444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
Market Overview
The Malaysia real estate market has witnessed significant growth in recent years, fueled by a robust economy, favorable government policies, and increasing urbanization. As one of the most dynamic and attractive real estate markets in Southeast Asia, Malaysia offers a wide range of investment opportunities across various segments, including residential, commercial, and industrial properties.
Meaning
The real estate market in Malaysia refers to the buying, selling, renting, and development of properties within the country. It encompasses both residential and commercial properties, including houses, apartments, office buildings, retail spaces, and industrial properties. The market plays a crucial role in driving economic growth, attracting foreign investments, and providing housing solutions for the population.
Executive Summary
The Malaysia real estate market has experienced steady growth over the past decade, driven by several factors such as a growing population, urbanization, and favorable government policies. The market offers diverse opportunities for investors and developers, with attractive returns and a stable regulatory framework. However, like any market, it also faces challenges and risks that need to be considered.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
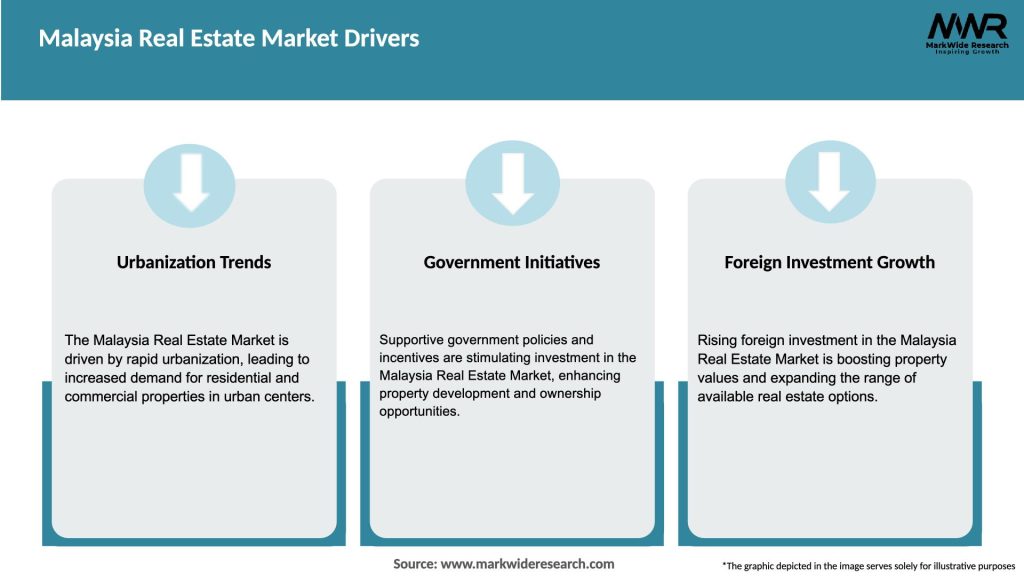
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The Malaysia real estate market is characterized by a combination of local and international players, with strong competition among developers, real estate agencies, and property management companies. The market dynamics are influenced by factors such as population growth, economic conditions, government policies, and global trends. Continuous innovation, market research, and adaptation to changing consumer preferences are essential for success in this dynamic industry.
