444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
The Mexico textile manufacturing market represents a cornerstone of the nation’s industrial landscape, establishing itself as a critical component of North American supply chains and global textile production networks. Mexico’s strategic positioning between major consumer markets in the United States and emerging economies in Latin America has created unprecedented opportunities for textile manufacturers seeking cost-effective production solutions while maintaining proximity to key distribution channels.
Manufacturing capabilities across Mexico have evolved significantly, with the industry experiencing robust growth driven by favorable trade agreements, competitive labor costs, and substantial infrastructure investments. The sector encompasses diverse manufacturing segments including cotton processing, synthetic fiber production, fabric weaving, garment assembly, and technical textile manufacturing. Regional clusters have emerged in states such as Puebla, Tlaxcala, Estado de México, and Coahuila, each specializing in specific textile manufacturing processes and product categories.
Trade relationships continue to strengthen Mexico’s position as a preferred textile manufacturing destination, with the USMCA agreement providing enhanced market access and regulatory certainty. The industry benefits from growing demand for nearshoring solutions, as international brands seek to reduce supply chain complexities and transportation costs. Technological advancement initiatives are transforming traditional manufacturing processes, with automation and digital integration driving efficiency improvements of approximately 25-30% across modern facilities.
Export performance demonstrates the sector’s competitive strength, with Mexican textile products gaining market share in premium segments and technical applications. The industry’s growth trajectory reflects broader economic trends toward regional manufacturing consolidation and sustainable production practices, positioning Mexico as an increasingly important player in global textile value chains.
The Mexico textile manufacturing market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of companies, facilities, and supply chains engaged in the production, processing, and assembly of textile products within Mexican territory. This market encompasses raw material processing, fiber production, fabric manufacturing, garment assembly, and specialized textile applications across industrial, consumer, and technical segments.
Manufacturing scope includes traditional textile processes such as spinning, weaving, knitting, dyeing, and finishing, alongside advanced technical textile production for automotive, aerospace, medical, and industrial applications. The market integrates both domestic consumption and export-oriented production, serving regional and international customers through established distribution networks and trade partnerships.
Economic significance extends beyond direct manufacturing activities to include supporting industries such as machinery suppliers, chemical providers, logistics services, and technology vendors. The market represents a vital employment source for millions of Mexican workers while contributing substantially to national export revenues and industrial development initiatives.
Strategic positioning leverages Mexico’s geographic advantages, trade agreements, and manufacturing expertise to create competitive advantages in cost, quality, and delivery performance compared to alternative production locations in Asia and other regions.
Market dynamics in Mexico’s textile manufacturing sector reflect a period of significant transformation and growth, driven by evolving global supply chain strategies and increasing demand for nearshore production capabilities. The industry has successfully positioned itself as a preferred alternative to Asian manufacturing, offering competitive advantages in lead times, logistics costs, and regulatory compliance for North American markets.
Production capacity expansion continues across multiple segments, with particular strength in garment assembly, technical textiles, and sustainable manufacturing processes. Investment flows from international brands and domestic manufacturers are modernizing facilities and introducing advanced technologies that enhance productivity and product quality. Employment growth in the sector has reached approximately 8-12% annually in key manufacturing regions, reflecting robust industry expansion.
Trade performance demonstrates the sector’s competitive positioning, with Mexican textile exports capturing increased market share in premium segments and specialized applications. The industry benefits from preferential trade access through USMCA provisions, creating sustainable competitive advantages over alternative production locations. Innovation initiatives are driving development of sustainable materials, smart textiles, and advanced manufacturing processes that align with evolving consumer preferences and regulatory requirements.
Future prospects indicate continued growth potential, supported by ongoing nearshoring trends, infrastructure investments, and technological advancement programs that strengthen Mexico’s position as a leading textile manufacturing destination in the Americas.
Strategic positioning analysis reveals several critical factors driving Mexico’s textile manufacturing competitiveness and market development trajectory:
Market segmentation reveals diverse opportunities across traditional apparel manufacturing, technical textiles, and specialized applications serving automotive, medical, and industrial markets. Regional specialization patterns have emerged, with different states developing expertise in specific textile categories and manufacturing processes.
Nearshoring trends represent the primary catalyst for Mexico’s textile manufacturing growth, as international brands seek to reduce supply chain risks and improve responsiveness to market demands. The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated these trends, highlighting vulnerabilities in extended Asian supply chains and creating opportunities for regional manufacturing alternatives. Cost optimization strategies increasingly favor Mexico’s combination of competitive labor rates, reduced transportation expenses, and favorable trade terms.
