444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The Canadian biosimilar market has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand for cost-effective healthcare solutions. Biosimilars, also known as follow-on biologics, are highly similar versions of reference biologic drugs that have lost patent protection. They offer a more affordable alternative to their originator counterparts, making them an attractive option for healthcare providers and patients.
Meaning
Biosimilars are developed using a complex and costly process, involving the use of living cells to create therapeutic proteins. The manufacturing process ensures that the biosimilar is highly similar to the reference product in terms of efficacy, safety, and quality. Regulatory bodies, such as Health Canada, rigorously evaluate biosimilars to ensure their comparability to the reference product.
Executive Summary
The Canadian biosimilar market has experienced substantial growth in recent years, driven by factors such as increasing healthcare costs, patent expirations of biologic drugs, and favorable government policies. The market offers significant opportunities for pharmaceutical companies, healthcare providers, and patients seeking affordable treatment options. However, there are also challenges to be addressed, including market barriers and regulatory complexities.
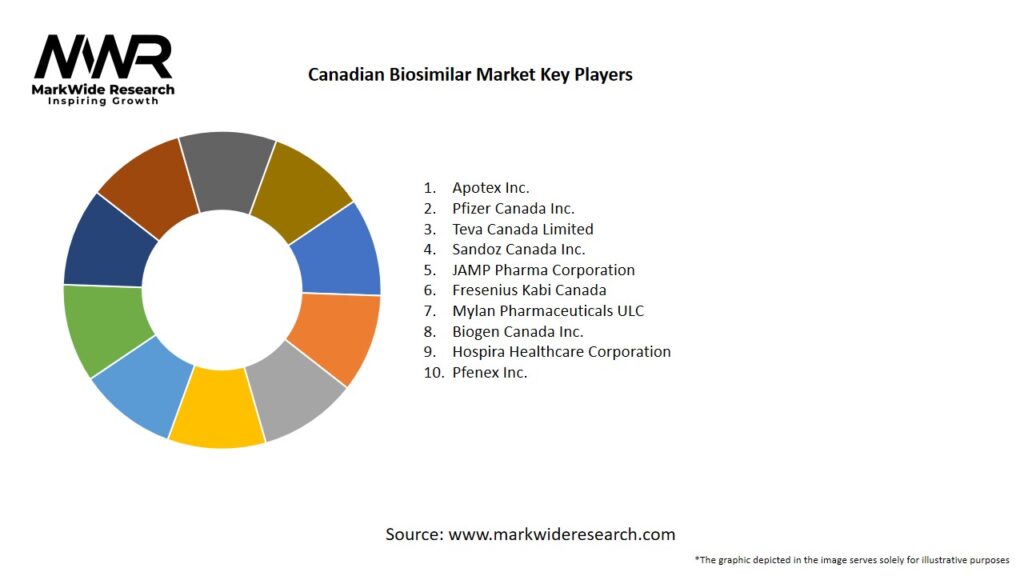
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The Canadian biosimilar market is characterized by intense competition among pharmaceutical companies, ongoing regulatory developments, and evolving market dynamics. Key players in the market are focusing on product development, strategic partnerships, and educational initiatives to enhance market penetration. Additionally, collaborations between biosimilar manufacturers and healthcare providers are fostering a conducive environment for market growth.
