444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2750
The Asia-Pacific automotive logistics software market represents one of the most dynamic and rapidly evolving segments within the global automotive technology landscape. This comprehensive market encompasses sophisticated software solutions designed to optimize supply chain management, inventory control, transportation planning, and warehouse operations specifically tailored for automotive manufacturers, suppliers, and distributors across the Asia-Pacific region.
Market dynamics in this region are characterized by unprecedented digital transformation initiatives, with automotive companies increasingly adopting cloud-based logistics platforms to enhance operational efficiency. The market is experiencing robust growth driven by the region’s position as a global automotive manufacturing hub, with countries like China, Japan, South Korea, and India leading the charge in automotive production and innovation.
Regional significance cannot be overstated, as the Asia-Pacific region accounts for approximately 58% of global automotive production, creating substantial demand for sophisticated logistics software solutions. The integration of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies into automotive logistics platforms is revolutionizing how companies manage their complex supply chains across multiple countries and time zones.
Technology adoption rates are accelerating rapidly, with industry reports indicating that 72% of automotive companies in the region have implemented or are planning to implement advanced logistics software solutions within the next three years. This surge in adoption is primarily driven by the need to manage increasingly complex global supply chains, reduce operational costs, and improve customer satisfaction through enhanced delivery performance.
The Asia-Pacific automotive logistics software market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of digital solutions specifically designed to streamline, optimize, and automate logistics operations within the automotive industry across Asia-Pacific countries. These software platforms encompass a wide range of functionalities including supply chain visibility, demand forecasting, inventory management, transportation optimization, and real-time tracking capabilities.
Core components of automotive logistics software include warehouse management systems (WMS), transportation management systems (TMS), enterprise resource planning (ERP) integration modules, and advanced analytics platforms. These solutions are specifically configured to handle the unique challenges of automotive logistics, such as managing complex bill-of-materials, coordinating just-in-time delivery schedules, and ensuring compliance with automotive industry standards and regulations.
Functional scope extends beyond traditional logistics management to include predictive maintenance scheduling, supplier relationship management, quality control tracking, and sustainability reporting. Modern automotive logistics software platforms leverage artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to provide predictive insights, optimize routing decisions, and automate routine operational tasks.
Industry integration is a critical aspect, as these software solutions must seamlessly connect with existing manufacturing execution systems, customer relationship management platforms, and financial management systems to provide comprehensive visibility across the entire automotive value chain.
Market trajectory for Asia-Pacific automotive logistics software demonstrates exceptional growth potential, driven by the region’s dominant position in global automotive manufacturing and the accelerating digital transformation of supply chain operations. The market is characterized by increasing adoption of cloud-based solutions, integration of advanced technologies, and growing emphasis on sustainability and operational efficiency.
Key growth drivers include the expansion of electric vehicle manufacturing, which requires specialized logistics solutions for battery management and charging infrastructure deployment. Additionally, the rise of autonomous vehicle development is creating new demands for sophisticated logistics software capable of managing complex testing and deployment schedules across multiple geographic locations.
Technology trends are reshaping the competitive landscape, with artificial intelligence and machine learning becoming standard features in modern automotive logistics platforms. Companies are increasingly seeking solutions that offer real-time visibility, predictive analytics, and automated decision-making capabilities to maintain competitive advantages in rapidly evolving markets.
Regional dynamics vary significantly across Asia-Pacific countries, with developed markets like Japan and South Korea focusing on advanced automation and Industry 4.0 integration, while emerging markets such as India and Southeast Asian countries prioritize cost-effective solutions that can scale rapidly with growing automotive production volumes.
Investment patterns indicate strong confidence in the market’s future, with venture capital and private equity firms increasing their focus on automotive logistics technology startups. This influx of capital is accelerating innovation and enabling the development of next-generation solutions that address emerging challenges in the automotive supply chain.
