444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The Internet of Things (IoT) has revolutionized various industries, and the insurance sector is no exception. IoT insurance, also known as telematics insurance or usage-based insurance (UBI), utilizes connected devices to gather data and provide customized insurance policies. This emerging market is witnessing significant growth as insurance companies leverage IoT technology to enhance risk assessment, improve customer engagement, and streamline claims processes. The IoT insurance market is poised to transform the traditional insurance landscape, offering numerous benefits to both insurers and policyholders.
Meaning
Internet of Things (IoT) insurance refers to the integration of IoT devices and data analytics into insurance products and services. IoT devices such as telematics devices, wearables, and smart sensors collect real-time data related to the insured asset or individual’s behavior. This data is then used by insurance companies to calculate premiums, tailor policies, and offer personalized services. The IoT enables insurers to assess risks more accurately, prevent losses through real-time monitoring, and provide value-added services to policyholders.
Executive Summary
The IoT insurance market is experiencing remarkable growth, driven by the increasing adoption of IoT devices, advancements in data analytics, and the need for personalized insurance solutions. Insurers are actively embracing IoT technology to gain a competitive edge by improving underwriting accuracy, reducing claims fraud, and enhancing customer experiences. With IoT-enabled devices becoming more prevalent in homes, vehicles, and commercial spaces, the scope for IoT insurance is expanding rapidly. However, challenges such as data privacy concerns and regulatory issues need to be addressed to fully unlock the market’s potential.

Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The IoT insurance market is characterized by rapid technological advancements, changing consumer expectations, and evolving regulatory frameworks. Insurers are investing heavily in IoT infrastructure, data analytics capabilities, and partnerships to stay ahead in this dynamic landscape. The market is witnessing intense competition as both traditional insurance players and insurtech startups vie for market share. The ability to harness IoT data effectively, protect consumer privacy, and deliver seamless customer experiences will be crucial for sustained success in this evolving market.
Regional Analysis
The IoT insurance market exhibits varying levels of maturity and adoption across different regions. North America and Europe currently dominate the market, driven by favorable regulatory environments, advanced IoT infrastructure, and high awareness among consumers. Asia Pacific is expected to witness significant growth due to increasing IoT adoption and a large population base. Latin America and the Middle East & Africa are gradually embracing IoT insurance, presenting long-term growth opportunities as awareness and technological infrastructure improve in these regions.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Internet of Things Insurance Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Segmentation
The IoT insurance market can be segmented based on various factors, including:
Segmentation allows insurers to target specific customer segments, tailor insurance offerings, and optimize their marketing and distribution strategies.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of IoT insurance in several ways:
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future of IoT insurance looks promising, with significant growth potential across industries and regions. As IoT adoption continues to expand, insurance companies will increasingly integrate IoT devices, data analytics, and AI technologies into their operations. The market will witness the emergence of new insurance products, improved risk management solutions, and enhanced customer experiences. However, addressing data privacy concerns, establishing standardized protocols, and navigating evolving regulations will be crucial for sustainable growth in the IoT insurance market.
Conclusion
The Internet of Things (IoT) insurance market is transforming the insurance industry by leveraging connected devices and data analytics. IoT-enabled insurance policies offer personalized coverage, real-time risk assessment, and value-added services. Despite challenges related to data privacy, standardization, and customer awareness, the market is witnessing rapid growth due to technological advancements and changing customer expectations. Insurers, IoT device manufacturers, and data analytics firms are actively participating in this market, driven by the opportunities presented by emerging markets, partnerships, and data-driven services. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated the adoption of IoT insurance, emphasizing the importance of remote risk assessment, contactless claims processing, and cybersecurity. With continued advancements in IoT technology and increased focus on data privacy, the future of IoT insurance holds immense potential for insurers and policyholders alike.
What is Internet of Things Insurance?