Trade policy advantages through USMCA provisions create substantial incentives for textile manufacturing investment in Mexico. Duty-free access to North American markets, combined with rules of origin requirements that favor regional production, establishes sustainable competitive advantages over alternative manufacturing locations. Regulatory alignment between Mexico and its North American partners reduces compliance complexities and facilitates seamless cross-border trade operations.
Infrastructure investments by both government and private sector entities are expanding Mexico’s manufacturing capabilities and operational efficiency. Transportation network improvements, energy infrastructure development, and telecommunications upgrades create enabling conditions for textile manufacturing expansion. Industrial park development provides modern facilities with integrated utilities and services that attract international manufacturers.
Workforce development initiatives are enhancing Mexico’s human capital advantages in textile manufacturing. Technical education programs, skills training initiatives, and industry-academia partnerships are producing qualified workers capable of operating advanced manufacturing systems. Cultural factors including strong work ethic, manufacturing tradition, and adaptability to new technologies support industry growth and competitiveness.
Competition intensity from established Asian manufacturing centers continues to challenge Mexico’s textile industry, particularly in high-volume, price-sensitive product categories. Countries such as China, Vietnam, and Bangladesh maintain significant cost advantages in certain segments, requiring Mexican manufacturers to focus on value-added services and specialized applications. Price pressure from international buyers demands continuous efficiency improvements and cost optimization initiatives.
Infrastructure limitations in certain regions constrain manufacturing expansion and operational efficiency. While major industrial centers benefit from modern infrastructure, secondary locations may lack adequate transportation, energy, or telecommunications capabilities. Logistics challenges including port capacity constraints and transportation bottlenecks can impact delivery performance and cost competitiveness.
Skills shortages in specialized technical areas limit industry growth potential and technological advancement. While Mexico possesses a strong manufacturing workforce, specific expertise in advanced textile technologies, automation systems, and quality management requires ongoing development. Training investments represent significant costs for manufacturers seeking to upgrade workforce capabilities.
Regulatory complexity across different jurisdictions can create compliance challenges for manufacturers serving multiple markets. Environmental regulations, labor standards, and trade requirements demand sophisticated management systems and ongoing monitoring. Currency fluctuations between the Mexican peso and major trading partner currencies introduce financial risks that require active management strategies.
Technical textiles represent a high-growth opportunity segment for Mexican manufacturers, with applications in automotive, aerospace, medical, and industrial markets offering premium pricing and stable demand patterns. The automotive industry’s expansion in Mexico creates substantial demand for specialized textile components including airbags, seat fabrics, interior trim, and filtration materials. Innovation potential in smart textiles and functional materials aligns with evolving consumer preferences and technological advancement trends.
Sustainable manufacturing initiatives create competitive advantages and market access opportunities as brands increasingly prioritize environmental responsibility. Mexican manufacturers can leverage renewable energy resources, water management technologies, and circular economy principles to develop sustainable production capabilities. Certification programs for organic, recycled, and environmentally friendly textiles open premium market segments with higher margins and customer loyalty.
E-commerce growth and direct-to-consumer business models create opportunities for flexible, responsive manufacturing capabilities that can support smaller batch sizes and faster turnaround times. Mexican manufacturers’ proximity to North American markets provides advantages in serving online retailers and custom manufacturing applications. Digital integration technologies enable real-time production monitoring and customer communication capabilities.
Regional market expansion throughout Latin America offers growth opportunities for Mexican textile manufacturers seeking to diversify customer bases and reduce dependence on North American markets. Trade agreements and economic integration initiatives facilitate market access across the region. Brand development opportunities exist for Mexican companies to establish their own textile brands and move up the value chain from contract manufacturing to branded product sales.
Supply chain evolution continues to reshape Mexico’s textile manufacturing landscape, with companies adapting to changing customer requirements and global market conditions. The shift toward regional supply chains has accelerated investment in Mexican manufacturing capabilities, while technological advancement enables more sophisticated production processes and quality standards. Integration levels between Mexican manufacturers and international brands are deepening, creating long-term partnership relationships that support sustained growth.