Strategic insights reveal several critical factors shaping the Asia-Pacific automotive logistics software market landscape. The following key insights provide a comprehensive understanding of market dynamics and future opportunities:
Market maturity levels vary significantly across different Asia-Pacific countries, with Japan and South Korea leading in advanced technology adoption, while emerging markets focus on fundamental logistics optimization and cost reduction strategies.
Primary growth catalysts propelling the Asia-Pacific automotive logistics software market include several interconnected factors that are fundamentally transforming how automotive companies approach supply chain management and logistics operations.
Digital transformation initiatives represent the most significant driver, as automotive companies across the region recognize the critical importance of modernizing their logistics operations to remain competitive. The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated these initiatives, highlighting the vulnerability of traditional supply chain models and the need for more resilient, technology-enabled logistics solutions.
Manufacturing expansion throughout the Asia-Pacific region is creating substantial demand for sophisticated logistics software. Countries like Vietnam, Thailand, and Indonesia are emerging as important automotive manufacturing hubs, requiring advanced logistics solutions to manage complex multi-country supply chains and coordinate production schedules across different time zones.
E-commerce growth is fundamentally changing customer expectations for delivery speed and transparency. Automotive companies are adapting their logistics operations to meet these evolving expectations, requiring software solutions that can optimize last-mile delivery, provide real-time tracking, and manage complex inventory across multiple channels.
Regulatory compliance requirements are becoming increasingly complex, particularly for companies operating across multiple Asia-Pacific countries. Automotive logistics software helps companies navigate diverse regulatory environments, manage customs documentation, and ensure compliance with safety and environmental standards.
Cost optimization pressures continue to drive adoption, as companies seek to reduce logistics costs while maintaining service quality. Advanced software solutions enable companies to optimize routing, reduce inventory carrying costs, and improve asset utilization through better planning and execution capabilities.
Implementation challenges represent significant barriers to market growth, particularly for small and medium-sized automotive companies that may lack the technical expertise and financial resources required for comprehensive logistics software deployment. The complexity of integrating new software solutions with existing legacy systems often creates substantial implementation hurdles.
High initial investment costs continue to constrain market adoption, especially among smaller automotive suppliers and distributors. While cloud-based solutions have reduced some cost barriers, comprehensive logistics software implementations still require significant upfront investments in software licensing, customization, training, and system integration.
Data security concerns are increasingly important as automotive companies become more cautious about sharing sensitive supply chain and operational data with third-party software providers. Cybersecurity threats and data privacy regulations create additional complexity for companies considering cloud-based logistics solutions.
Skills shortage in the region poses ongoing challenges, as companies struggle to find qualified personnel capable of implementing, managing, and optimizing advanced logistics software systems. The rapid pace of technological change requires continuous training and skill development, which can be resource-intensive for many organizations.
Cultural resistance to change within traditional automotive organizations can slow adoption rates. Many companies have established logistics processes and relationships that have been successful for decades, making it difficult to justify the disruption and risk associated with implementing new software solutions.
Technology standardization issues across different countries and regions create additional complexity. Varying technical standards, communication protocols, and regulatory requirements make it challenging to implement standardized logistics software solutions across multiple Asia-Pacific markets.
Emerging market expansion presents substantial opportunities for automotive logistics software providers, as developing countries in Southeast Asia and South Asia continue to build their automotive manufacturing capabilities. These markets offer significant growth potential for companies that can provide cost-effective, scalable solutions tailored to local requirements.
Electric vehicle logistics represents a transformative opportunity, as the rapid growth of EV manufacturing creates unique logistics challenges and requirements. Battery management, charging infrastructure deployment, and specialized transportation requirements for electric vehicles demand innovative software solutions that can address these specific needs.
Autonomous vehicle development is creating new logistics requirements for testing, validation, and deployment of self-driving vehicle technologies. Companies involved in autonomous vehicle development require sophisticated logistics software to coordinate complex testing schedules, manage specialized equipment, and track development progress across multiple locations.
