444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
The Philippines telecommunication industry represents one of the most dynamic and rapidly evolving sectors in Southeast Asia, characterized by intense competition, technological advancement, and substantial infrastructure development. The market has experienced remarkable transformation over the past decade, driven by increasing smartphone penetration, growing demand for high-speed internet connectivity, and the government’s push for digital transformation initiatives.
Market dynamics indicate that the telecommunications landscape is experiencing unprecedented growth, with mobile subscriber penetration reaching approximately 148% of the population, reflecting the prevalence of multiple SIM card ownership among Filipino consumers. The industry encompasses various segments including mobile telecommunications, fixed-line services, internet service provision, and emerging technologies such as 5G networks and Internet of Things (IoT) solutions.
Infrastructure development has become a critical focus area, with major telecommunications companies investing heavily in network expansion and modernization. The rollout of fiber optic networks has accelerated significantly, with fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) connections growing at an impressive annual rate of 35%, transforming the country’s digital connectivity landscape.
Regulatory environment plays a crucial role in shaping market dynamics, with the National Telecommunications Commission (NTC) implementing policies to enhance competition, improve service quality, and ensure affordable access to telecommunications services across the archipelago’s diverse geographical terrain.
The Philippines telecommunication industry market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of companies, services, and infrastructure that provide voice, data, and multimedia communication services to consumers, businesses, and government entities across the Philippine archipelago. This market encompasses traditional telecommunications services such as voice calling and text messaging, as well as modern digital services including broadband internet, mobile data, cloud computing, and emerging technologies.
Market participants include major telecommunications operators, internet service providers, tower companies, equipment manufacturers, and technology solution providers who collectively work to deliver seamless connectivity solutions. The industry serves as the backbone for the country’s digital economy, enabling e-commerce, digital banking, online education, telemedicine, and various digital government services.
Service categories within this market include mobile telecommunications, fixed-line telephony, broadband internet services, enterprise solutions, data center services, and value-added services such as mobile payments and digital entertainment platforms. The market’s significance extends beyond traditional communication, serving as an enabler for economic growth, social development, and technological innovation across the Philippines.
The Philippines telecommunication industry stands at a pivotal juncture, experiencing robust growth driven by digital transformation initiatives, increasing consumer demand for high-speed connectivity, and substantial infrastructure investments. The market demonstrates strong fundamentals with mobile services dominating the landscape, while fixed broadband services show exceptional growth potential.
Key market characteristics include intense competition among major players, rapid technological advancement, and evolving consumer preferences toward data-centric services. The industry has witnessed significant consolidation activities, strategic partnerships, and foreign investments aimed at enhancing network capabilities and service quality.
Growth drivers encompass the government’s digitalization agenda, increasing smartphone adoption rates reaching 76% of the population, growing demand for remote work solutions, and the expansion of digital financial services. The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated digital adoption, creating new opportunities for telecommunications service providers.
Market challenges include geographical complexities due to the archipelagic nature of the country, regulatory compliance requirements, infrastructure deployment costs, and the need for continuous technology upgrades. Despite these challenges, the market outlook remains positive with strong growth prospects across all service segments.
Strategic market insights reveal several critical trends shaping the Philippines telecommunication industry landscape:
Digital transformation initiatives across government and private sectors serve as primary catalysts for telecommunications market growth. The Philippine government’s digitalization agenda, including smart city projects, digital government services, and e-governance initiatives, creates substantial demand for robust telecommunications infrastructure and services.
Increasing smartphone penetration continues to drive market expansion, with affordable device availability and flexible payment schemes making smartphones accessible to broader population segments. This trend directly correlates with growing demand for mobile data services, mobile applications, and digital content consumption.
Remote work adoption has permanently altered communication patterns, creating sustained demand for high-speed internet connectivity, video conferencing solutions, and cloud-based collaboration tools. The hybrid work model has become standard practice for many organizations, requiring reliable telecommunications infrastructure.
E-commerce growth significantly impacts telecommunications demand, as online businesses require robust connectivity, payment processing capabilities, and logistics coordination systems. The rapid expansion of digital marketplaces and online retail platforms drives continuous infrastructure investment.
Educational technology adoption has accelerated dramatically, with online learning platforms, virtual classrooms, and digital educational resources requiring stable internet connectivity and advanced telecommunications services across educational institutions nationwide.
Financial technology expansion creates new opportunities for telecommunications providers, particularly in mobile payments, digital banking, and financial inclusion initiatives targeting unbanked populations in rural areas.
