444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
Argentina’s solar energy market represents one of South America’s most dynamic renewable energy sectors, experiencing unprecedented growth driven by favorable government policies, abundant solar resources, and increasing private sector investment. The country’s vast territory offers exceptional solar irradiation levels, particularly in the northern and western regions, making it an ideal location for large-scale photovoltaic installations and distributed generation systems.
Market expansion has been remarkable, with solar capacity growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 45% over the past five years. This growth trajectory positions Argentina as a regional leader in solar energy adoption, supported by the RenovAr program and other government initiatives designed to diversify the energy matrix and reduce dependence on fossil fuels.
Investment flows into the sector have intensified significantly, with both domestic and international players recognizing Argentina’s potential. The market encompasses utility-scale solar farms, commercial rooftop installations, and residential systems, each segment contributing to the overall expansion of solar energy infrastructure across the country.
Regional development varies considerably, with provinces like Jujuy, San Juan, and Mendoza leading in terms of installed capacity and project development. These regions benefit from optimal solar conditions, supportive local policies, and established infrastructure that facilitates large-scale solar project implementation.
Argentina’s solar energy market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of solar photovoltaic technology deployment, including utility-scale solar farms, distributed generation systems, commercial installations, and residential rooftop solutions across the Argentine territory, encompassing manufacturing, installation, operation, and maintenance services.
This market encompasses various stakeholders including government entities, private developers, equipment manufacturers, financial institutions, and end-users who collectively drive the adoption and expansion of solar energy technologies. The sector includes both grid-connected and off-grid applications, serving diverse energy needs from large industrial consumers to remote rural communities.
Key components of the market include photovoltaic panels, inverters, mounting systems, energy storage solutions, and associated infrastructure required for solar energy generation and distribution. The market also encompasses services such as project development, engineering, procurement, construction, and long-term operation and maintenance contracts.
Argentina’s solar energy sector has emerged as a cornerstone of the country’s renewable energy transition, driven by exceptional solar resources and supportive policy frameworks. The market demonstrates robust growth potential with solar installations expanding rapidly across multiple segments and geographical regions.
Government initiatives have played a crucial role in market development, with the RenovAr program facilitating over 85% of utility-scale solar capacity additions in recent years. These programs have successfully attracted international investment and technology transfer, establishing Argentina as an attractive destination for solar energy development.
Market diversification is evident across utility-scale, commercial, and residential segments, with distributed generation showing particularly strong growth momentum. The regulatory framework continues to evolve, supporting net metering, virtual net billing, and other mechanisms that encourage solar adoption across different consumer categories.
Technological advancement and cost reductions have made solar energy increasingly competitive with conventional generation sources. According to MarkWide Research analysis, solar energy costs have decreased by 60% over the past decade, making it one of the most cost-effective electricity generation options in many regions of Argentina.
Strategic insights reveal several critical factors driving Argentina’s solar energy market expansion and long-term sustainability:
Primary drivers propelling Argentina’s solar energy market include a combination of economic, environmental, and strategic factors that create compelling conditions for continued expansion.
Government policy support remains the most significant driver, with comprehensive renewable energy laws, tax incentives, and procurement programs providing long-term market certainty. The RenovAr program has been particularly effective in attracting investment and establishing a competitive market environment for utility-scale solar development.
Economic competitiveness of solar energy has improved dramatically, with levelized costs of electricity from solar installations becoming competitive with conventional generation sources. This cost advantage is particularly pronounced in regions with high solar irradiation and favorable development conditions.
Energy security concerns drive government and private sector interest in domestic renewable energy sources. Solar energy reduces dependence on imported fuels and provides price stability compared to volatile fossil fuel markets, enhancing long-term energy security.
Environmental awareness and climate commitments create additional momentum for solar energy adoption. Argentina’s participation in international climate agreements and domestic environmental goals support policies favoring renewable energy development.
Technological advancement continues to improve solar energy efficiency and reduce costs, making installations more attractive to investors and consumers. Improvements in energy storage technology also enhance the value proposition of solar energy systems.
Significant challenges continue to impact Argentina’s solar energy market development, requiring strategic solutions and policy interventions to maintain growth momentum.
