444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
Market Overview
The Singapore e-commerce market has witnessed significant growth in recent years, fueled by the rapid adoption of digital technologies and changing consumer behavior. E-commerce, also known as electronic commerce, refers to the buying and selling of goods and services over the internet. Singapore, a thriving business hub in Southeast Asia, has emerged as a vibrant e-commerce ecosystem, attracting both local and international players.
Meaning
E-commerce has revolutionized the way businesses operate by providing a platform for online transactions. It allows companies to showcase and sell their products or services to a wider audience, transcending geographical boundaries. With the advancement of technology and the widespread use of smartphones and internet connectivity, e-commerce has become an integral part of the modern business landscape.
Executive Summary
The Singapore e-commerce market is experiencing robust growth, driven by factors such as increasing internet penetration, rising smartphone usage, and a growing preference for online shopping. The market offers a wide range of opportunities for businesses across various sectors. However, it also poses challenges related to competition, logistics, and consumer trust. Understanding the market dynamics and leveraging the right strategies is crucial for success in the Singapore e-commerce landscape.
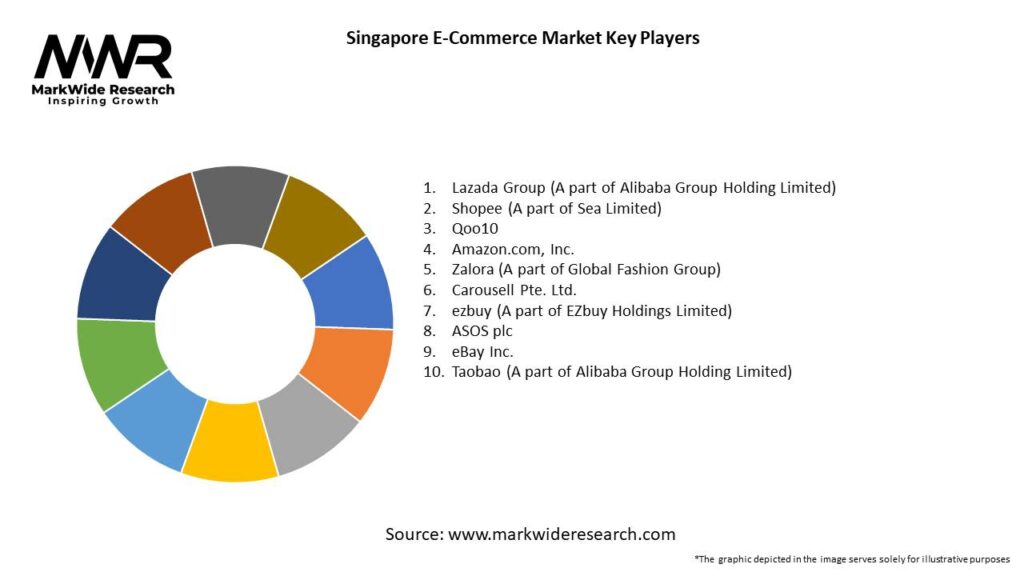
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The Singapore e-commerce market is dynamic and ever-evolving. Several factors influence its growth and shape its future trajectory. Key dynamics include technological advancements, changing consumer preferences, government policies, market competition, and industry collaborations.
Technological advancements, such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and blockchain, are revolutionizing the e-commerce landscape. These technologies enable personalized marketing, supply chain optimization, and enhanced customer experiences.
Consumer preferences are shifting towards online shopping due to its convenience, competitive pricing, and wider product selection. Younger generations, particularly millennials and Gen Z, are driving this trend, being more digitally native and comfortable with online transactions.
The Singaporean government plays a crucial role in shaping the e-commerce market through supportive policies and initiatives. These include funding schemes, grants, and digital transformation programs aimed at encouraging businesses to adopt e-commerce strategies and enhance their digital capabilities.
Intense competition characterizes the e-commerce market in Singapore. Established players and new startups compete for market share, leading to continuous innovation and improved customer offerings. Market consolidation and strategic collaborations are common strategies employed by companies to strengthen their position.
Regional Analysis
The Singapore e-commerce market serves as a hub for regional e-commerce activities, attracting businesses from neighboring countries and beyond. Its strategic location, well-developed infrastructure, and favorable business environment make it an ideal base for expanding into Southeast Asian markets.
Singapore’s proximity to countries such as Malaysia, Indonesia, Thailand, and Vietnam presents opportunities for cross-border e-commerce. E-commerce companies can leverage Singapore’s logistics capabilities to reach a larger customer base and establish a regional presence.
Each Southeast Asian country has its unique characteristics, cultural nuances, and regulatory frameworks. E-commerce businesses must tailor their strategies to cater to the specific needs and preferences of each market while complying with local regulations.
The diversity in consumer behavior, internet penetration rates, and payment preferences across Southeast Asia underscores the importance of market research and localized approaches for successful regional expansion.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Singapore E-Commerce Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.