Sustainability initiatives are driving demand for logistics software that can optimize carbon footprint, reduce waste, and improve environmental performance. Companies are increasingly seeking solutions that can provide detailed sustainability reporting and help optimize logistics operations for environmental impact reduction.
Cross-border trade facilitation offers significant opportunities as Asia-Pacific countries continue to strengthen trade relationships and reduce barriers to automotive trade. Logistics software that can streamline customs processes, manage international documentation, and optimize cross-border transportation will be increasingly valuable.
Small and medium enterprise (SME) market remains largely underserved, presenting opportunities for software providers that can develop simplified, cost-effective solutions tailored to the needs of smaller automotive suppliers and distributors throughout the region.
Competitive dynamics within the Asia-Pacific automotive logistics software market are characterized by intense competition between global software providers and emerging regional players. Established international companies leverage their extensive experience and comprehensive solution portfolios, while local providers compete on the basis of regional expertise, cost-effectiveness, and specialized knowledge of local market conditions.
Technology evolution is accelerating at an unprecedented pace, with artificial intelligence, machine learning, and blockchain technologies becoming increasingly integrated into automotive logistics platforms. Companies that fail to keep pace with technological advancement risk losing market share to more innovative competitors.
Customer expectations are continuously evolving, with automotive companies demanding more sophisticated features, better user experiences, and greater integration capabilities. The shift toward outcome-based pricing models is also changing how software providers structure their offerings and engage with customers.
Partnership strategies are becoming increasingly important, as software providers seek to expand their capabilities through strategic alliances with technology companies, system integrators, and industry specialists. These partnerships enable companies to offer more comprehensive solutions and access new market segments.
Market consolidation trends are evident as larger software providers acquire smaller specialized companies to enhance their capabilities and expand their geographic reach. This consolidation is creating more comprehensive solution providers while potentially reducing competition in certain market segments.
Innovation cycles are shortening as companies face pressure to continuously enhance their solutions and introduce new features. The rapid pace of innovation requires significant ongoing investment in research and development, creating challenges for smaller providers with limited resources.
Comprehensive research approach employed for analyzing the Asia-Pacific automotive logistics software market combines multiple methodologies to ensure accuracy, reliability, and depth of insights. The research framework incorporates both primary and secondary research techniques to provide a holistic view of market dynamics, competitive landscape, and future trends.
Primary research activities include extensive interviews with key industry stakeholders, including automotive manufacturers, logistics software providers, system integrators, and end-users across major Asia-Pacific markets. These interviews provide valuable insights into market needs, adoption patterns, and emerging trends that may not be captured through secondary research sources.
Secondary research methodology involves comprehensive analysis of industry reports, company financial statements, regulatory filings, and academic research papers. This approach ensures that the research findings are grounded in verified data and established industry knowledge while identifying potential gaps or inconsistencies in available information.
Data validation processes include cross-referencing information from multiple sources, conducting follow-up interviews to clarify ambiguous findings, and employing statistical analysis techniques to identify patterns and trends. This rigorous validation approach helps ensure the accuracy and reliability of research conclusions.
Market sizing methodology utilizes bottom-up and top-down approaches to develop comprehensive market assessments. The bottom-up approach involves analyzing individual market segments and geographic regions, while the top-down approach considers overall market dynamics and macroeconomic factors that influence market development.
Forecasting techniques employ advanced statistical models and scenario analysis to project future market trends and growth patterns. These forecasting models consider multiple variables including technological advancement, regulatory changes, economic conditions, and competitive dynamics to provide robust projections.
China dominates the Asia-Pacific automotive logistics software market, representing approximately 42% of regional market share due to its massive automotive manufacturing base and rapid digital transformation initiatives. Chinese automotive companies are increasingly adopting sophisticated logistics software to manage complex supply chains and improve operational efficiency in highly competitive domestic and international markets.