Technology adoption patterns reveal increasing investment in automation, digital monitoring systems, and advanced manufacturing technologies. Mexican textile manufacturers are implementing Industry 4.0 solutions that enhance productivity, reduce waste, and improve quality consistency. Efficiency gains from technology integration typically range from 20-35% in production throughput and quality metrics, supporting competitiveness improvements.
Market consolidation trends are creating larger, more capable manufacturing entities through mergers, acquisitions, and strategic partnerships. This consolidation enables investment in advanced technologies and expanded production capabilities while improving economies of scale. Specialization patterns are emerging as manufacturers focus on specific product categories or market segments where they can develop competitive advantages.
Customer relationship dynamics are evolving toward longer-term partnerships with shared investment in capabilities development and technology advancement. International brands are increasingly willing to invest in Mexican supplier capabilities to secure reliable, high-quality production capacity. Collaboration initiatives include joint technology development, sustainability programs, and workforce training partnerships that strengthen competitive positioning.
Data collection for this comprehensive analysis employed multiple research methodologies to ensure accuracy and completeness of market insights. Primary research activities included structured interviews with industry executives, manufacturing facility visits, and surveys of key stakeholders across the Mexican textile manufacturing ecosystem. Secondary research incorporated analysis of government statistics, trade data, industry reports, and company financial information to validate primary findings.
Market analysis techniques utilized both quantitative and qualitative approaches to assess industry dynamics, competitive positioning, and growth prospects. Statistical analysis of production data, trade flows, and economic indicators provided quantitative foundations for market assessments. Qualitative insights from industry experts, technology providers, and customer interviews added depth and context to numerical findings.
Validation processes included cross-referencing multiple data sources, expert review panels, and sensitivity analysis to ensure reliability of conclusions and recommendations. MarkWide Research methodologies incorporated industry best practices for market research accuracy and analytical rigor. Geographic coverage encompassed all major textile manufacturing regions within Mexico, ensuring comprehensive representation of industry conditions and trends.
Analytical frameworks applied established market research techniques including Porter’s Five Forces analysis, SWOT assessment, and value chain analysis to provide structured insights into competitive dynamics and strategic opportunities. Forecasting models incorporated multiple scenarios to account for various market development possibilities and risk factors affecting industry growth trajectories.
Puebla and Tlaxcala constitute Mexico’s primary textile manufacturing corridor, accounting for approximately 35-40% of national production capacity. This region benefits from established industrial infrastructure, skilled workforce availability, and proximity to major transportation networks connecting to North American markets. Manufacturing specialization includes cotton processing, synthetic fiber production, and garment assembly operations serving both domestic and export markets.
Estado de México represents another significant manufacturing center, with particular strength in technical textiles and specialized applications. The region’s proximity to Mexico City provides access to financial services, logistics infrastructure, and skilled technical personnel. Investment activity in this region focuses on advanced manufacturing technologies and high-value product segments that leverage the area’s technical capabilities.
Northern border states including Coahuila, Chihuahua, and Nuevo León have developed substantial textile manufacturing capabilities focused primarily on export markets. These regions benefit from proximity to U.S. markets, established maquiladora infrastructure, and experienced manufacturing workforces. Production focus emphasizes garment assembly, automotive textiles, and technical applications serving North American customers.
Emerging regions in central and southern Mexico are attracting textile manufacturing investment through competitive cost structures and government incentive programs. States such as Guanajuato, Aguascalientes, and Yucatán are developing textile manufacturing capabilities while leveraging existing automotive and industrial infrastructure. Growth potential in these regions reflects opportunities for geographic diversification and cost optimization strategies.
Market leadership in Mexico’s textile manufacturing sector includes both international corporations and domestic companies that have established significant production capabilities and market presence. The competitive environment reflects diverse business models ranging from large-scale contract manufacturers to specialized producers focusing on specific product categories or market segments.
Competitive strategies focus on technology advancement, sustainability initiatives, and customer relationship development to maintain market position and growth momentum. Investment patterns reveal ongoing facility modernization, capacity expansion, and workforce development initiatives across major market participants.
By Product Type: The Mexican textile manufacturing market encompasses diverse product categories serving different customer segments and applications. Apparel textiles represent the largest segment, including cotton fabrics, synthetic blends, and specialty materials for garment manufacturing. Technical textiles constitute a rapidly growing segment with applications in automotive, medical, industrial, and aerospace markets.
By Manufacturing Process: Production methodologies vary significantly across different textile categories and customer requirements. Integrated manufacturing operations encompass the complete value chain from fiber processing through finished product assembly. Specialized processing focuses on specific manufacturing stages such as spinning, weaving, dyeing, or finishing operations.
