444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The light rail market has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for sustainable and efficient public transportation systems. Light rail refers to a mode of urban transportation that utilizes low-floor trams or trains operating on dedicated tracks. These systems are designed to provide a comfortable and convenient commuting experience for passengers, while also reducing traffic congestion and environmental pollution.
Meaning
Light rail systems are characterized by their ability to operate in both urban and suburban areas, connecting various neighborhoods, business districts, and transportation hubs. These systems typically have multiple stops along their routes, allowing passengers to board and alight conveniently. Light rail vehicles are powered by electricity, either through overhead power lines or an on-board energy storage system, making them an eco-friendly alternative to traditional diesel-powered buses or cars.
Executive Summary
The light rail market has experienced steady growth in recent years, driven by several factors such as increasing urbanization, government initiatives to promote sustainable transportation, and the growing need for efficient public transit systems. The market is expected to continue its upward trajectory, with a strong focus on expanding light rail networks and upgrading existing infrastructure to accommodate higher passenger capacity.
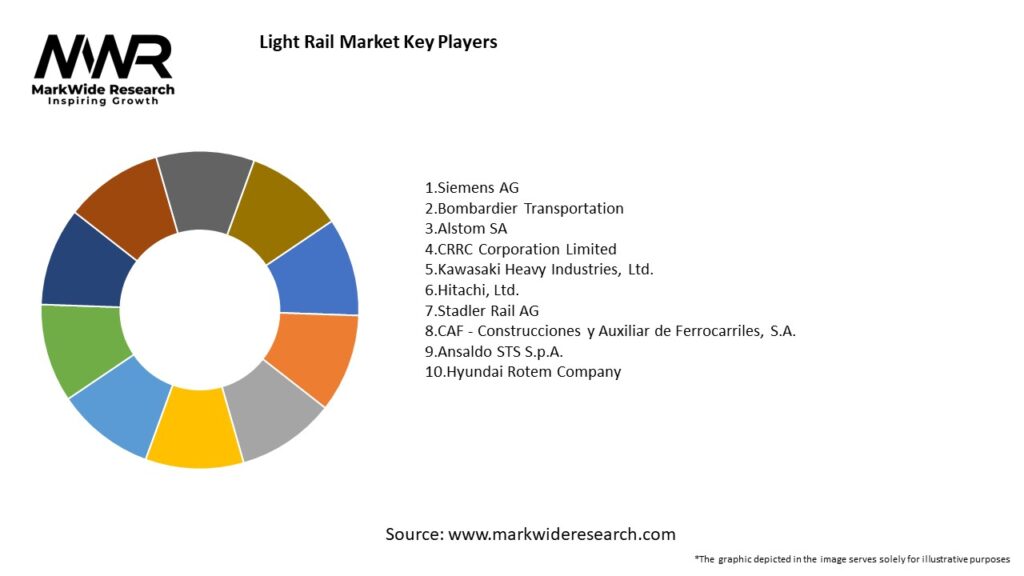
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The light rail market is characterized by dynamic factors that influence its growth and development. The market dynamics are shaped by various elements, including government policies, urbanization trends, technological advancements, and passenger preferences.
Government policies play a crucial role in driving market growth by providing financial incentives, regulatory frameworks, and strategic planning for light rail projects. The focus on sustainability, reduction of traffic congestion, and improving urban mobility often aligns with the goals of governments, making light rail an attractive option.
Urbanization trends, especially in densely populated areas, drive the demand for efficient transportation systems. As cities expand and traffic congestion worsens, the need for reliable and sustainable transportation options becomes more apparent. Light rail systems offer a viable solution by providing convenient and environmentally friendly commuting choices.
Technological advancements in the light rail industry contribute to improved system efficiency, passenger safety, and operational performance. Innovations such as advanced signaling systems, real-time passenger information, and energy-efficient technologies enhance the overall user experience and attract more passengers to choose light rail as their preferred mode of transportation.
Passenger preferences and expectations play a vital role in shaping the light rail market. Commuters seek reliable, comfortable, and cost-effective transportation options. Light rail systems that offer spacious interiors, air conditioning, convenient boarding, and shorter travel times are more likely to attract and retain passengers.