Japan maintains a strong market position with advanced technology adoption and emphasis on precision manufacturing. Japanese automotive companies prioritize high-quality logistics software solutions that can support their lean manufacturing principles and just-in-time delivery requirements. The market is characterized by sophisticated integration requirements and emphasis on continuous improvement.
South Korea represents a technologically advanced market with strong adoption of Industry 4.0 concepts and smart manufacturing initiatives. Korean automotive companies are leaders in integrating artificial intelligence and IoT technologies into their logistics operations, creating demand for cutting-edge software solutions.
India emerges as a high-growth market driven by expanding automotive manufacturing capabilities and increasing focus on cost optimization. The Indian market is characterized by price sensitivity and demand for scalable solutions that can accommodate rapid business growth and varying levels of technological sophistication.
Southeast Asian countries including Thailand, Indonesia, and Vietnam are experiencing rapid growth as automotive manufacturing hubs. These markets offer significant opportunities for logistics software providers that can offer cost-effective solutions tailored to emerging market requirements and local business practices.
Australia and New Zealand represent mature markets with emphasis on regulatory compliance and sustainability. These markets demand sophisticated reporting capabilities and integration with environmental management systems to meet stringent regulatory requirements.
Market leadership in the Asia-Pacific automotive logistics software market is distributed among several categories of providers, each offering distinct advantages and targeting different market segments. The competitive landscape is characterized by intense competition and continuous innovation as companies strive to differentiate their offerings.
Global enterprise software providers dominate the large enterprise segment with comprehensive solution portfolios:
Specialized logistics software providers focus on automotive-specific requirements:
Regional providers compete on local expertise and cost-effectiveness, offering solutions specifically designed for Asia-Pacific market requirements and business practices. These companies often provide more flexible pricing models and faster implementation timelines compared to global providers.
Emerging technology companies are disrupting traditional market dynamics by offering innovative solutions based on artificial intelligence, machine learning, and blockchain technologies. These companies often target specific market niches or offer specialized capabilities that complement existing logistics software platforms.
Technology-based segmentation reveals distinct market categories based on underlying software architecture and deployment models:
Application-based segmentation categorizes solutions according to primary functional focus:
End-user segmentation identifies distinct customer categories with specific requirements:
Warehouse Management Systems represent the largest category within the automotive logistics software market, driven by the need to optimize complex inventory management requirements. Modern automotive warehouses must handle thousands of different parts and components while maintaining precise inventory accuracy and supporting just-in-time manufacturing schedules.
Advanced features in warehouse management systems include automated picking optimization, real-time inventory tracking, and integration with robotic systems. These capabilities are essential for automotive companies seeking to reduce operational costs while improving accuracy and efficiency in their warehouse operations.
Transportation Management Systems are experiencing rapid growth as companies seek to optimize their logistics networks and reduce transportation costs. These systems provide sophisticated routing optimization, carrier management, and shipment tracking capabilities that are essential for managing complex automotive supply chains.
Integration capabilities are becoming increasingly important as automotive companies require seamless connectivity between transportation management systems and other enterprise applications. Modern TMS solutions must integrate with ERP systems, warehouse management platforms, and customer relationship management applications.
Supply Chain Planning solutions are gaining importance as automotive companies face increasing complexity in their global operations. These systems provide advanced analytics and forecasting capabilities that help companies optimize inventory levels, plan production schedules, and manage supplier relationships more effectively.
Artificial intelligence integration is transforming supply chain planning capabilities, enabling more accurate demand forecasting, automated exception management, and predictive maintenance scheduling. Companies implementing AI-powered planning solutions report significant improvements in forecast accuracy and operational efficiency.
Operational efficiency improvements represent the primary benefit for automotive companies implementing advanced logistics software solutions. Companies typically experience 25-35% reduction in logistics costs through optimized routing, improved inventory management, and enhanced coordination between different operational functions.