Regional Analysis
The Canadian biosimilar market exhibits regional variations in terms of market penetration and adoption rates. Urban centers, such as Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver, have shown higher adoption due to better healthcare infrastructure and awareness. However, efforts are being made to bridge the gap and ensure equal access to biosimilars across the country.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Canadian Biosimilar Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Segmentation
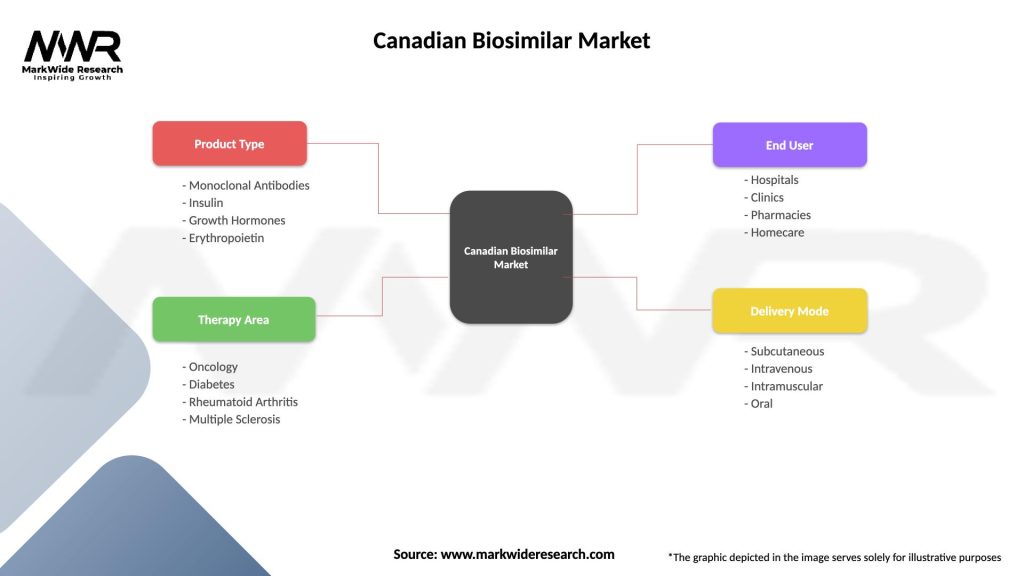
The Canadian biosimilar market can be segmented based on product type, therapeutic area, and distribution channel. Product types include monoclonal antibodies, insulin, growth factors, and others. Therapeutic areas encompass oncology, immunology, diabetes, and more. Distribution channels include hospitals, retail pharmacies, and online pharmacies.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has had both positive and negative impacts on the Canadian biosimilar market. On one hand, the pandemic has highlighted the importance of affordable treatment options, leading to increased interest in biosimilars. On the other hand, the healthcare system’s focus on managing the pandemic has led to delays in regulatory processes and disrupted supply chains, affecting the market growth to some extent.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The Canadian biosimilar market is poised for continued growth in the coming years. The increasing acceptance of biosimilars, expanding therapeutic areas, and supportive government policies are expected to drive market expansion. However, challenges such as regulatory complexities and market barriers need to be addressed to fully realize the market’s potential.
Conclusion
The Canadian biosimilar market presents significant opportunities for pharmaceutical companies, healthcare providers, and patients seeking affordable treatment options. With increasing acceptance, growing therapeutic areas, and supportive government policies, biosimilars are expected to play a crucial role in the Canadian healthcare landscape. However, addressing regulatory complexities, market barriers, and fostering collaboration among stakeholders will be essential for maximizing the benefits of biosimilars and ensuring their widespread adoption.
What is Biosimilar?
Biosimilars are biologic medical products highly similar to already approved reference biologics. They are used in various therapeutic areas, including oncology, autoimmune diseases, and diabetes management.
What are the key players in the Canadian Biosimilar Market?
Key players in the Canadian Biosimilar Market include Amgen, Sandoz, and Pfizer, among others. These companies are involved in the development and commercialization of biosimilars across multiple therapeutic areas.
What are the growth factors driving the Canadian Biosimilar Market?
The Canadian Biosimilar Market is driven by factors such as the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, the need for cost-effective treatment options, and the growing acceptance of biosimilars among healthcare providers and patients.
What challenges does the Canadian Biosimilar Market face?
Challenges in the Canadian Biosimilar Market include regulatory hurdles, the need for extensive clinical data to demonstrate similarity, and competition from established biologics that may hinder market entry.
What opportunities exist in the Canadian Biosimilar Market?
Opportunities in the Canadian Biosimilar Market include expanding therapeutic indications, increasing patient access to biologic treatments, and potential collaborations between biosimilar manufacturers and healthcare systems.
What trends are shaping the Canadian Biosimilar Market?
Trends in the Canadian Biosimilar Market include the growing focus on personalized medicine, advancements in biotechnology, and increasing investment in research and development to enhance biosimilar offerings.
Canadian Biosimilar Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Monoclonal Antibodies, Insulin, Growth Hormones, Erythropoietin |
| Therapy Area | Oncology, Diabetes, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Multiple Sclerosis |
| End User | Hospitals, Clinics, Pharmacies, Homecare |
| Delivery Mode | Subcutaneous, Intravenous, Intramuscular, Oral |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Canadian Biosimilar Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at