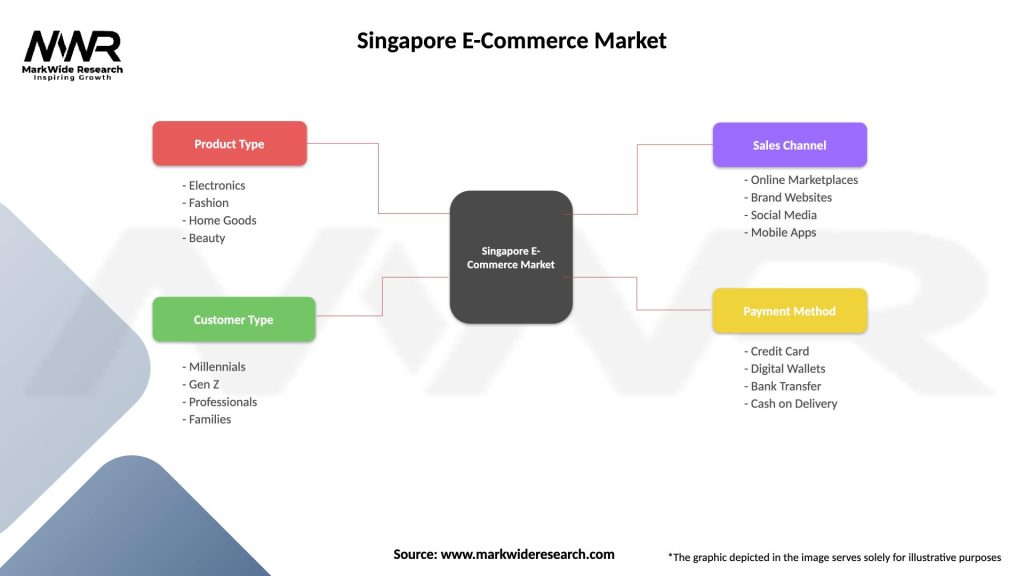
Segmentation
The Singapore e-commerce market can be segmented based on various parameters, including product categories, business models, and consumer segments. Some common segmentation approaches include:
Segmentation allows e-commerce businesses to tailor their strategies, marketing campaigns, and product offerings to specific customer groups, leading to better customer satisfaction and increased sales.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
A SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) analysis provides a comprehensive understanding of the Singapore e-commerce market.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Understanding these internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats, allows businesses to develop effective strategies and mitigate potential risks.
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a profound impact on the Singapore e-commerce market, accelerating its growth and shaping consumer behavior. The lockdown measures and social distancing restrictions imposed during the pandemic led to a surge in online shopping. Key impacts include:
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future outlook for the Singapore e-commerce market is promising. The market is expected to continue its growth trajectory, driven by technological advancements, evolving consumer preferences, and supportive government initiatives. Key trends that will shape the future of e-commerce include:
Conclusion
The Singapore e-commerce market presents significant opportunities for businesses to tap into a tech-savvy and digitally connected consumer base. With increasing internet penetration, smartphone usage, and government support, the market is poised for further growth. However, businesses must navigate challenges such as intense competition, logistics complexities, and consumer trust issues. By leveraging key market insights, embracing emerging trends, and focusing on customer-centric strategies, e-commerce businesses can thrive in the dynamic Singapore e-commerce market.
What is Singapore E-Commerce?
Singapore E-Commerce refers to the buying and selling of goods and services over the internet within Singapore. It encompasses various online retail platforms, digital payment systems, and logistics services that facilitate online transactions.
What are the key players in the Singapore E-Commerce Market?
Key players in the Singapore E-Commerce Market include Shopee, Lazada, and Qoo10, which dominate the online retail space. These companies offer a wide range of products and services, catering to diverse consumer needs, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the Singapore E-Commerce Market?
The growth of the Singapore E-Commerce Market is driven by increasing internet penetration, a growing preference for online shopping, and advancements in mobile payment technologies. Additionally, the rise of social media marketing has significantly influenced consumer purchasing behavior.
What challenges does the Singapore E-Commerce Market face?
The Singapore E-Commerce Market faces challenges such as intense competition among platforms, issues related to cybersecurity, and logistical hurdles in last-mile delivery. These factors can impact customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
What opportunities exist in the Singapore E-Commerce Market?
Opportunities in the Singapore E-Commerce Market include the expansion of cross-border e-commerce, the integration of artificial intelligence for personalized shopping experiences, and the growth of subscription-based services. These trends can enhance customer engagement and drive sales.
What trends are shaping the Singapore E-Commerce Market?
Trends shaping the Singapore E-Commerce Market include the rise of mobile commerce, the increasing use of social media for product discovery, and the adoption of sustainable practices in packaging and delivery. These trends reflect changing consumer preferences and environmental considerations.
Singapore E-Commerce Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Electronics, Fashion, Home Goods, Beauty |
| Customer Type | Millennials, Gen Z, Professionals, Families |
| Sales Channel | Online Marketplaces, Brand Websites, Social Media, Mobile Apps |
| Payment Method | Credit Card, Digital Wallets, Bank Transfer, Cash on Delivery |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Singapore E-Commerce Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at