Enhanced visibility across the entire supply chain enables better decision-making and faster response to disruptions or changes in demand. Real-time tracking and monitoring capabilities provide stakeholders with comprehensive insights into logistics performance and potential issues before they impact operations.
Improved customer satisfaction results from more accurate delivery promises, better communication, and faster resolution of logistics issues. Automotive companies using advanced logistics software report significant improvements in on-time delivery performance and customer service metrics.
Risk mitigation capabilities help companies identify and address potential supply chain disruptions before they impact operations. Advanced analytics and predictive modeling enable proactive management of supplier risks, transportation delays, and inventory shortages.
Regulatory compliance automation reduces the administrative burden and risk associated with managing complex international trade requirements. Automated documentation, customs clearance, and regulatory reporting capabilities help companies avoid costly compliance violations and delays.
Scalability advantages enable companies to expand their operations without proportional increases in logistics management complexity. Cloud-based solutions particularly provide the flexibility to accommodate rapid business growth and seasonal demand fluctuations.
Data-driven insights support strategic decision-making by providing comprehensive analytics on logistics performance, cost trends, and optimization opportunities. Companies can use these insights to identify areas for improvement and develop more effective logistics strategies.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Artificial Intelligence Integration is transforming automotive logistics software capabilities, with 78% of new implementations including AI-powered features for predictive analytics, automated decision-making, and optimization algorithms. Machine learning capabilities enable systems to continuously improve performance and adapt to changing operational conditions.
Cloud-First Strategies are becoming standard practice as automotive companies recognize the benefits of cloud-based logistics solutions. The shift toward cloud deployment models is driven by scalability requirements, cost optimization objectives, and the need for rapid implementation and updates.
Mobile Accessibility is essential for modern logistics operations, with field personnel requiring real-time access to logistics data and decision-making tools. Mobile-first design approaches ensure that logistics software can support operations across diverse geographic locations and varying technological infrastructure.
Sustainability Integration is becoming a core requirement as automotive companies face increasing pressure to reduce their environmental impact. Logistics software must provide comprehensive carbon footprint tracking, optimization for environmental impact, and detailed sustainability reporting capabilities.
Blockchain Technology is gaining traction for supply chain transparency and traceability applications. Automotive companies are exploring blockchain solutions for parts authentication, supplier verification, and compliance documentation to enhance supply chain security and reliability.
Internet of Things (IoT) Integration enables real-time monitoring and tracking of assets, inventory, and shipments throughout the logistics network. IoT sensors and devices provide valuable data for optimizing operations and preventing potential issues before they impact performance.
Predictive Analytics capabilities are becoming standard features, enabling companies to anticipate potential disruptions, optimize maintenance schedules, and improve demand forecasting accuracy. Advanced analytics help companies transition from reactive to proactive logistics management approaches.
Strategic partnerships between logistics software providers and automotive manufacturers are accelerating innovation and market adoption. These collaborations enable software companies to better understand industry-specific requirements while providing automotive companies with access to cutting-edge technology solutions.
Acquisition activities are reshaping the competitive landscape as larger software providers acquire specialized companies to enhance their automotive logistics capabilities. Recent acquisitions have focused on companies offering artificial intelligence, blockchain, and IoT technologies for logistics applications.
Technology investments by automotive companies are increasing significantly, with many organizations establishing dedicated digital transformation teams focused on logistics optimization. These investments are driving demand for more sophisticated software solutions and accelerating adoption rates.
Regulatory developments across Asia-Pacific countries are influencing software requirements, particularly in areas such as data privacy, cybersecurity, and environmental compliance. Software providers must continuously adapt their solutions to meet evolving regulatory requirements.
Industry standardization efforts are progressing to improve interoperability between different logistics software systems and facilitate data exchange across the automotive supply chain. These standardization initiatives are expected to reduce integration complexity and costs.