By End-Use Application: Market segmentation reflects diverse customer industries and application requirements. Consumer apparel represents traditional textile applications including clothing, footwear, and accessories. Industrial applications include automotive components, filtration materials, geotextiles, and protective equipment.
By Technology Level: Manufacturing capabilities range from traditional textile processes to advanced automated systems. Conventional manufacturing utilizes established production methods with manual and semi-automated processes. Advanced manufacturing incorporates Industry 4.0 technologies, robotics, and digital integration systems for enhanced efficiency and quality control.
Cotton Textiles: Mexico’s cotton textile segment benefits from domestic raw material availability and established processing infrastructure. Production capabilities include spinning, weaving, and finishing operations that serve both domestic consumption and export markets. Quality standards meet international requirements while maintaining competitive cost structures. Sustainability initiatives focus on water management, energy efficiency, and organic cotton processing to align with evolving market preferences.
Synthetic Textiles: The synthetic textile category demonstrates strong growth potential driven by technical applications and performance requirements. Manufacturing expertise includes polyester, nylon, and specialty fiber processing for automotive, industrial, and consumer applications. Investment in advanced production technologies enables high-quality output with consistent performance characteristics. Innovation focus includes development of recycled synthetic materials and functional textile properties.
Technical Textiles: This high-value segment represents significant growth opportunities for Mexican manufacturers seeking premium market positioning. Application areas include automotive components, medical textiles, filtration materials, and protective equipment. Manufacturing requirements demand specialized equipment, quality control systems, and technical expertise. Market access depends on certification compliance and customer qualification processes that validate performance capabilities.
Garment Assembly: Mexico’s garment assembly capabilities serve major international brands through established maquiladora operations and contract manufacturing relationships. Production flexibility enables handling of diverse product categories from basic apparel to complex technical garments. Proximity to North American markets provides competitive advantages in lead times and logistics costs. Quality systems meet international standards while maintaining competitive pricing structures.
Manufacturing Cost Advantages: Mexican textile manufacturers benefit from competitive labor costs, reduced transportation expenses, and favorable energy pricing compared to alternative production locations. Operational efficiency improvements through technology adoption and process optimization create additional cost benefits. Trade agreement provisions eliminate or reduce tariff burdens for qualifying products, enhancing price competitiveness in key markets.
Market Access Benefits: USMCA provisions provide preferential access to North American markets while rules of origin requirements create competitive advantages over non-regional producers. Geographic proximity enables faster delivery times, reduced inventory requirements, and improved customer service capabilities. Cultural and business practice similarities facilitate communication and relationship development with North American customers.
Supply Chain Advantages: Established supplier networks and logistics infrastructure support efficient procurement and distribution operations. Integration opportunities with automotive, aerospace, and other industrial sectors create synergies and shared infrastructure benefits. Proximity to raw material sources and component suppliers reduces supply chain complexity and transportation costs.
Investment Incentives: Government programs provide tax incentives, infrastructure support, and regulatory assistance for textile manufacturing investments. Industrial park development offers modern facilities with integrated utilities and services. Workforce training programs and educational partnerships support human capital development initiatives that benefit industry participants.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Automation Integration: Mexican textile manufacturers are increasingly adopting automated production systems to enhance efficiency, quality consistency, and cost competitiveness. Technology implementation includes robotic systems for material handling, automated cutting and sewing equipment, and digital monitoring systems for quality control. Investment in automation typically generates productivity improvements of 25-40% while reducing labor dependency and operational costs.
Sustainability Initiatives: Environmental responsibility has become a critical competitive factor, with manufacturers implementing comprehensive sustainability programs covering energy efficiency, water management, waste reduction, and circular economy principles. Certification programs for sustainable manufacturing practices are gaining importance for market access and customer relationships. Renewable energy adoption and carbon footprint reduction initiatives align with global sustainability trends.
Digital Transformation: Industry 4.0 technologies are transforming traditional textile manufacturing through real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and data-driven decision making. Digital integration enables improved supply chain visibility, customer communication, and operational optimization. Cloud-based systems facilitate remote monitoring and management capabilities that enhance operational flexibility.