Regional Analysis
The real estate market in Malaysia exhibits regional variations in terms of demand, supply, and price trends. The major urban centers like Kuala Lumpur, Penang, and Johor Bahru are the primary drivers of the market, benefiting from infrastructure development, economic growth, and high population density. Meanwhile, secondary cities and suburban areas also offer potential investment opportunities, especially in emerging locations with growth potential.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Malaysia Real Estate Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
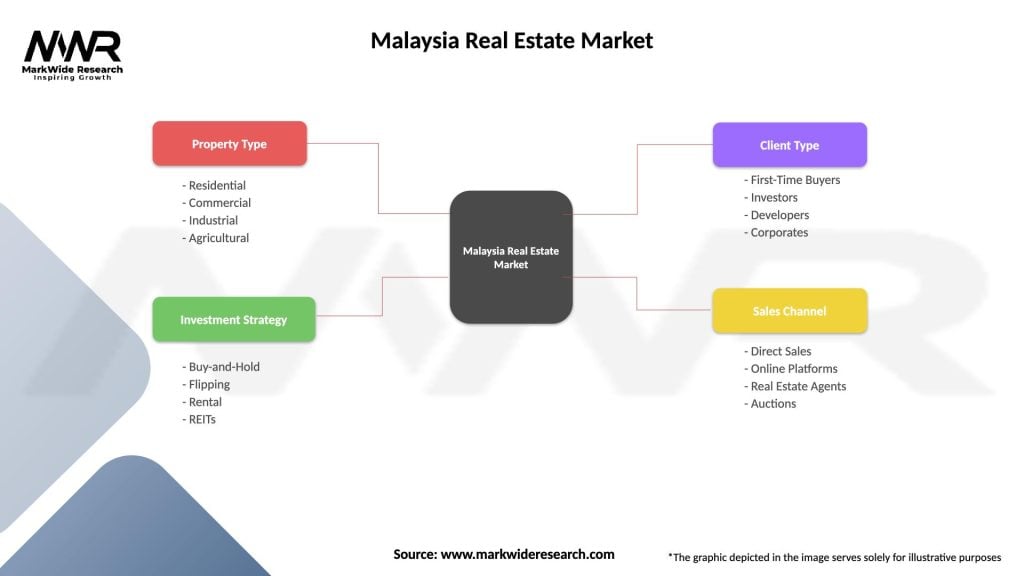
Segmentation
The Malaysia real estate market can be segmented into residential, commercial, and industrial properties. Residential properties include houses, apartments, condominiums, and gated communities, catering to various income segments. Commercial properties comprise office buildings, retail spaces, and hotels, while industrial properties include factories, warehouses, and logistics hubs.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The Covid-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on the Malaysia real estate market, causing disruptions and changes in consumer behavior. During the lockdowns and movement restrictions, property transactions and construction activities were temporarily halted, leading to a slowdown in the market. However, the pandemic has also accelerated certain trends, such as the adoption of digital technologies and remote work arrangements, which have influenced property preferences and investment decisions.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The Malaysia real estate market is expected to continue its growth trajectory in the coming years, supported by favorable government policies, urbanization, and infrastructure development. The focus on affordable housing, sustainable development, and technology integration will shape the future of the market. However, challenges such as housing affordability, oversupply concerns, and economic uncertainties will require proactive measures and adaptability from industry participants.
Conclusion
The Malaysia real estate market offers a diverse range of investment opportunities across residential, commercial, and industrial segments. With a growing middle class, urbanization, and favorable government policies, the market continues to attract local and international investors. While challenges exist, such as housing affordability and oversupply concerns, proactive strategies and innovation can help industry participants capitalize on the market’s potential. By staying informed about market trends, embracing sustainability and technology, and differentiating their offerings, stakeholders can navigate the dynamic real estate landscape and thrive in this lucrative industry.
What is Malaysia Real Estate?
Malaysia Real Estate refers to the buying, selling, and leasing of properties in Malaysia, including residential, commercial, and industrial real estate. It encompasses various activities such as property development, investment, and management.
What are the key players in the Malaysia Real Estate Market?
Key players in the Malaysia Real Estate Market include property developers like Sunway Group and SP Setia, as well as real estate agencies such as Knight Frank and CBRE. These companies are involved in various segments, including residential, commercial, and mixed-use developments, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the Malaysia Real Estate Market?
The growth of the Malaysia Real Estate Market is driven by urbanization, increasing disposable incomes, and a growing middle class. Additionally, government initiatives to promote affordable housing and infrastructure development further stimulate market demand.
What challenges does the Malaysia Real Estate Market face?
The Malaysia Real Estate Market faces challenges such as regulatory hurdles, fluctuating property prices, and economic uncertainties. These factors can impact investor confidence and slow down property transactions.
What opportunities exist in the Malaysia Real Estate Market?
Opportunities in the Malaysia Real Estate Market include the development of smart cities and sustainable housing projects. Additionally, the increasing interest in eco-friendly properties presents a chance for innovation and growth in the sector.
What trends are shaping the Malaysia Real Estate Market?
Trends in the Malaysia Real Estate Market include a shift towards digital property transactions and the rise of co-living spaces. Furthermore, there is a growing emphasis on sustainability and green building practices among developers.
Malaysia Real Estate Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Property Type | Residential, Commercial, Industrial, Agricultural |
| Investment Strategy | Buy-and-Hold, Flipping, Rental, REITs |
| Client Type | First-Time Buyers, Investors, Developers, Corporates |
| Sales Channel | Direct Sales, Online Platforms, Real Estate Agents, Auctions |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Malaysia Real Estate Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at