444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2750
Market Overview
The Europe gas market has been a key player in the region’s energy sector for several decades. Gas, also known as natural gas, is a versatile and environmentally friendly source of energy. It is primarily composed of methane and is extracted from underground reservoirs. Europe has a well-developed gas infrastructure, including pipelines and liquefied natural gas (LNG) terminals, which facilitate the transportation and distribution of gas across the continent.
Meaning
The Europe gas market refers to the buying and selling of natural gas within the European region. This market encompasses various stakeholders, including gas producers, suppliers, distributors, and consumers. The demand for gas in Europe is driven by a wide range of sectors, including residential, commercial, industrial, and power generation. The market operates through contracts and agreements, ensuring a reliable supply of gas to meet the region’s energy needs.
Executive Summary
The Europe gas market has experienced significant growth and transformation in recent years. The market is driven by several factors, including the transition towards cleaner energy sources, increasing gas demand from various sectors, and the development of new infrastructure. However, there are also challenges and opportunities that need to be addressed to ensure the sustainable growth of the market.
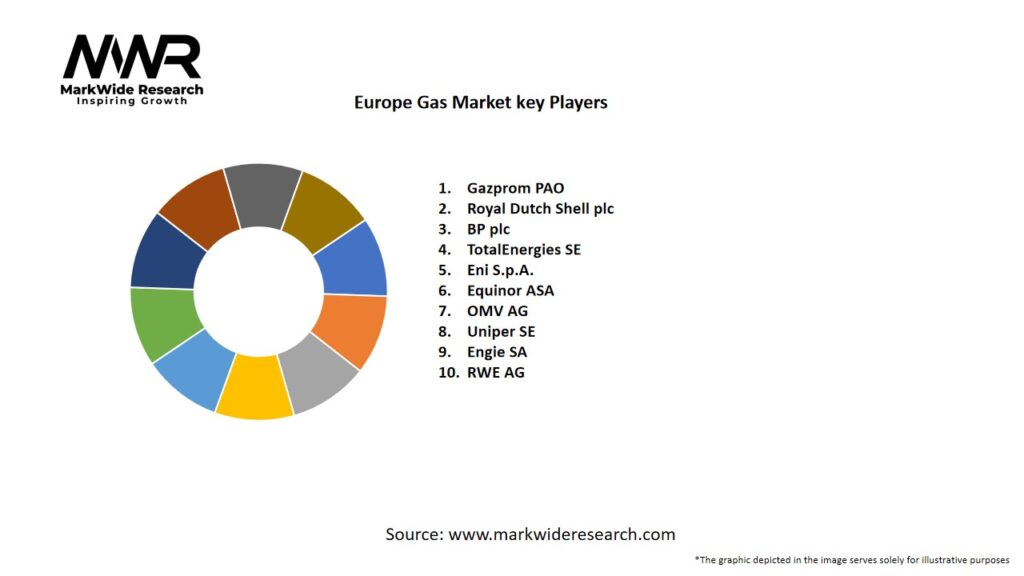
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
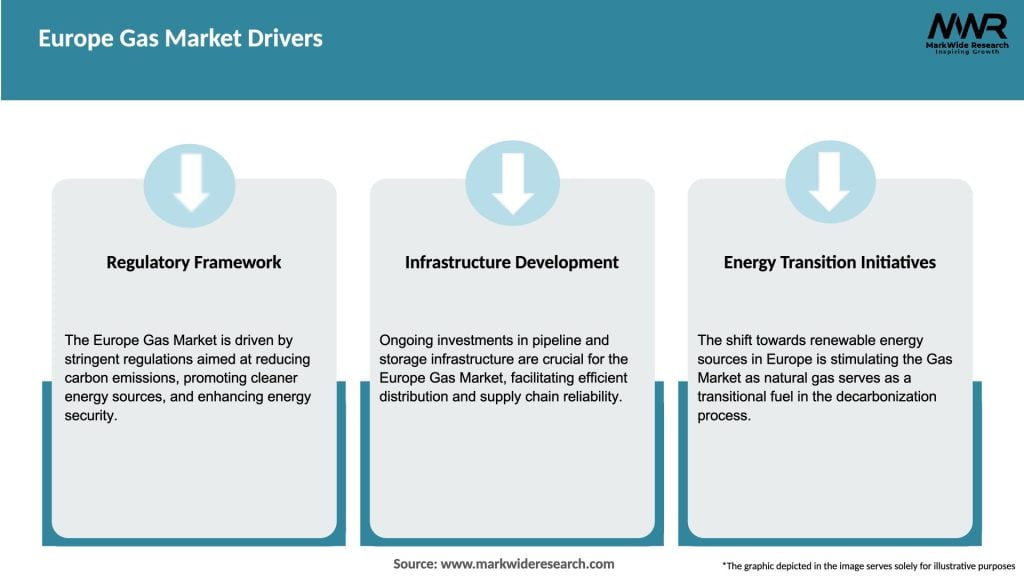
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The Europe gas market is characterized by dynamic interactions between supply, demand, and various market players. The market dynamics are influenced by factors such as government policies, regulatory frameworks, technological advancements, and market competition. Changes in these dynamics can impact gas prices, supply security, infrastructure development, and the overall competitiveness of the market. It is crucial for industry participants to closely monitor these dynamics and adapt their strategies accordingly.