Grid infrastructure limitations pose substantial constraints, particularly in remote regions with excellent solar resources but limited transmission capacity. Upgrading and expanding transmission infrastructure requires significant investment and coordination between multiple stakeholders.
Financing challenges affect project development, especially for smaller-scale installations and distributed generation systems. Limited access to long-term, low-cost financing can delay project implementation and increase overall development costs.
Regulatory uncertainty occasionally impacts investor confidence, particularly regarding long-term policy stability and tariff structures. Changes in government priorities or economic conditions can affect the regulatory environment for renewable energy development.
Currency volatility creates additional risks for projects with significant imported component costs. Exchange rate fluctuations can impact project economics and financing arrangements, particularly for international investors and equipment suppliers.
Technical workforce limitations constrain rapid market expansion, as specialized skills for solar project development, installation, and maintenance require ongoing training and capacity building programs.
Emerging opportunities in Argentina’s solar energy market present significant potential for stakeholders across the value chain, driven by evolving market conditions and technological developments.
Distributed generation expansion offers substantial growth potential, particularly in commercial and industrial segments where solar energy can provide immediate cost savings and energy security benefits. Net metering regulations and virtual power purchase agreements create new business models for distributed solar development.
Energy storage integration presents opportunities to enhance solar energy value and grid stability. Battery storage systems can address intermittency challenges and provide additional revenue streams through grid services and peak demand management.
Rural electrification programs create opportunities for off-grid solar solutions in remote areas where grid extension is economically unfeasible. These applications can improve quality of life and economic opportunities in underserved communities.
Industrial applications represent a growing market segment, with energy-intensive industries seeking to reduce electricity costs and improve sustainability profiles through on-site solar installations and long-term renewable energy contracts.
Export potential for solar-generated electricity and green hydrogen production could create new revenue streams and position Argentina as a regional renewable energy hub, leveraging abundant solar resources for international markets.
Market dynamics in Argentina’s solar energy sector reflect the complex interplay between policy frameworks, economic conditions, technological developments, and stakeholder interests that shape market evolution.
Supply chain development continues to evolve, with increasing emphasis on local content requirements and domestic manufacturing capabilities. This trend creates opportunities for local suppliers while potentially affecting project costs and timelines in the short term.
Competitive landscape intensification drives innovation and cost reductions, benefiting end-users through improved technology and more competitive pricing. The entry of international players brings advanced technology and financing capabilities while creating competitive pressure on domestic companies.
Regulatory evolution responds to market developments and stakeholder feedback, with ongoing refinements to policies and procedures that govern solar energy development. These changes aim to address market barriers while maintaining investor confidence and consumer protection.
Technology integration trends include smart grid capabilities, energy management systems, and digital monitoring platforms that enhance solar energy system performance and grid integration. These developments improve operational efficiency and create new service opportunities.
Market maturation processes involve standardization of contracts, procedures, and technical requirements that reduce transaction costs and development risks. This standardization facilitates market growth and attracts new participants.
Comprehensive research methodology employed for analyzing Argentina’s solar energy market incorporates multiple data sources and analytical approaches to ensure accuracy and reliability of market insights.
Primary research activities include structured interviews with key market participants including government officials, project developers, equipment suppliers, financial institutions, and end-users. These interviews provide firsthand insights into market conditions, challenges, and opportunities.
Secondary research sources encompass government publications, industry reports, academic studies, and international organization databases that provide statistical data, policy information, and market trends analysis. These sources ensure comprehensive coverage of market dynamics and historical developments.
Data validation processes involve cross-referencing information from multiple sources, conducting follow-up interviews for clarification, and applying analytical frameworks to ensure consistency and accuracy of findings.
Market modeling techniques utilize quantitative and qualitative analysis methods to project future market developments, assess growth scenarios, and evaluate the impact of various factors on market evolution.
Expert consultation with industry specialists, academic researchers, and policy experts provides additional validation and insights into market trends, technological developments, and regulatory implications.
Regional market distribution across Argentina reveals significant variations in solar energy development, driven by resource availability, infrastructure conditions, and local policy support.
