444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The Arthropod-Borne Viral Infections market refers to the market for viral infections transmitted to humans through arthropod vectors such as mosquitoes, ticks, and flies. These infections pose significant global health challenges, with several diseases causing substantial morbidity and mortality worldwide. This comprehensive article provides insights into the Arthropod-Borne Viral Infections market, including its meaning, executive summary, key market insights, market drivers, market restraints, market opportunities, market dynamics, regional analysis, competitive landscape, segmentation, category-wise insights, key benefits for industry participants and stakeholders, SWOT analysis, market key trends, Covid-19 impact, key industry developments, analyst suggestions, future outlook, and conclusion.
Meaning
Arthropod-Borne Viral Infections, also known as vector-borne viral infections, are viral diseases transmitted to humans through the bites of infected arthropod vectors. These vectors, such as mosquitoes, ticks, and flies, serve as carriers for the viruses, which can replicate in the vector’s body and then be transmitted to humans during subsequent blood meals. Examples of arthropod-borne viral infections include dengue fever, Zika virus disease, chikungunya, West Nile virus, and yellow fever.
Executive Summary
The Arthropod-Borne Viral Infections market is a significant public health concern, with increasing incidence rates and global spread of these infections. The market encompasses various diseases transmitted by arthropod vectors and poses challenges in terms of diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. This executive summary provides an overview of the key market findings, highlighting the prevalence of arthropod-borne viral infections, the impact of these diseases on public health, key market drivers and restraints, and future growth prospects.

Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
The Arthropod-Borne Viral Infections market is influenced by various factors that shape its dynamics and growth potential. These key market insights provide a deeper understanding of the market landscape and the factors driving its development.
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The Arthropod-Borne Viral Infections market is characterized by dynamic factors that influence its growth and development. These dynamics include market drivers, restraints, and opportunities that shape the market landscape. Factors such as the global expansion of arthropod vectors, climate change, lack of effective vaccines and treatments, diagnostic challenges, and inadequate vector control measures impact the market dynamics.
Regional Analysis
The prevalence and impact of arthropod-borne viral infections vary across different regions due to variations in climate, vector ecology, healthcare infrastructure, and public health measures. This regional analysis provides insights into the regional distribution of arthropod-borne viral infections, disease burden, prevention and control strategies, and market trends in different geographic areas.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Arthropod-Borne Viral Infections Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
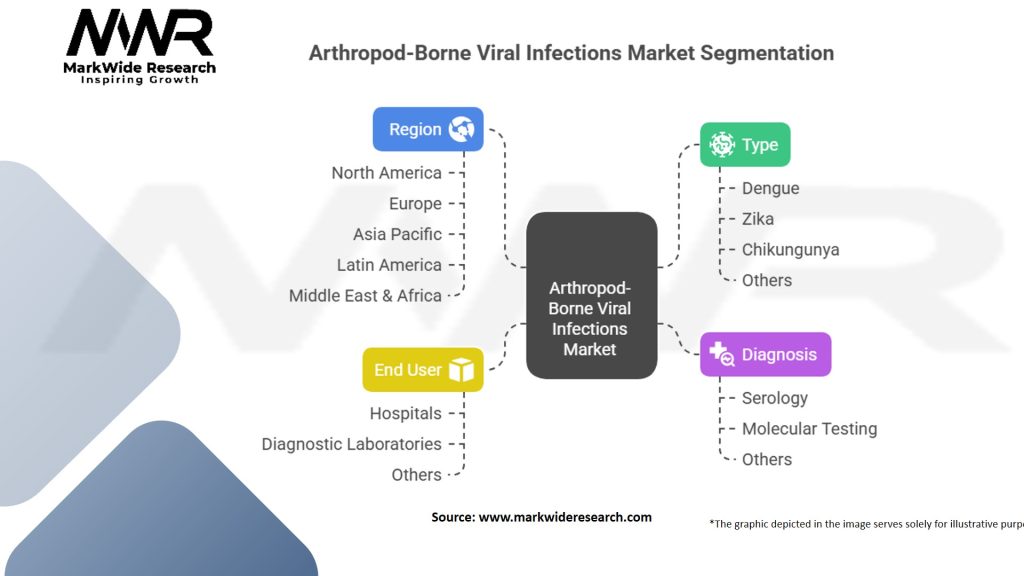
Segmentation
The Arthropod-Borne Viral Infections market can be segmented based on disease type, vector species, diagnostic methods, treatment approaches, and geography. This segmentation allows for a comprehensive analysis of the market, highlighting specific disease trends, vector ecology, diagnostic advancements, and treatment options.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
The Arthropod-Borne Viral Infections market is subject to evolving trends that shape its trajectory and growth potential. This section highlights key market trends such as advancements in diagnostic techniques, emerging vector-borne diseases, changes in vector distribution, and the impact of climate change on disease transmission.
Covid-19 Impact
The Covid-19 pandemic has had a profound impact on global health systems, including the management of arthropod-borne viral infections. This section examines the effects of the pandemic on the Arthropod-Borne Viral Infections market, including disruptions in disease surveillance, vector control programs, and healthcare delivery. It also discusses the implications of the pandemic on future market trends and opportunities.
Key Industry Developments
This section provides an overview of key industry developments in the Arthropod-Borne Viral Infections market. It covers recent advancements in diagnostic technologies, treatment approaches, vector control strategies, and public health policies. These developments influence market growth, research priorities, and healthcare practices.
Analyst Suggestions
Based on market analysis, analysts suggest the following strategies for industry participants:
Future Outlook
The future outlook for the Arthropod-Borne Viral Infections market is promising, albeit with several challenges to overcome. Continued efforts in disease surveillance, prevention, vector control, and research and development are crucial for reducing the burden of these infections. The market is expected to witness advancements in diagnostics, therapeutics, and public health strategies, leading to improved patient outcomes and effective control of arthropod-borne viral infections.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Arthropod-Borne Viral Infections market presents significant challenges and opportunities in the field of public health. The market overview, meaning, executive summary, key market insights, market drivers, market restraints, market opportunities, market dynamics, regional analysis, competitive landscape, segmentation, category-wise insights, key benefits for industry participants and stakeholders, SWOT analysis, market key trends, Covid-19 impact, key industry developments, analyst suggestions, future outlook, and conclusion provide a comprehensive understanding of the market dynamics, trends, and strategies required to combat arthropod-borne viral infections. By addressing these challenges and capitalizing on the opportunities, we can work towards effective prevention, diagnosis, and control of these diseases, ultimately improving global health outcomes.
Arthropod-Borne Viral Infections Market:
| Segmentation | Details |
|---|---|
| Type | Dengue, Zika, Chikungunya, Others |
| Diagnosis | Serology, Molecular Testing, Others |
| End User | Hospitals, Diagnostic Laboratories, Others |
| Region | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Arthropod-Borne Viral Infections Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at