Internet of Things Insurance refers to insurance products designed to cover risks associated with IoT devices and systems. This includes protection against data breaches, device malfunctions, and liability arising from the use of connected devices in various sectors such as healthcare, automotive, and smart homes.
What are the key players in the Internet of Things Insurance Market?
Key players in the Internet of Things Insurance Market include companies like Allianz, AXA, and Zurich Insurance Group. These companies are actively developing IoT insurance solutions to address the unique risks posed by connected devices, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the Internet of Things Insurance Market?
The growth of the Internet of Things Insurance Market is driven by the increasing adoption of IoT devices across industries, the rising need for data security, and the growing awareness of liability risks associated with connected technologies. Additionally, advancements in technology and regulatory support are contributing to market expansion.
What challenges does the Internet of Things Insurance Market face?
The Internet of Things Insurance Market faces challenges such as the complexity of assessing risks associated with IoT devices, the rapid pace of technological change, and regulatory uncertainties. These factors can hinder the development of comprehensive insurance products tailored for IoT applications.
What opportunities exist in the Internet of Things Insurance Market?
Opportunities in the Internet of Things Insurance Market include the potential for innovative insurance products tailored to specific industries, such as smart cities and connected vehicles. Additionally, partnerships between insurers and technology providers can enhance product offerings and improve risk assessment capabilities.
What trends are shaping the Internet of Things Insurance Market?
Trends shaping the Internet of Things Insurance Market include the integration of artificial intelligence for risk assessment, the development of usage-based insurance models, and the increasing focus on cybersecurity coverage. These trends reflect the evolving landscape of IoT and the need for adaptive insurance solutions.
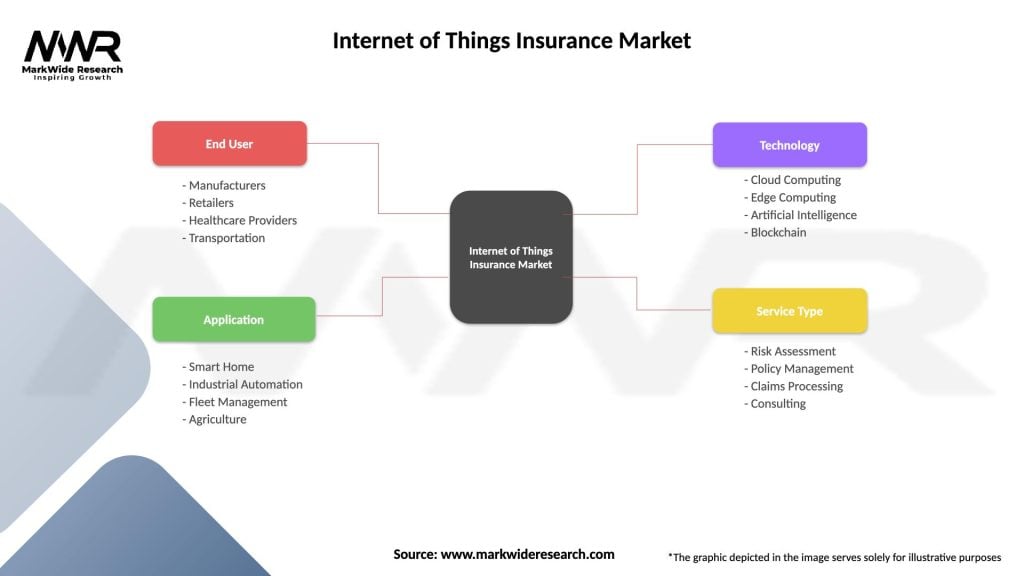
Internet of Things Insurance Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| End User | Manufacturers, Retailers, Healthcare Providers, Transportation |
| Application | Smart Home, Industrial Automation, Fleet Management, Agriculture |
| Technology | Cloud Computing, Edge Computing, Artificial Intelligence, Blockchain |
| Service Type | Risk Assessment, Policy Management, Claims Processing, Consulting |
Leading Companies in the Internet of Things Insurance Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at