444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The artificial meat products market, also known as lab-grown or cultured meat, is an emerging sector within the global food industry. It involves producing meat through cell culture technology rather than traditional livestock farming. This innovative approach aims to address several critical issues, including environmental sustainability, animal welfare, and food security. With its potential to revolutionize the way meat is produced and consumed, the artificial meat market has garnered significant attention from researchers, investors, and consumers alike.
Meaning
Artificial meat, or cultured meat, is produced by cultivating animal cells in a controlled environment. The process starts with extracting cells from a live animal, which are then placed in a nutrient-rich culture medium. These cells multiply and differentiate to form muscle tissue, which can be harvested and processed into meat products. Unlike plant-based meat alternatives, cultured meat is biologically identical to conventional meat, providing the same taste, texture, and nutritional profile without the need for animal slaughter.
Executive Summary
The artificial meat products market is poised for substantial growth, driven by increasing consumer awareness of sustainability issues, advancements in biotechnology, and a rising demand for ethical and environmentally friendly food options. Despite facing significant challenges, including high production costs and regulatory hurdles, the market presents numerous opportunities for innovation and expansion. Key players in the industry are investing heavily in research and development to scale production and bring affordable cultured meat products to market.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The artificial meat products market operates within a dynamic environment influenced by technological advancements, regulatory changes, consumer preferences, and environmental considerations. Companies in this sector must stay agile and innovative to navigate these factors and capitalize on emerging opportunities. Understanding market dynamics is crucial for strategic planning and decision-making in this rapidly evolving industry.
Regional Analysis
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Artificial Meat Products Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
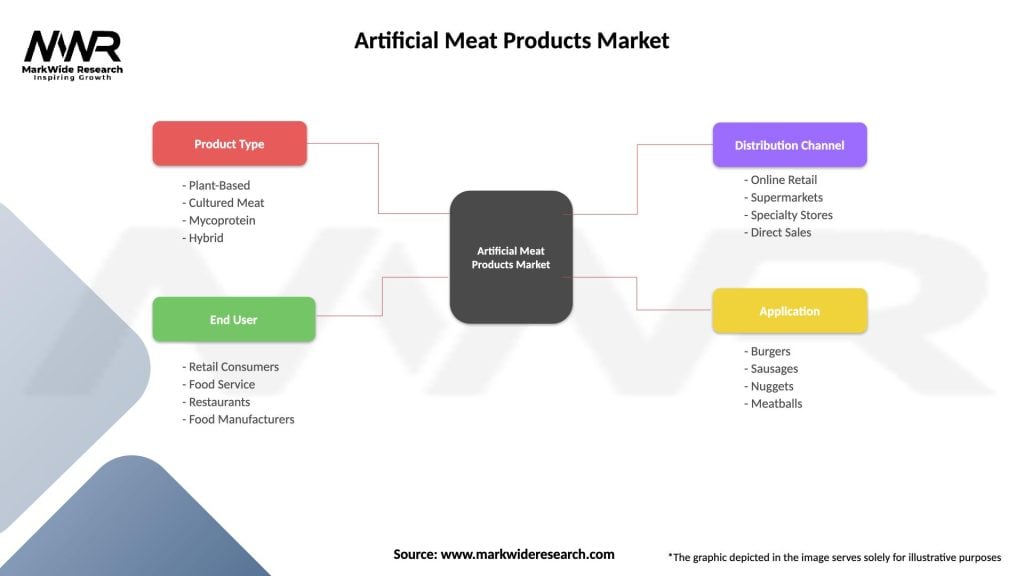
Segmentation
The artificial meat products market can be segmented based on various factors:
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a mixed impact on the artificial meat products market:
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future outlook for the artificial meat products market is promising, with significant potential for growth and innovation. Technological advancements, increased investment, and supportive regulatory frameworks will drive the market forward. As consumer awareness and acceptance of cultured meat grow, the market will expand, offering a sustainable and ethical alternative to conventional meat. However, addressing challenges such as high production costs, regulatory hurdles, and consumer perception will be crucial for realizing the full potential of cultured meat.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the artificial meat products market represents a groundbreaking shift in the global food industry, offering sustainable, ethical, and innovative solutions to meet the growing demand for protein-rich foods. By harnessing advancements in biotechnology and addressing key challenges, the cultured meat sector can achieve significant growth and contribute to a more sustainable and resilient food system. Stakeholders, including companies, investors, regulators, and consumers, play a vital role in shaping the future of this transformative industry. Through collaboration, innovation, and strategic planning, the artificial meat products market can pave the way for a more sustainable and ethical future for food production and consumption.
What is Artificial Meat Products?
Artificial meat products refer to meat alternatives created through various technologies, including plant-based ingredients and cultured meat processes. These products aim to replicate the taste and texture of traditional meat while offering a more sustainable and ethical option for consumers.
What are the key players in the Artificial Meat Products Market?
Key players in the Artificial Meat Products Market include Beyond Meat, Impossible Foods, and Memphis Meats, among others. These companies are at the forefront of developing innovative meat alternatives that cater to the growing demand for sustainable food options.
What are the growth factors driving the Artificial Meat Products Market?
The growth of the Artificial Meat Products Market is driven by increasing consumer awareness of health and environmental issues, rising demand for sustainable food sources, and advancements in food technology. Additionally, changing dietary preferences towards plant-based diets contribute to market expansion.
What challenges does the Artificial Meat Products Market face?
The Artificial Meat Products Market faces challenges such as regulatory hurdles, consumer acceptance, and competition from traditional meat products. Additionally, the high cost of production and the need for widespread distribution can hinder market growth.
What opportunities exist in the Artificial Meat Products Market?
Opportunities in the Artificial Meat Products Market include expanding product lines to cater to diverse dietary needs, increasing partnerships with food service providers, and leveraging technological advancements to improve product quality. The growing trend of flexitarian diets also presents a significant opportunity for market players.
What trends are shaping the Artificial Meat Products Market?
Trends shaping the Artificial Meat Products Market include the rise of clean label products, increased investment in research and development, and a focus on sustainability in production processes. Additionally, consumer preferences are shifting towards more innovative and flavorful meat alternatives.
Artificial Meat Products Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Plant-Based, Cultured Meat, Mycoprotein, Hybrid |
| End User | Retail Consumers, Food Service, Restaurants, Food Manufacturers |
| Distribution Channel | Online Retail, Supermarkets, Specialty Stores, Direct Sales |
| Application | Burgers, Sausages, Nuggets, Meatballs |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Artificial Meat Products Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at