Research and development initiatives are focusing on next-generation technologies such as quantum computing, advanced robotics integration, and autonomous logistics systems. These developments will likely transform automotive logistics operations over the next decade.
Investment priorities should focus on companies that demonstrate strong capabilities in artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and mobile accessibility. According to MarkWide Research analysis, organizations that prioritize these technology areas are best positioned to capitalize on emerging market opportunities and maintain competitive advantages.
Market entry strategies for new providers should emphasize partnership approaches with established system integrators and automotive industry consultants. These partnerships can provide valuable market access and credibility while reducing the time and investment required to establish market presence.
Customer engagement approaches should emphasize outcome-based value propositions rather than feature-based selling. Automotive companies are increasingly focused on measurable business results such as cost reduction, efficiency improvement, and customer satisfaction enhancement.
Technology development roadmaps should prioritize integration capabilities, user experience optimization, and industry-specific functionality. Companies that can provide seamless integration with existing systems while delivering superior user experiences will have significant competitive advantages.
Geographic expansion strategies should focus on emerging markets with growing automotive manufacturing capabilities. Countries such as Vietnam, Indonesia, and Bangladesh offer significant growth potential for companies that can provide cost-effective, scalable solutions.
Partnership opportunities exist with automotive manufacturers, system integrators, and technology providers. Strategic alliances can provide access to new markets, enhance solution capabilities, and reduce development costs while accelerating time-to-market for new features.
Market evolution over the next five years will be characterized by continued technological advancement, increasing adoption rates, and expanding geographic coverage. The Asia-Pacific automotive logistics software market is projected to experience robust growth driven by digital transformation initiatives and expanding automotive manufacturing capabilities throughout the region.
Technology trends will continue to shape market development, with artificial intelligence, machine learning, and blockchain technologies becoming standard features in automotive logistics software solutions. Companies that fail to incorporate these advanced technologies risk losing competitive position to more innovative providers.
Market consolidation is expected to continue as larger software providers acquire specialized companies to enhance their capabilities and expand their market reach. This consolidation will likely result in more comprehensive solution offerings while potentially reducing the number of independent providers in the market.
Emerging opportunities will be created by the continued growth of electric vehicle manufacturing, autonomous vehicle development, and sustainability initiatives. Companies that can develop specialized solutions for these emerging market segments will be well-positioned for future growth.
Regional dynamics will continue to evolve as developing countries in Southeast Asia and South Asia expand their automotive manufacturing capabilities. These emerging markets will require logistics software solutions that can accommodate local business practices while providing the scalability needed for rapid growth.
Customer expectations will continue to evolve toward more sophisticated functionality, better user experiences, and greater integration capabilities. Software providers must continuously innovate and enhance their solutions to meet these evolving requirements and maintain customer satisfaction.
The Asia-Pacific automotive logistics software market represents a dynamic and rapidly evolving landscape characterized by significant growth opportunities, technological innovation, and increasing adoption across diverse market segments. The market’s trajectory is fundamentally shaped by the region’s dominant position in global automotive manufacturing and the accelerating digital transformation of supply chain operations.
Key success factors for market participants include technological innovation, customer-centric solution development, and strategic partnerships that enhance market access and solution capabilities. Companies that can effectively combine advanced technology features with industry-specific expertise and local market knowledge will be best positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Future market development will be driven by continued expansion of automotive manufacturing capabilities throughout the Asia-Pacific region, increasing adoption of electric and autonomous vehicles, and growing emphasis on sustainability and operational efficiency. MWR projections indicate that companies investing in artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and mobile accessibility will experience the strongest growth rates over the next five years.
Strategic implications for industry stakeholders include the need for continuous innovation, investment in emerging technologies, and development of comprehensive solution portfolios that address evolving customer requirements. The market’s future success will depend on the ability of software providers to deliver measurable business value while adapting to rapidly changing technological and regulatory environments across diverse Asia-Pacific markets.
What is Automotive Logistics Software?
