems, and cost management to maintain competitiveness in price-sensitive markets. Companies should leverage digital technologies for demand forecasting, inventory management, and customer relationship management to improve operational efficiency and market responsiveness. Sustainability initiatives including environmental stewardship and social responsibility programs can enhance brand reputation and support long-term market positioning.
Market projections for the Asia-Pacific cotton seed market indicate sustained growth driven by technological innovations, expanding cotton cultivation, and increasing demand for high-quality cotton fiber. The market is expected to benefit from continued government support for agricultural modernization, growing adoption of precision farming technologies, and development of climate-resilient cotton varieties. Emerging economies in the region are likely to contribute significantly to market expansion as they develop their agricultural sectors and textile industries.
Technology evolution will continue to shape market dynamics, with next-generation GM varieties, gene editing technologies, and digital agriculture solutions creating new opportunities for market growth and differentiation. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in crop breeding and farm management is expected to accelerate the development of superior cotton varieties and optimize their performance in field conditions.
Market consolidation trends are likely to continue, with larger companies acquiring regional players to expand their market presence and enhance their product portfolios. This consolidation will create opportunities for improved research and development capabilities, enhanced distribution networks, and better customer service delivery. The market outlook remains positive, with MarkWide Research projecting continued expansion at a steady growth rate of 6.2% annually, supported by favorable demographic trends, technological advancement, and increasing cotton consumption across the region.
The Asia-Pacific cotton seed market presents substantial opportunities for growth and innovation, driven by technological advancement, expanding agricultural sectors, and increasing demand for sustainable cotton production. The market’s strong fundamentals, including large cultivation areas, supportive government policies, and continuous research and development investments, position it for sustained expansion in the coming years.
Key success factors for market participants include developing climate-smart cotton varieties, building strong farmer relationships, investing in digital technologies, and maintaining focus on sustainability and environmental stewardship. The market’s evolution toward more sophisticated seed technologies, precision agriculture integration, and sustainable farming practices creates opportunities for companies that can adapt to changing market requirements and farmer needs.
Strategic positioning in this dynamic market requires comprehensive understanding of regional differences, regulatory environments, and farmer preferences across diverse Asia-Pacific countries. Companies that can successfully navigate these complexities while delivering superior products and services are well-positioned to capitalize on the market’s growth potential and establish long-term competitive advantages in this vital agricultural sector.
What is Cotton Seed?
Cotton seed refers to the seeds of the cotton plant, which are used for various purposes including oil extraction, animal feed, and as a source of fiber. The seeds are rich in protein and oil, making them valuable in agricultural and industrial applications.
What are the key players in the Asia-pacific Cotton Seed Market?
Key players in the Asia-pacific Cotton Seed Market include Bayer Crop Science, Syngenta, and Dow AgroSciences, among others. These companies are involved in the development and distribution of genetically modified and conventional cotton seeds.
What are the growth factors driving the Asia-pacific Cotton Seed Market?
The growth of the Asia-pacific Cotton Seed Market is driven by increasing demand for cotton in the textile industry, advancements in seed technology, and the rising adoption of genetically modified cotton varieties. Additionally, the need for higher yield and pest resistance contributes to market expansion.
What challenges does the Asia-pacific Cotton Seed Market face?
The Asia-pacific Cotton Seed Market faces challenges such as regulatory hurdles regarding genetically modified organisms, fluctuating cotton prices, and environmental concerns related to pesticide use. These factors can impact the adoption and cultivation of cotton seeds.
What opportunities exist in the Asia-pacific Cotton Seed Market?
Opportunities in the Asia-pacific Cotton Seed Market include the development of sustainable cotton farming practices, increasing investments in agricultural biotechnology, and the potential for expanding into emerging markets. These factors can enhance the market’s growth prospects.
What trends are shaping the Asia-pacific Cotton Seed Market?
Trends in the Asia-pacific Cotton Seed Market include the rise of organic cotton production, the integration of precision agriculture technologies, and the focus on sustainable farming practices. These trends are influencing how cotton seeds are developed and utilized.
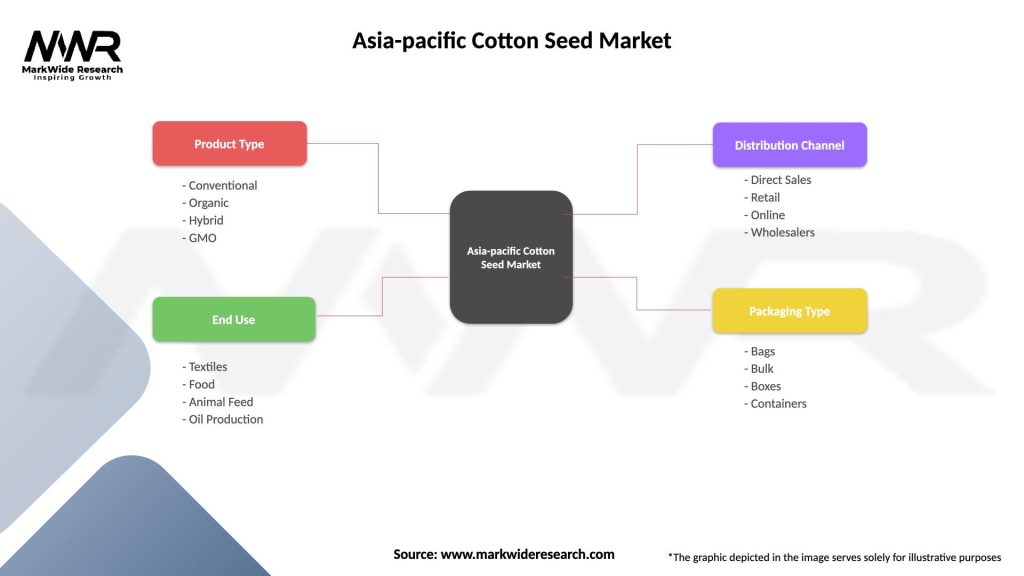
Asia-pacific Cotton Seed Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Conventional, Organic, Hybrid, GMO |
| End Use | Textiles, Food, Animal Feed, Oil Production |
| Distribution Channel | Direct Sales, Retail, Online, Wholesalers |
| Packaging Type | Bags, Bulk, Boxes, Containers |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the Asia-pacific Cotton Seed Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at