Northern provinces including Jujuy, Salta, and Catamarca lead in utility-scale solar development, accounting for approximately 70% of total installed capacity. These regions benefit from exceptional solar irradiation levels exceeding 2,000 kWh/m² annually and supportive local governments that facilitate project development.
Cuyo region comprising San Juan, Mendoza, and San Luis demonstrates strong growth in both utility-scale and distributed generation segments. The region’s established infrastructure and industrial base create favorable conditions for commercial and industrial solar applications.
Central provinces including Buenos Aires, Córdoba, and Santa Fe show increasing activity in distributed generation and commercial installations, driven by high electricity demand and favorable net metering regulations. These regions account for 55% of distributed solar capacity despite lower solar irradiation levels.
Patagonian provinces present emerging opportunities for solar development, particularly in combination with wind energy resources. While solar irradiation is lower than northern regions, the area offers potential for hybrid renewable energy projects and industrial applications.
Regional infrastructure development varies significantly, with northern provinces requiring transmission upgrades to accommodate large-scale solar installations, while central regions benefit from existing grid infrastructure that facilitates distributed generation integration.
Competitive dynamics in Argentina’s solar energy market involve diverse stakeholders including international developers, domestic companies, equipment suppliers, and service providers competing across different market segments.
Leading market participants include:
Market competition intensifies across technology supply, project development, and financing segments, driving innovation and cost reductions that benefit end-users and accelerate market growth.
Strategic partnerships between international technology providers and domestic companies facilitate technology transfer, local capacity building, and market development while ensuring compliance with local content requirements.
Market segmentation analysis reveals distinct characteristics and growth patterns across different applications, technologies, and end-user categories in Argentina’s solar energy market.
By Application:
By Technology:
Utility-scale segment dominates Argentina’s solar market, driven by government procurement programs and competitive auction mechanisms. This segment benefits from economies of scale, favorable financing conditions, and long-term revenue certainty through power purchase agreements.
Distributed generation category shows the highest growth rates, expanding at over 80% annually as net metering regulations and declining system costs make solar installations attractive for commercial and residential users. This segment benefits from immediate electricity bill savings and relatively simple installation procedures.
Commercial and industrial applications represent a rapidly expanding market segment, with businesses seeking to reduce electricity costs and improve sustainability profiles. Large industrial consumers particularly benefit from on-site solar installations that can significantly reduce electricity expenses.
Residential solar adoption accelerates as system costs decline and financing options improve. Government programs supporting residential installations through subsidies and favorable loan terms contribute to market growth in this segment.
Off-grid applications serve important social and economic development objectives, providing electricity access to remote communities and supporting telecommunications, water pumping, and other essential services in areas without grid connectivity.
Stakeholder benefits from Argentina’s solar energy market development extend across the entire value chain, creating value for diverse participants and supporting broader economic and social objectives.
For Investors:
For Consumers:
For Government:
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Emerging trends shape Argentina’s solar energy market evolution, reflecting technological advancement, policy development, and changing stakeholder preferences.
Distributed generation acceleration represents the most significant trend, with small-scale installations growing rapidly as costs decline and regulatory barriers diminish. This trend democratizes energy production and creates new business models for solar development and financing.
Energy storage integration becomes increasingly important as solar penetration increases and grid stability requirements evolve. Battery storage systems enhance solar energy value through peak shaving, grid services, and improved energy security for consumers.
Corporate renewable energy procurement expands as businesses seek to reduce costs and meet sustainability goals. Long-term power purchase agreements and virtual power purchase agreements create new market mechanisms for solar energy sales.
Technology localization efforts increase focus on domestic manufacturing and assembly capabilities to reduce costs, create employment, and comply with local content requirements. This trend supports industrial development and technology transfer.
Hybrid renewable projects combining solar with wind and storage technologies optimize resource utilization and improve grid integration characteristics. These projects leverage Argentina’s diverse renewable energy resources for enhanced performance.
Digitalization and smart grid integration improve solar energy system performance through advanced monitoring, predictive maintenance, and grid optimization technologies. These developments enhance operational efficiency and reduce maintenance costs.