Geographical challenges pose significant constraints for telecommunications infrastructure development in the Philippines. The archipelagic nature of the country, with over 7,000 islands, creates complex logistical and technical challenges for network deployment, particularly in remote and island communities where connectivity costs are substantially higher.
Regulatory complexities can slow market development, with lengthy approval processes for infrastructure projects, spectrum allocation procedures, and compliance requirements creating delays in network expansion and service launches. Regulatory uncertainty occasionally impacts investment decisions and strategic planning.
High infrastructure costs represent a major barrier, particularly for fiber optic network deployment, cell tower construction, and submarine cable installations. The substantial capital requirements for network modernization and expansion can strain financial resources, especially for smaller operators.
Skilled workforce shortage in telecommunications and technology sectors limits growth potential. The rapid pace of technological advancement requires specialized expertise in areas such as 5G deployment, network security, and digital service development, creating talent acquisition challenges.
Cybersecurity threats increasingly impact market operations, requiring substantial investments in security infrastructure, threat monitoring systems, and compliance measures. The growing sophistication of cyber attacks creates ongoing operational and financial risks.
Economic volatility can affect consumer spending patterns and business investment decisions, potentially impacting demand for premium telecommunications services and advanced technology solutions during economic downturns.
5G technology deployment presents unprecedented opportunities for telecommunications providers to offer enhanced services, support emerging applications, and create new revenue streams. The technology enables advanced use cases including autonomous vehicles, smart manufacturing, augmented reality, and massive IoT deployments.
Rural connectivity expansion offers significant growth potential, with government initiatives and international funding supporting infrastructure development in underserved areas. The digital divide presents opportunities for innovative service delivery models and public-private partnerships.
Enterprise digital transformation creates substantial market opportunities as businesses across industries seek comprehensive telecommunications and technology solutions. Cloud migration, digital workplace solutions, and industry-specific applications drive demand for specialized services.
Internet of Things (IoT) applications are emerging across various sectors including agriculture, manufacturing, healthcare, and smart cities. Telecommunications providers can leverage their network infrastructure to offer IoT connectivity, data analytics, and managed services.
Edge computing deployment represents a growing opportunity as applications require low-latency processing capabilities. Telecommunications companies can establish edge computing facilities to support real-time applications and reduce network congestion.
Submarine cable investments offer opportunities to enhance international connectivity, reduce latency for global communications, and position the Philippines as a regional telecommunications hub connecting Asia-Pacific markets.
Digital financial services integration allows telecommunications providers to expand into fintech, mobile payments, and digital banking services, leveraging their customer base and network infrastructure to capture additional revenue streams.
Competitive intensity within the Philippines telecommunication industry has reached unprecedented levels, with major operators engaging in aggressive pricing strategies, service differentiation initiatives, and network quality improvements. This competition benefits consumers through improved services and competitive pricing while challenging operators to maintain profitability.
Technology convergence is reshaping market dynamics as traditional telecommunications boundaries blur with information technology, media, and entertainment services. Operators are evolving into integrated digital service providers, offering comprehensive solutions spanning connectivity, content, and applications.
Customer expectations continue to evolve rapidly, with consumers demanding higher speeds, better coverage, more reliable services, and innovative digital solutions. The shift toward data-centric services has fundamentally altered revenue models and service delivery approaches.
Investment patterns show increasing focus on infrastructure modernization, with fiber optic networks receiving approximately 60% of total infrastructure investments. This shift reflects the growing importance of high-speed broadband services and the need for future-ready network capabilities.
Partnership strategies are becoming increasingly important, with telecommunications companies forming alliances with technology providers, content creators, and international operators to enhance service offerings and expand market reach. These collaborations enable access to new technologies and markets while sharing investment risks.
Regulatory evolution continues to shape market dynamics, with policies promoting infrastructure sharing, spectrum efficiency, and service quality standards. Recent regulatory changes have encouraged foreign investment and competition while maintaining focus on consumer protection and national security considerations.
Comprehensive market analysis for the Philippines telecommunication industry employs a multi-faceted research approach combining primary and secondary research methodologies to ensure accuracy, reliability, and depth of insights. The research framework incorporates quantitative and qualitative analysis techniques to provide a holistic view of market dynamics.
Primary research activities include structured interviews with industry executives, telecommunications operators, regulatory officials, and technology vendors. Survey methodologies capture consumer behavior patterns, service preferences, and satisfaction levels across different demographic segments and geographical regions.