Regional Analysis
The Europe gas market can be analyzed on a regional basis to understand the specific dynamics and trends in each submarket. Europe is divided into several gas market regions, including Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Southern Europe, and Northern Europe. Each region has its unique characteristics in terms of gas production, consumption patterns, infrastructure development, and regulatory frameworks. A comprehensive regional analysis helps identify market opportunities, challenges, and the potential for cross-border cooperation.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Europe Gas Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
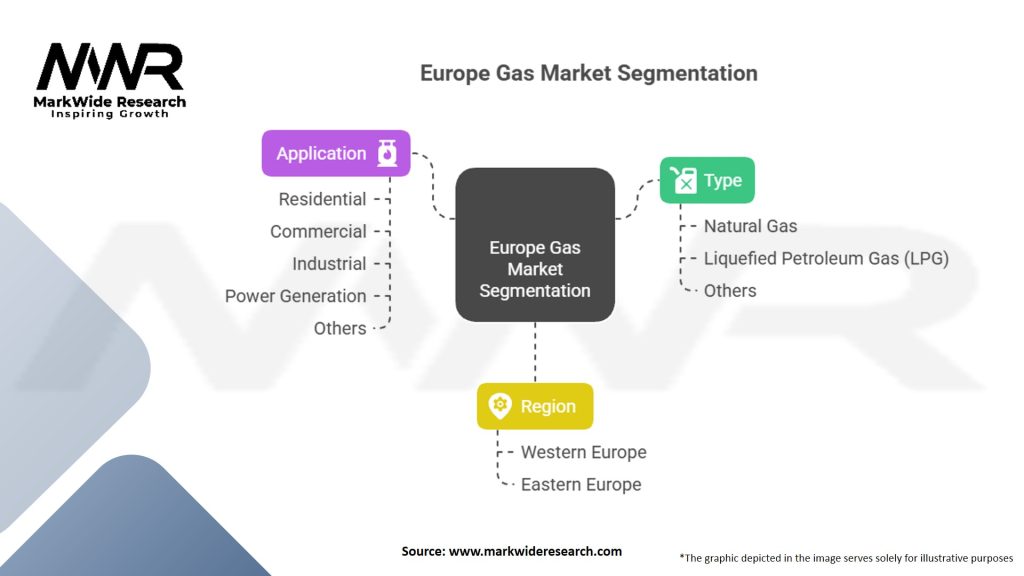
Segmentation
The Europe gas market can be segmented based on various criteria, including gas type, end-use sector, and geography. Gas types include natural gas, LNG, and renewable gas. End-use sectors encompass power generation, residential and commercial, industrial, and transportation. Geographically, the market can be segmented into Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Southern Europe, and Northern Europe. Each segment has its specific demand drivers, market dynamics, and growth opportunities.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The Covid-19 pandemic had a significant impact on the Europe gas market. The lockdown measures and economic slowdown resulted in a temporary decline in gas demand, particularly in the commercial and industrial sectors. However, the residential sector experienced increased gas consumption as people spent more time at home. The pandemic also disrupted gas supply chains, including production, transportation, and storage operations. Despite the short-term challenges, the gas market demonstrated resilience and proved to be a reliable energy source during the crisis. The post-pandemic recovery is expected to drive the demand for gas, especially in sectors such as power generation and industrial manufacturing.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future outlook for the Europe gas market is influenced by a range of factors, including energy transition goals, technological advancements, regulatory frameworks, and geopolitical dynamics. While the market faces challenges, such as competition from renewables and environmental concerns, it also presents opportunities in renewable gases, energy storage, and international cooperation. The gas market will continue to play a significant role in Europe’s energy mix, providing a reliable and cleaner-burning fuel source to meet the region’s diverse energy needs.
Conclusion
The Europe gas market is a vital component of the region’s energy sector, providing a versatile, reliable, and cleaner alternative to coal and oil. The market has witnessed significant growth and transformation, driven by factors such as increasing demand for cleaner energy, infrastructure development, and geopolitical dynamics. While the market faces challenges, including environmental concerns and competition from renewables, there are opportunities to embrace renewable gases, enhance infrastructure, and foster international cooperation. By adapting to the evolving market dynamics, industry participants can navigate the changing energy landscape and contribute to a sustainable and resilient gas market in Europe.
What is Gas?
Gas refers to a state of matter that is composed of molecules in constant motion, often used as a fuel source in various applications, including heating, electricity generation, and industrial processes.
What are the key players in the Europe Gas Market?
Key players in the Europe Gas Market include companies such as Gazprom, TotalEnergies, and BP, which are involved in the exploration, production, and distribution of natural gas, among others.
What are the main drivers of the Europe Gas Market?
The main drivers of the Europe Gas Market include the increasing demand for cleaner energy sources, the transition from coal to gas in power generation, and the growth of industrial applications that require natural gas.
What challenges does the Europe Gas Market face?
The Europe Gas Market faces challenges such as regulatory pressures for emissions reductions, competition from renewable energy sources, and geopolitical tensions that can affect supply stability.
What opportunities exist in the Europe Gas Market?
Opportunities in the Europe Gas Market include the development of liquefied natural gas (LNG) infrastructure, advancements in gas storage technologies, and the potential for hydrogen production from natural gas.
What trends are shaping the Europe Gas Market?
Trends shaping the Europe Gas Market include the increasing integration of renewable energy, the rise of digital technologies for monitoring and optimizing gas usage, and a shift towards more sustainable practices in gas extraction and consumption.
Europe Gas Market Segmentation
| Segmentation Details | Information |
|---|---|
| Type | Natural Gas, Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG), Others |
| Application | Residential, Commercial, Industrial, Power Generation, Others |
| Region | Western Europe, Eastern Europe |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Europe Gas Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at