444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
The global vector control market plays a crucial role in combating the spread of vector-borne diseases such as malaria, dengue fever, Zika virus, and Lyme disease. Vector control refers to the methods and strategies employed to prevent or reduce the transmission of these diseases by controlling the vectors responsible for their spread. These vectors primarily include mosquitoes, ticks, fleas, and flies.
Vector control involves a range of interventions aimed at controlling vector populations and minimizing their contact with humans. This includes the use of insecticides, larvicides, repellents, trapping devices, biological control agents, and environmental management techniques. The ultimate goal is to prevent or reduce the incidence of vector-borne diseases, thus safeguarding public health.
Executive Summary
The global vector control market has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing incidence of vector-borne diseases and the rising awareness about their prevention. Governments, healthcare organizations, and research institutions are actively involved in implementing vector control programs to curb the spread of these diseases.

Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
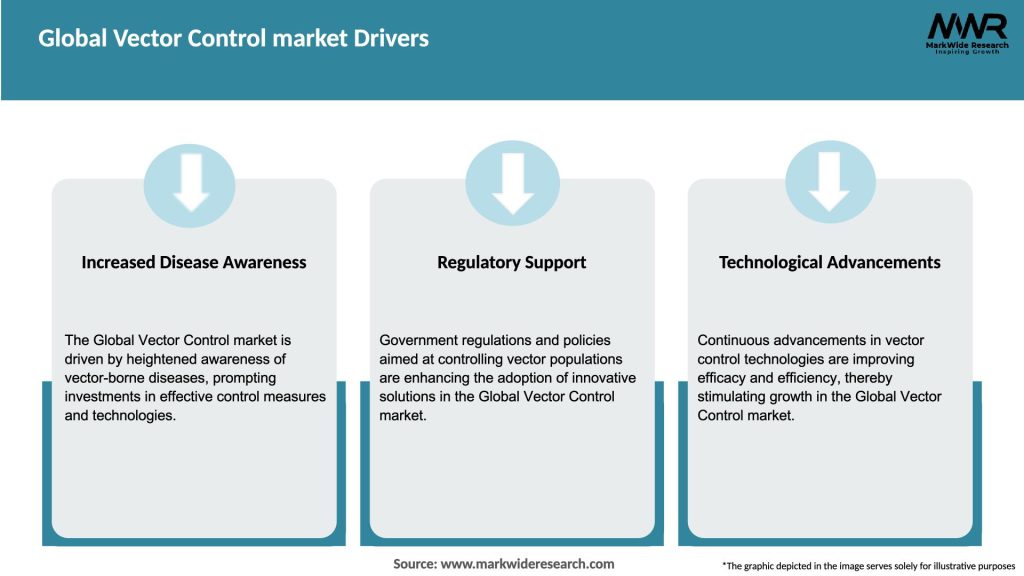
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The global vector control market is characterized by dynamic trends driven by the interplay of various factors. Key dynamics include technological advancements, regulatory landscape, shifting disease patterns, funding initiatives, and partnerships between industry players and government agencies.
Regional Analysis
The vector control market varies significantly across different regions. Regions with a high burden of vector-borne diseases, such as Africa, Southeast Asia, and Latin America, require extensive vector control interventions. Developed regions, including North America and Europe, focus on surveillance, research, and development of innovative vector control methods.