Automotive Logistics Software refers to specialized applications designed to manage and optimize the supply chain and logistics processes within the automotive industry. This includes functions such as inventory management, transportation planning, and order fulfillment.
What are the key players in the Asia-Pacific Automotive Logistics Software Market?
Key players in the Asia-Pacific Automotive Logistics Software Market include companies like SAP, Oracle, and JDA Software, which provide comprehensive solutions for logistics management in the automotive sector, among others.
What are the main drivers of the Asia-Pacific Automotive Logistics Software Market?
The main drivers of the Asia-Pacific Automotive Logistics Software Market include the increasing demand for efficient supply chain management, the rise of e-commerce in automotive parts, and the need for real-time data analytics to enhance decision-making.
What challenges does the Asia-Pacific Automotive Logistics Software Market face?
Challenges in the Asia-Pacific Automotive Logistics Software Market include the complexity of integrating new software with existing systems, the high costs associated with implementation, and the need for continuous updates to meet evolving industry standards.
What opportunities exist in the Asia-Pacific Automotive Logistics Software Market?
Opportunities in the Asia-Pacific Automotive Logistics Software Market include the growing trend of digital transformation in logistics, the adoption of artificial intelligence for predictive analytics, and the increasing focus on sustainability in supply chain practices.
What trends are shaping the Asia-Pacific Automotive Logistics Software Market?
Trends shaping the Asia-Pacific Automotive Logistics Software Market include the rise of cloud-based solutions, the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies for better tracking, and the emphasis on automation to improve operational efficiency.
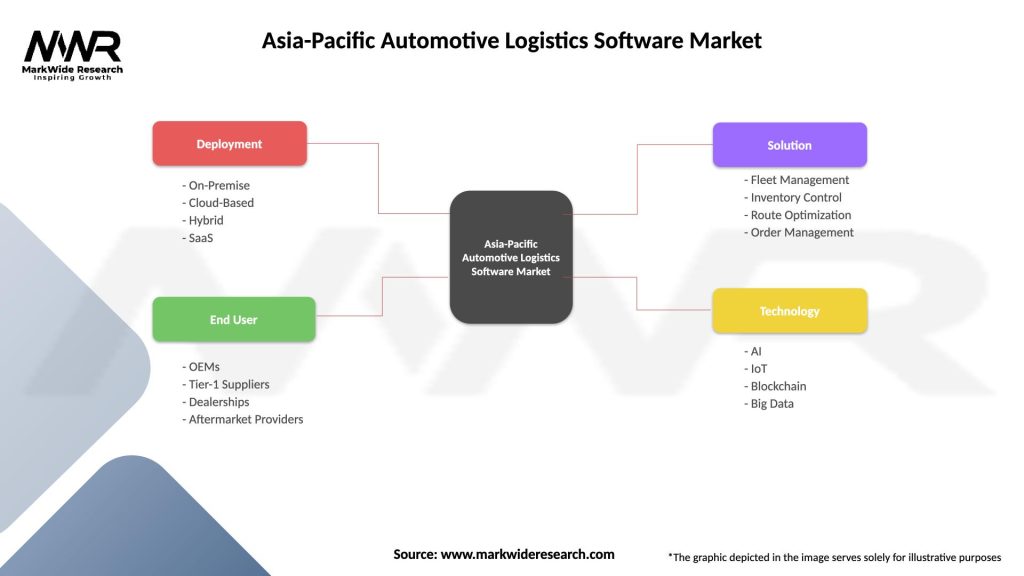
Asia-Pacific Automotive Logistics Software Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Deployment | On-Premise, Cloud-Based, Hybrid, SaaS |
| End User | OEMs, Tier-1 Suppliers, Dealerships, Aftermarket Providers |
| Solution | Fleet Management, Inventory Control, Route Optimization, Order Management |
| Technology | AI, IoT, Blockchain, Big Data |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the Asia-Pacific Automotive Logistics Software Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at