Customization Capabilities: Growing demand for personalized and small-batch production is driving investment in flexible manufacturing systems that can efficiently handle diverse product requirements. Quick response manufacturing capabilities enable faster turnaround times and reduced inventory requirements for customers. Digital printing and on-demand production technologies support customization trends while maintaining cost effectiveness.
Infrastructure Investments: Major transportation and logistics infrastructure projects are enhancing Mexico’s textile manufacturing competitiveness through improved connectivity and reduced operational costs. Port expansion projects in Veracruz and other coastal locations increase import-export capacity for raw materials and finished products. Highway and rail network improvements facilitate efficient domestic distribution and cross-border trade operations.
Technology Partnerships: Collaboration between Mexican manufacturers and international technology providers is accelerating adoption of advanced manufacturing systems and digital technologies. Innovation centers and research partnerships with universities are developing new materials, processes, and applications that enhance competitive positioning. Government-supported technology transfer programs facilitate knowledge sharing and capability development.
Market Expansion: Mexican textile manufacturers are diversifying customer bases through expansion into new geographic markets and application segments. Latin American markets represent growing opportunities for regional expansion, while technical textile applications provide access to higher-value market segments. Strategic partnerships with international brands are creating long-term growth opportunities and market access.
Workforce Development: Industry-academia partnerships and government training programs are addressing skills shortages and preparing workers for advanced manufacturing technologies. Technical education initiatives focus on automation, quality management, and specialized textile processes. Apprenticeship programs and continuing education opportunities support career development and industry competitiveness.
Technology Investment Priorities: MarkWide Research analysis indicates that Mexican textile manufacturers should prioritize automation and digital integration investments to maintain competitiveness against low-cost Asian alternatives. Strategic focus should emphasize technologies that enhance productivity, quality consistency, and operational flexibility while reducing labor dependency and production costs.
Market Diversification Strategies: Industry participants should develop comprehensive market diversification plans that reduce dependence on North American customers while leveraging established capabilities and competitive advantages. Technical textile applications offer particular opportunities for premium pricing and stable demand patterns that support sustainable growth and profitability.
Sustainability Implementation: Environmental responsibility initiatives should be integrated into core business strategies rather than treated as compliance requirements. Competitive advantages from sustainability programs include improved customer relationships, cost reductions, and access to premium market segments that value environmental responsibility.
Partnership Development: Strategic partnerships with technology providers, raw material suppliers, and customer organizations can accelerate capability development and market access while sharing investment risks and costs. Collaboration opportunities should focus on areas where shared interests create mutual benefits and competitive advantages.
Growth trajectory for Mexico’s textile manufacturing market remains positive, supported by continued nearshoring trends, infrastructure development, and technology advancement initiatives. Market expansion is expected to accelerate as international brands increasingly prioritize supply chain resilience and regional manufacturing capabilities. Investment flows into Mexican textile manufacturing are projected to maintain strong momentum driven by competitive advantages and market access benefits.
Technology evolution will continue transforming industry capabilities through automation, digitalization, and advanced manufacturing processes. Productivity improvements from technology adoption are expected to reach 30-45% over the next five years, enabling Mexican manufacturers to compete effectively with low-cost alternatives while maintaining quality and service advantages. Innovation in sustainable materials and processes will create new market opportunities and competitive differentiation.
Market segmentation trends indicate growing opportunities in technical textiles, sustainable materials, and customized production capabilities. Value chain integration will deepen as manufacturers develop closer partnerships with customers and suppliers, creating more stable and profitable business relationships. Regional market expansion throughout Latin America offers additional growth potential beyond traditional North American focus areas.
Competitive positioning will increasingly depend on technology capabilities, sustainability performance, and customer relationship quality rather than purely cost-based competition. MWR projections indicate that successful manufacturers will be those that effectively combine competitive costs with advanced capabilities and superior customer service to create sustainable competitive advantages in evolving global markets.
Mexico’s textile manufacturing market represents a dynamic and rapidly evolving industry positioned for sustained growth and competitive success in global markets. The combination of strategic geographic advantages, favorable trade relationships, competitive cost structures, and ongoing technology advancement creates a compelling value proposition for both domestic and international market participants.
Industry transformation through automation, sustainability initiatives, and digital integration is enhancing competitive capabilities while addressing evolving customer requirements and market trends. The sector’s ability to adapt to changing global supply chain dynamics while maintaining cost competitiveness and quality standards demonstrates resilience and strategic positioning for future growth opportunities.