Competitive Landscape
Leading companies in the Global Vector Control market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
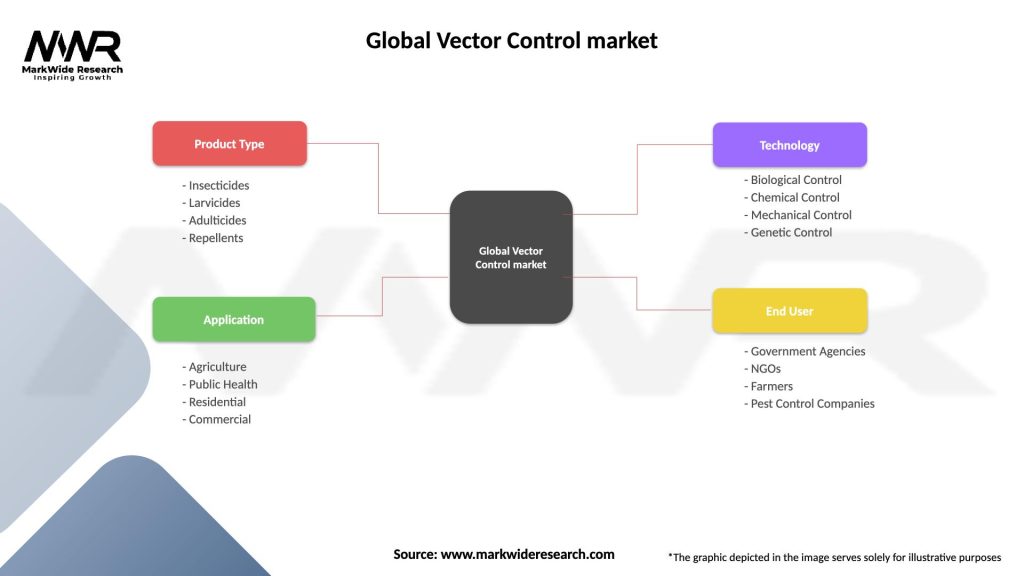
Segmentation
The vector control market can be segmented based on control method, vector type, end-user, and geography. Control methods include chemical control, biological control, and environmental management. Vector types comprise mosquitoes, ticks, fleas, and flies. End-users primarily include government agencies, healthcare organizations, research institutions, and residential users.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic had an indirect impact on the vector control market. While the immediate focus was on combating the virus, disruptions in healthcare systems, resource allocation, and travel restrictions affected vector control programs. However, the pandemic also highlighted the importance of preparedness and resilient healthcare systems, leading to increased attention on vector control as a preventive measure.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The global vector control market is expected to grow significantly in the coming years. Factors such as rising incidence of vector-borne diseases, technological advancements, increasing government initiatives, and the focus on integrated vector management are likely to drive market expansion. The adoption of sustainable and eco-friendly solutions, along with collaborations and partnerships, will shape the future of the industry.
Conclusion
The global vector control market plays a vital role in combating the spread of vector-borne diseases and safeguarding public health. Technological advancements, government initiatives, and increasing awareness have fueled the demand for effective vector control measures. While challenges such as insecticide resistance and environmental concerns persist, innovations in control methods, collaborations, and the adoption of integrated vector management approaches provide opportunities for industry participants. By investing in research, leveraging technology, and strengthening partnerships, the vector control industry can make a significant impact in preventing and reducing the burden of vector-borne diseases worldwide.
What is Vector Control?
Vector Control refers to methods and strategies aimed at managing and reducing populations of vectors, such as mosquitoes and ticks, that transmit diseases to humans and animals. This includes various techniques like insecticide application, biological control, and environmental management.
What are the key players in the Global Vector Control market?
Key players in the Global Vector Control market include companies like Bayer AG, Syngenta, and BASF, which develop and supply vector control products and solutions. These companies focus on innovative pest management strategies and sustainable practices, among others.
What are the main drivers of growth in the Global Vector Control market?
The main drivers of growth in the Global Vector Control market include the rising incidence of vector-borne diseases, increased public health awareness, and advancements in vector control technologies. Additionally, government initiatives and funding for disease prevention contribute to market expansion.
What challenges does the Global Vector Control market face?
The Global Vector Control market faces challenges such as resistance to insecticides, regulatory hurdles, and environmental concerns regarding chemical use. These factors can hinder the effectiveness of vector control measures and complicate implementation strategies.
What opportunities exist in the Global Vector Control market?
Opportunities in the Global Vector Control market include the development of eco-friendly and sustainable control methods, integration of technology such as drones for monitoring, and increased investment in research and development. These trends can enhance the effectiveness of vector management strategies.
What trends are shaping the Global Vector Control market?
Trends shaping the Global Vector Control market include the growing emphasis on integrated pest management, the use of genetically modified organisms for vector control, and the adoption of digital tools for data collection and analysis. These innovations aim to improve efficiency and effectiveness in vector management.
Global Vector Control market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Insecticides, Larvicides, Adulticides, Repellents |
| Application | Agriculture, Public Health, Residential, Commercial |
| Technology | Biological Control, Chemical Control, Mechanical Control, Genetic Control |
| End User | Government Agencies, NGOs, Farmers, Pest Control Companies |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the Global Vector Control market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at