Recent industry developments demonstrate the dynamic nature of Argentina’s solar energy market and the ongoing evolution of technology, policy, and business models.
RenovAr program expansion continues to drive utility-scale solar development through competitive auctions and long-term contracts. Recent rounds have achieved record-low prices and attracted significant international investment to the sector.
Distributed generation regulations have been updated to improve net metering conditions and expand eligibility for different consumer categories. These regulatory improvements facilitate market growth and enhance the value proposition for distributed solar installations.
International financing initiatives from multilateral development banks and export credit agencies provide additional capital sources for solar project development. These financing mechanisms help address capital constraints and reduce project costs.
Technology partnerships between international equipment suppliers and domestic companies facilitate technology transfer and local capacity building. These partnerships support market development while ensuring compliance with local content requirements.
Grid modernization investments improve transmission and distribution infrastructure to accommodate increasing renewable energy penetration. These investments address key market constraints and enable further solar energy development.
Research and development initiatives at universities and research institutions advance solar technology adaptation to local conditions and develop innovative applications for Argentine market needs.
Strategic recommendations for market participants focus on addressing key challenges while capitalizing on growth opportunities in Argentina’s evolving solar energy landscape.
For Policymakers: Continue strengthening regulatory frameworks while addressing grid infrastructure constraints through coordinated transmission planning and investment. Maintain long-term policy stability to preserve investor confidence while adapting regulations to market evolution and technological advancement.
For Investors: Focus on distributed generation opportunities where market growth is strongest and regulatory support is most stable. Consider partnerships with local companies to navigate regulatory requirements and access domestic market knowledge while managing currency and political risks through appropriate hedging strategies.
For Developers: Diversify project portfolios across different market segments and geographical regions to reduce concentration risks. Invest in local capacity building and stakeholder relationships to ensure long-term market success and regulatory compliance.
For Equipment Suppliers: Establish local assembly or manufacturing capabilities to comply with local content requirements and reduce costs. Develop service capabilities to support long-term customer relationships and capture ongoing revenue opportunities.
For Financial Institutions: Develop specialized renewable energy financing products and risk assessment capabilities to capture growing market opportunities. Consider innovative financing structures such as green bonds and blended finance mechanisms to expand capital availability.
Future market prospects for Argentina’s solar energy sector remain highly positive, supported by favorable fundamentals and ongoing policy support despite potential challenges from economic and political uncertainties.
Growth projections indicate continued rapid expansion across all market segments, with distributed generation expected to maintain the highest growth rates at over 50% annually through the next five years. MarkWide Research analysis suggests that solar energy could account for 15-20% of electricity generation by 2030 under favorable policy scenarios.
Technology evolution will continue driving cost reductions and performance improvements, making solar energy increasingly competitive across all applications. Energy storage integration will become standard practice, enhancing solar energy value and grid integration capabilities.
Market maturation processes will standardize procedures, reduce transaction costs, and improve access to financing for smaller projects. This maturation will facilitate broader market participation and accelerate adoption rates across different consumer segments.
Regional development will expand beyond traditional solar resource areas as technology improvements and grid infrastructure investments enable economically viable projects in previously marginal locations. This geographic diversification will support balanced national development.
International integration opportunities through electricity exports and green hydrogen production could position Argentina as a regional renewable energy hub, leveraging abundant solar resources for broader economic development and export revenue generation.
Argentina’s solar energy market represents a compelling success story in renewable energy development, demonstrating how favorable natural resources, supportive policies, and international investment can combine to create rapid market growth and transformation.
Market fundamentals remain strong despite ongoing challenges, with exceptional solar resources, improving cost competitiveness, and diverse application opportunities supporting continued expansion across utility-scale, commercial, and residential segments. The regulatory framework continues to evolve in response to market needs while maintaining investor confidence and consumer protection.
Future prospects indicate sustained growth momentum driven by technology advancement, cost reductions, and expanding market opportunities. The integration of energy storage, development of hybrid renewable projects, and emergence of new business models will further enhance the sector’s contribution to Argentina’s energy security and economic development objectives.