Strategic opportunities in technical textiles, sustainable manufacturing, and regional market expansion provide pathways for value creation and competitive differentiation beyond traditional cost-based competition. Investment in workforce development, technology advancement, and infrastructure improvement will continue supporting industry competitiveness and market leadership in the Americas region.
The future outlook for Mexico’s textile manufacturing market remains highly positive, with continued growth expected across multiple segments and applications. Success in this evolving market environment will require strategic focus on technology adoption, sustainability implementation, and customer relationship development to capitalize on emerging opportunities while maintaining competitive advantages in cost, quality, and service delivery.
What is Textile Manufacturing?
Textile manufacturing refers to the processes involved in producing fabrics and textiles, including spinning, weaving, dyeing, and finishing. This sector plays a crucial role in the production of clothing, home textiles, and industrial fabrics.
What are the key players in the Mexico Textile Manufacturing Market?
Key players in the Mexico Textile Manufacturing Market include Grupo Kaltex, Alpek, and Textiles de México, among others. These companies are involved in various aspects of textile production, from raw material processing to finished goods.
What are the growth factors driving the Mexico Textile Manufacturing Market?
The Mexico Textile Manufacturing Market is driven by factors such as increasing demand for sustainable textiles, growth in the fashion industry, and the country’s strategic location for export. Additionally, advancements in technology are enhancing production efficiency.
What challenges does the Mexico Textile Manufacturing Market face?
The Mexico Textile Manufacturing Market faces challenges such as competition from low-cost imports, fluctuating raw material prices, and regulatory compliance issues. These factors can impact profitability and operational efficiency.
What opportunities exist in the Mexico Textile Manufacturing Market?
Opportunities in the Mexico Textile Manufacturing Market include the rising trend of eco-friendly textiles, potential for innovation in smart fabrics, and expanding export markets. Companies can leverage these trends to enhance their product offerings.
What trends are shaping the Mexico Textile Manufacturing Market?
Trends shaping the Mexico Textile Manufacturing Market include the increasing adoption of automation and digital technologies, a focus on sustainability, and the growth of e-commerce in textile sales. These trends are transforming how textiles are produced and marketed.
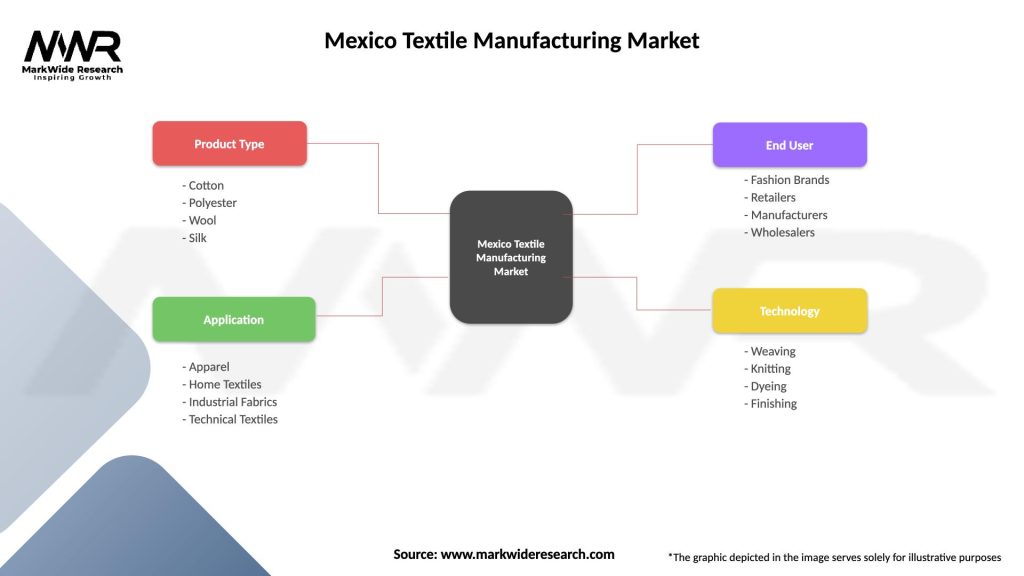
Mexico Textile Manufacturing Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Cotton, Polyester, Wool, Silk |
| Application | Apparel, Home Textiles, Industrial Fabrics, Technical Textiles |
| End User | Fashion Brands, Retailers, Manufacturers, Wholesalers |
| Technology | Weaving, Knitting, Dyeing, Finishing |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the Mexico Textile Manufacturing Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at