Regional Analysis
The light rail market exhibits regional variations driven by factors such as urbanization rates, government policies, transportation infrastructure development, and economic growth. Here is a regional analysis of key markets:
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Light Rail Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
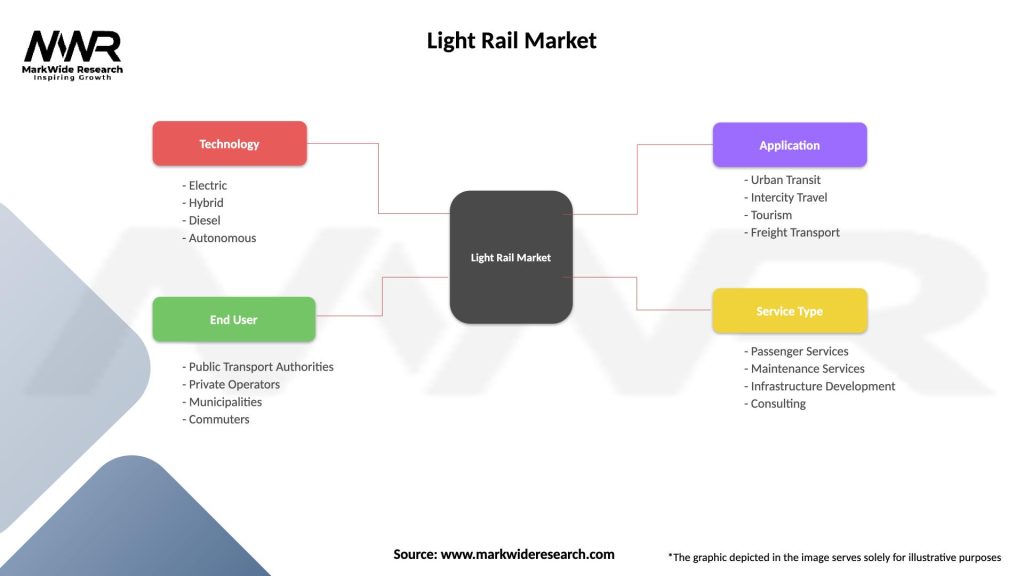
Segmentation
The light rail market can be segmented based on various factors, including:
Segmentation allows for a more detailed analysis of the light rail market, enabling stakeholders to understand specific market dynamics, opportunities, and challenges within each segment.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis of the light rail market can provide insights into its internal strengths, weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic had a significant impact on the light rail market, leading to changes in passenger demand, operations, and investment priorities. The pandemic resulted in a temporary decline in ridership as lockdowns and travel restrictions were implemented. However, as restrictions eased and the world transitioned to a new normal, the light rail market started to recover.
During the pandemic, light rail systems implemented various measures to ensure passenger safety, including increased sanitization, social distancing protocols, and mandatory mask-wearing. These measures were essential to regain passenger trust and confidence in using public transportation.
The pandemic also highlighted the importance of resilient and sustainable transportation systems. Light rail, with its ability to provide socially distanced travel and low carbon emissions, emerged as a preferred choice for many commuters seeking safe and reliable transportation options.
Furthermore, the pandemic prompted governments and transportation authorities to reevaluate their investment priorities. The focus shifted towards enhancing public transportation infrastructure, including light rail systems, to promote sustainable mobility and reduce reliance on private vehicles.
While the COVID-19 pandemic posed temporary challenges for the light rail market, it also created opportunities for innovation, technological advancements, and increased recognition of the importance of sustainable urban transportation.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future outlook for the light rail market is promising, driven by the need for sustainable urban transportation solutions, government support, and advancements in technology. The market is expected to witness continued expansion, with the development of new light rail networks and the expansion of existing ones.
Rapid urbanization, increasing population density, and environmental concerns will drive the demand for light rail systems as an efficient and eco-friendly mode of transportation. Governments will continue to invest in light rail projects to address traffic congestion, reduce carbon emissions, and improve urban mobility.
Technological advancements will play a crucial role in shaping the future of the light rail market. Innovations in areas such as automation, predictive maintenance, and connectivity will enhance system efficiency, passenger experience, and overall performance.
The integration of light rail systems with smart city initiatives will further optimize operations, improve connectivity, and provide passengers with seamless travel experiences. The use of data analytics, IoT-based technologies, and advanced communication systems will contribute to the evolution of smart and sustainable light rail networks.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the light rail market holds significant potential for growth and development. As cities strive for sustainable and efficient transportation solutions, light rail systems offer a viable option. The market will continue to evolve, driven by technological advancements, supportive government policies, and the changing preferences of passengers seeking reliable and eco-friendly commuting options.
What is Light Rail?
Light rail refers to a form of urban rail transit that typically operates on tracks embedded in city streets or dedicated rights-of-way. It is characterized by lower capacity and speed compared to heavy rail systems, making it suitable for urban environments and short-distance travel.
What are the key players in the Light Rail Market?
Key players in the Light Rail Market include Siemens Mobility, Bombardier Transportation, Alstom, and CAF. These companies are involved in the manufacturing of light rail vehicles and the development of associated infrastructure, among others.
What are the main drivers of growth in the Light Rail Market?
The main drivers of growth in the Light Rail Market include increasing urbanization, the need for sustainable transportation solutions, and government investments in public transit infrastructure. Additionally, light rail systems help reduce traffic congestion and lower greenhouse gas emissions.
What challenges does the Light Rail Market face?
The Light Rail Market faces challenges such as high initial capital costs, land acquisition issues, and competition from other modes of transportation like buses and personal vehicles. Additionally, maintaining operational efficiency and safety standards can be demanding.
What opportunities exist in the Light Rail Market?
Opportunities in the Light Rail Market include the expansion of existing networks, the integration of smart technologies for improved efficiency, and the potential for public-private partnerships to fund new projects. There is also a growing interest in eco-friendly transit solutions.
What trends are shaping the Light Rail Market?
Trends shaping the Light Rail Market include the adoption of advanced signaling systems, the use of renewable energy sources for operations, and the development of autonomous light rail systems. Additionally, there is a focus on enhancing passenger experience through modern amenities.
Light Rail Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Technology | Electric, Hybrid, Diesel, Autonomous |
| End User | Public Transport Authorities, Private Operators, Municipalities, Commuters |
| Application | Urban Transit, Intercity Travel, Tourism, Freight Transport |
| Service Type | Passenger Services, Maintenance Services, Infrastructure Development, Consulting |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Light Rail Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at