Strategic success in this market requires understanding of local conditions, regulatory requirements, and stakeholder dynamics while maintaining focus on technological innovation and operational excellence. Participants who can navigate these complexities while delivering value to customers and communities will be best positioned to capitalize on Argentina’s solar energy market opportunities.
What is Solar Energy?
Solar energy refers to the energy harnessed from the sun’s rays, which can be converted into electricity or heat. It is a renewable energy source that plays a crucial role in reducing carbon emissions and promoting sustainability.
What are the key players in Argentina’s Solar Energy Market?
Key players in Argentina’s Solar Energy Market include companies like Enel Green Power, Genneia, and Solarpack, which are involved in the development and operation of solar power plants. These companies contribute significantly to the growth of solar energy capacity in the country, among others.
What are the growth factors driving Argentina’s Solar Energy Market?
Argentina’s Solar Energy Market is driven by factors such as the country’s abundant sunlight, government incentives for renewable energy projects, and increasing energy demand. Additionally, the global shift towards sustainable energy solutions is fostering investment in solar technologies.
What challenges does Argentina’s Solar Energy Market face?
Challenges in Argentina’s Solar Energy Market include regulatory hurdles, financing difficulties for large-scale projects, and competition from other energy sources. These factors can hinder the pace of solar energy adoption and infrastructure development.
What opportunities exist in Argentina’s Solar Energy Market?
Opportunities in Argentina’s Solar Energy Market include the potential for technological advancements in solar panel efficiency and energy storage solutions. Additionally, increasing public awareness of renewable energy benefits can lead to greater investment and consumer adoption.
What trends are shaping Argentina’s Solar Energy Market?
Trends in Argentina’s Solar Energy Market include the rise of decentralized energy systems, where consumers generate their own solar power, and the integration of smart grid technologies. These trends are enhancing energy management and promoting greater efficiency in solar energy use.
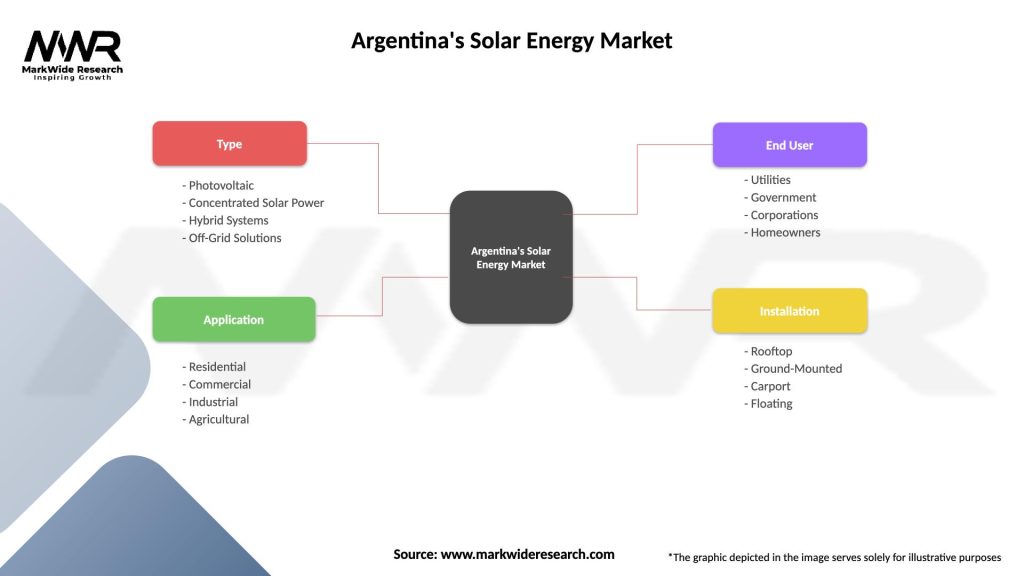
Argentina’s Solar Energy Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | Photovoltaic, Concentrated Solar Power, Hybrid Systems, Off-Grid Solutions |
| Application | Residential, Commercial, Industrial, Agricultural |
| End User | Utilities, Government, Corporations, Homeowners |
| Installation | Rooftop, Ground-Mounted, Carport, Floating |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the Argentina’s Solar Energy Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at