444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
Market Overview
The China cybersecurity market is a vital segment within the broader technology landscape, encompassing a wide range of products, services, and solutions aimed at safeguarding digital assets, data privacy, and network infrastructure from cyber threats. As one of the largest and fastest-growing digital economies globally, China faces significant cybersecurity challenges due to its extensive online presence, rapid digital transformation, and increasing cyber threats from both domestic and international sources.
Meaning
The China cybersecurity market refers to the ecosystem of technologies, policies, and practices designed to protect digital systems, networks, and data assets from cyber threats, including malware, hacking, data breaches, and cyber espionage. It encompasses a diverse range of cybersecurity solutions and services, including network security, endpoint protection, threat intelligence, identity and access management, and compliance frameworks, aimed at safeguarding critical infrastructure, businesses, and individuals from cyber attacks.
Executive Summary
The China cybersecurity market is experiencing rapid growth driven by factors such as increasing cyber threats, rising awareness of cybersecurity risks, stringent regulatory requirements, and the growing adoption of digital technologies across various sectors. While the market presents significant opportunities for cybersecurity vendors and service providers, it also faces challenges such as evolving threat landscapes, talent shortages, and geopolitical tensions impacting international cooperation on cybersecurity issues.

Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The China cybersecurity market operates in a dynamic and evolving landscape characterized by rapid technological advancements, shifting regulatory requirements, emerging cyber threats, and geopolitical tensions impacting international cybersecurity cooperation. Understanding the market dynamics is essential for cybersecurity vendors, service providers, and organizations to adapt to changing cybersecurity trends, anticipate future challenges, and capitalize on growth opportunities effectively.
Regional Analysis
The cybersecurity landscape in China varies across different regions, with key cybersecurity hubs, technology clusters, and industry concentrations influencing regional cybersecurity capabilities, investment trends, and cybersecurity readiness. Major cities such as Beijing, Shanghai, Shenzhen, and Hangzhou serve as key centers for cybersecurity innovation, research, development, and industry collaboration, contributing to regional cybersecurity resilience and economic growth.
Competitive Landscape
Leading companies in the China Cybersecurity market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
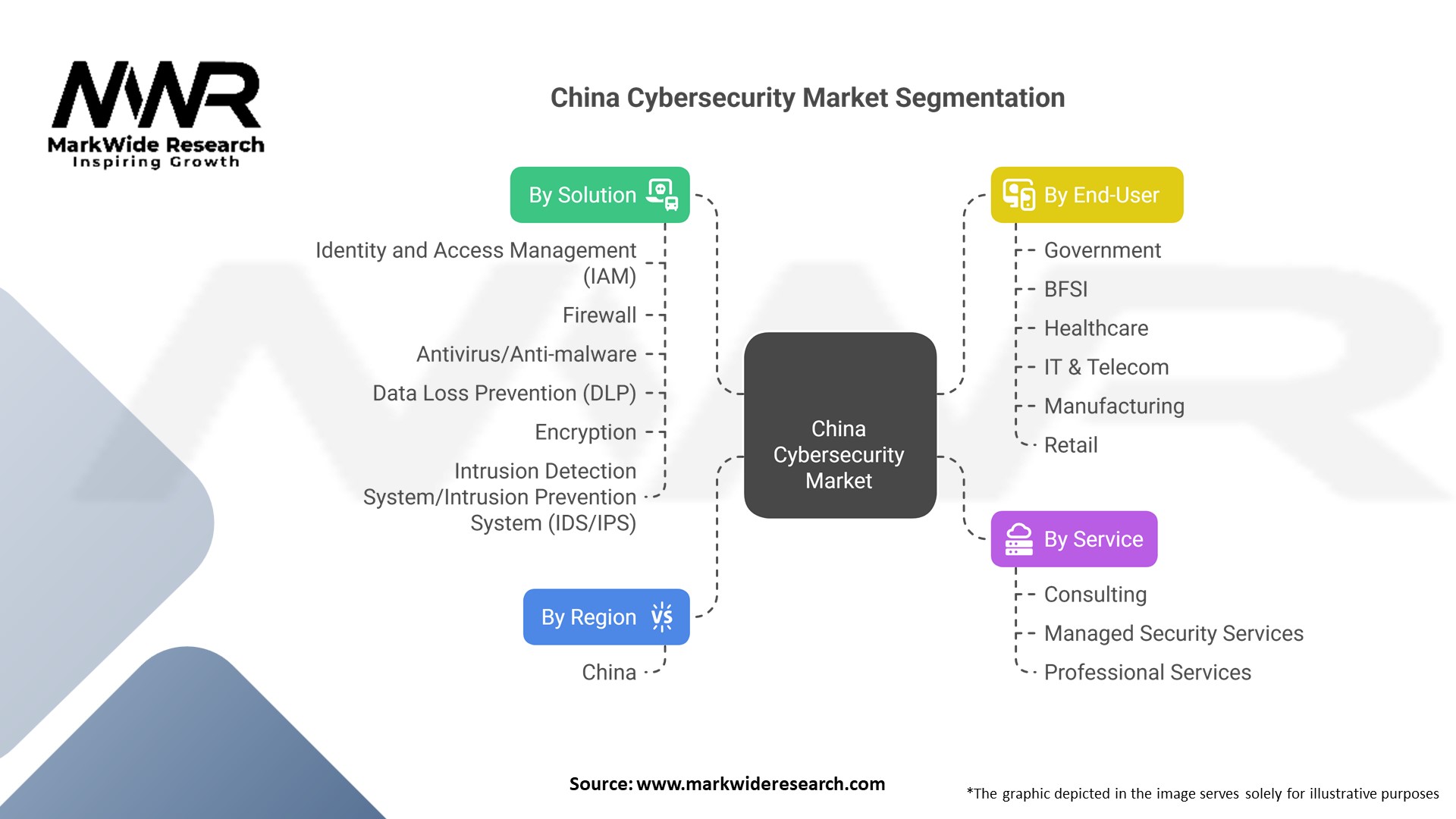
Segmentation
The China cybersecurity market can be segmented based on various factors such as:
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated digital transformation initiatives, remote work adoption, and cloud migration efforts in China, resulting in increased cyber threats, phishing attacks, and ransomware incidents targeting remote workers, online platforms, and critical infrastructure sectors. Organizations have responded by enhancing cybersecurity measures, implementing remote access controls, and investing in secure remote work solutions to mitigate cyber risks and ensure business continuity.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future outlook for the China cybersecurity market is positive, with continued growth expected driven by factors such as increasing cyber threats, digital transformation initiatives, regulatory compliance requirements, and cybersecurity investments across sectors. However, challenges such as geopolitical tensions, supply chain risks, and cybersecurity skills shortages will require proactive measures, collaboration, and innovation to address effectively. The adoption of emerging technologies, international cybersecurity cooperation, and regulatory reforms will shape the future trajectory of the China cybersecurity market, positioning it for sustained growth and resilience in an increasingly complex and dynamic cyber threat landscape.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the China cybersecurity market presents significant opportunities and challenges for organizations, government agencies, and cybersecurity stakeholders seeking to enhance their cybersecurity resilience and mitigate cyber threats effectively. With increasing cyber attacks, stringent regulatory requirements, and rapid digital transformation, cybersecurity has become a top priority for businesses, government entities, and individuals in China. By investing in advanced cybersecurity technologies, fostering cybersecurity talent development, and promoting international cybersecurity cooperation, China can strengthen its cybersecurity posture, safeguard critical infrastructure, and protect national security interests in cyberspace.
As China continues to navigate the complex cybersecurity landscape, collaboration, innovation, and strategic investments will be critical for building a secure, resilient, and trusted cyber environment that enables sustainable growth, innovation, and prosperity in the digital era. By embracing cybersecurity as a strategic priority and adopting a proactive, holistic approach to cybersecurity risk management, China can mitigate cyber threats effectively, promote responsible cyberspace behavior, and ensure a safer and more secure digital future for all stakeholders.
China Cybersecurity Market:
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| By Solution | Identity and Access Management (IAM), Firewall, Antivirus/Anti-malware, Data Loss Prevention (DLP), Encryption, Intrusion Detection System/Intrusion Prevention System (IDS/IPS), Others |
| By Service | Consulting, Managed Security Services, Professional Services |
| By End-User | Government, BFSI, Healthcare, IT & Telecom, Manufacturing, Retail, Others |
| By Region | China |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the China Cybersecurity market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at