444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2750
Market Overview: The Asia-Pacific cloud seeding market takes center stage as a transformative force in weather modification technologies. This comprehensive exploration delves into the market’s current landscape, shedding light on its intricate dynamics, growth catalysts, challenges, and future trajectories.
Meaning: Cloud seeding, within the context of the Asia-Pacific region, refers to the deliberate introduction of seeding agents into clouds to enhance precipitation. This practice aims to augment water resources, mitigate drought conditions, and optimize weather patterns, offering solutions to address water scarcity challenges.
Executive Summary: The Asia-Pacific cloud seeding market has witnessed significant advancements, propelled by the region’s diverse climate conditions and the pressing need for sustainable water management solutions. While presenting a promising avenue for addressing water-related challenges, the market faces complexities related to meteorological uncertainties and public perception. Navigating key market insights, drivers, restraints, and dynamics is essential for stakeholders seeking to harness the potential of cloud seeding technologies.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights:
Market Drivers:
Market Restraints:
Market Opportunities:
Market Dynamics: The Asia-Pacific cloud seeding market operates within a dynamic ecosystem shaped by factors such as climatic variations, technological advancements, regulatory frameworks, and societal considerations. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for stakeholders to navigate complexities and make informed decisions.
Regional Analysis:
Competitive Landscape:
Leading Companies in Asia-Pacific Cloud Seeding Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
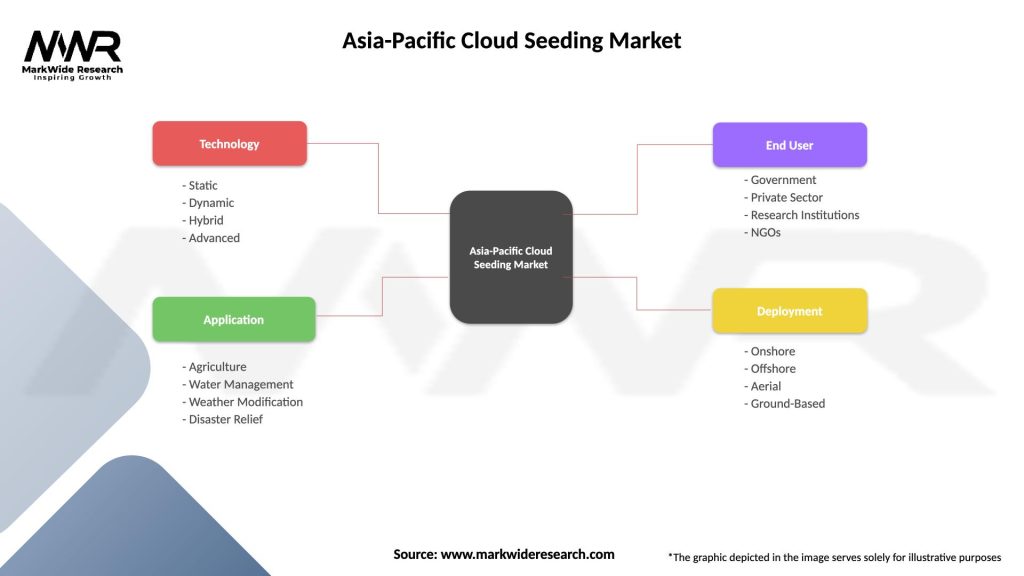
Segmentation: The Asia-Pacific cloud seeding market can be segmented based on various factors, including:
Segmentation provides a nuanced understanding of market dynamics, enabling stakeholders to tailor strategies to specific geographical and application-specific requirements.
Category-wise Insights:
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders:
SWOT Analysis:
Understanding these factors through a SWOT analysis empowers stakeholders to capitalize on strengths, address weaknesses, explore opportunities, and mitigate potential threats.
Market Key Trends:
Covid-19 Impact: The Covid-19 pandemic influenced the Asia-Pacific cloud seeding market in various ways:
Key Industry Developments:
Analyst Suggestions:
Future Outlook: The Asia-Pacific cloud seeding market is poised for transformative growth, driven by ongoing research, technological innovations, and collaborative efforts to address water-related challenges. The future will witness advancements in seeding technologies, expanded applications, and a growing emphasis on sustainable water resource management.
Conclusion: As the Asia-Pacific region grapples with the complexities of water scarcity and climatic variations, cloud seeding emerges as a beacon of hope and innovation. The Asia-Pacific cloud seeding market, marked by advancements in technology, cross-border collaboration, and a commitment to sustainable water management, stands at the forefront of transformative solutions. Navigating the future will require ongoing research, public engagement, and collaborative governance to harness the full potential of cloud seeding in shaping a resilient and water-secure future for the region.
What is Cloud Seeding?
Cloud seeding is a weather modification technique that aims to enhance precipitation by dispersing substances into the atmosphere. These substances, such as silver iodide or sodium chloride, encourage cloud condensation and can lead to increased rainfall in targeted areas.
What are the key players in the Asia-Pacific Cloud Seeding Market?
Key players in the Asia-Pacific Cloud Seeding Market include Weather Modification Inc., RAIN, and the China Meteorological Administration, among others. These companies are involved in various cloud seeding projects and research initiatives across the region.
What are the main drivers of the Asia-Pacific Cloud Seeding Market?
The main drivers of the Asia-Pacific Cloud Seeding Market include increasing water scarcity, the need for agricultural enhancement, and the growing demand for weather modification technologies. These factors are pushing governments and organizations to invest in cloud seeding initiatives.
What challenges does the Asia-Pacific Cloud Seeding Market face?
The Asia-Pacific Cloud Seeding Market faces challenges such as regulatory hurdles, environmental concerns, and the need for scientific validation of cloud seeding effectiveness. These issues can hinder the widespread adoption of cloud seeding practices.
What opportunities exist in the Asia-Pacific Cloud Seeding Market?
Opportunities in the Asia-Pacific Cloud Seeding Market include advancements in technology, increased collaboration between countries for regional weather management, and the potential for private sector investment in cloud seeding projects. These factors could enhance the effectiveness and reach of cloud seeding initiatives.
What trends are shaping the Asia-Pacific Cloud Seeding Market?
Trends shaping the Asia-Pacific Cloud Seeding Market include the integration of drone technology for cloud seeding operations, the use of artificial intelligence for weather prediction, and a growing focus on sustainable practices in weather modification. These innovations are expected to improve the efficiency and impact of cloud seeding efforts.
Asia-Pacific Cloud Seeding Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Technology | Static, Dynamic, Hybrid, Advanced |
| Application | Agriculture, Water Management, Weather Modification, Disaster Relief |
| End User | Government, Private Sector, Research Institutions, NGOs |
| Deployment | Onshore, Offshore, Aerial, Ground-Based |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at