Secondary research sources encompass government publications, regulatory filings, company annual reports, industry association data, and academic research papers. Financial analysis includes revenue trends, investment patterns, and profitability metrics across major market participants.
Data validation processes ensure information accuracy through cross-referencing multiple sources, expert consultations, and statistical verification methods. Market sizing and forecasting models incorporate historical trends, current market conditions, and future growth drivers.
Analytical frameworks include Porter’s Five Forces analysis, SWOT assessment, competitive positioning analysis, and technology adoption lifecycle evaluation. These methodologies provide strategic insights into market structure, competitive dynamics, and growth opportunities.
Geographic segmentation analysis covers urban and rural markets, regional variations, and island-specific considerations that impact service delivery and market development strategies across the Philippine archipelago.
Metro Manila dominates the Philippines telecommunication market, accounting for approximately 35% of total industry revenues despite representing only a small fraction of the country’s land area. The region benefits from the highest concentration of telecommunications infrastructure, including fiber optic networks, cell towers, and data centers.
Luzon region outside Metro Manila represents the second-largest market segment, with significant growth potential in provincial cities and industrial zones. Infrastructure development in this region focuses on connecting major economic centers and supporting manufacturing and agricultural sectors.
Visayas region demonstrates strong growth momentum, particularly in Cebu, which serves as a major business process outsourcing hub. The region’s telecommunications infrastructure has expanded significantly to support the growing IT-BPO industry and tourism sector.
Mindanao region presents both challenges and opportunities, with ongoing infrastructure development initiatives aimed at improving connectivity and supporting economic development. Security considerations and geographical complexities influence infrastructure deployment strategies.
Island communities across the archipelago represent underserved markets with significant growth potential. Satellite technology, submarine cables, and innovative connectivity solutions are being deployed to bridge the digital divide and provide essential telecommunications services.
Urban-rural divide remains a critical consideration, with urban areas enjoying advanced telecommunications services while rural communities often experience limited connectivity options. Government initiatives and private sector investments are working to address these disparities.
Market leadership in the Philippines telecommunication industry is characterized by intense competition among major operators, each pursuing distinct strategies to capture market share and enhance service quality. The competitive environment has intensified significantly with new market entrants and evolving consumer demands.
Competitive strategies include network quality improvements, service bundling, digital transformation services, and customer experience enhancements. Companies are investing heavily in 5G deployment, fiber infrastructure expansion, and digital service development to maintain competitive advantages.
Market consolidation trends show increasing merger and acquisition activities as companies seek to achieve economies of scale, expand geographical coverage, and enhance technological capabilities through strategic partnerships and acquisitions.
By Service Type:
By Technology:
By Customer Segment:
Mobile telecommunications continues to dominate the Philippines market, with prepaid services accounting for approximately 92% of mobile subscriptions. This preference reflects consumer behavior patterns, income levels, and the flexibility offered by prepaid service models. Mobile data consumption has grown exponentially, driven by social media usage, video streaming, and mobile gaming.
Fixed broadband services are experiencing unprecedented growth, particularly fiber-to-the-home connections which have become essential for remote work, online education, and digital entertainment. The segment benefits from government digitalization initiatives and increasing consumer awareness of high-speed internet benefits.
Enterprise telecommunications represents a high-value segment with strong growth potential as businesses undergo digital transformation. Cloud migration, cybersecurity services, and managed IT solutions are driving revenue growth and creating opportunities for service differentiation.
Value-added services including mobile payments, digital content, and IoT applications are emerging as significant revenue contributors. These services leverage existing network infrastructure while providing enhanced customer value and improved profit margins.
International services benefit from the Philippines’ position as a major source of overseas workers and business process outsourcing services. International calling, data roaming, and submarine cable services support global connectivity requirements.
Wholesale services play a crucial role in market dynamics, with infrastructure sharing, tower leasing, and network interconnection services enabling efficient resource utilization and market competition.
Telecommunications operators benefit from expanding market opportunities, technological advancement, and diversification possibilities. The growing demand for digital services enables revenue growth beyond traditional voice and messaging services, while infrastructure investments create long-term competitive advantages.
Consumers enjoy improved service quality, competitive pricing, and access to advanced telecommunications services. The competitive market environment drives innovation, service improvements, and affordability, while expanding coverage brings connectivity to previously underserved areas.
Businesses gain access to advanced telecommunications solutions that enable digital transformation, improve operational efficiency, and support growth initiatives. Reliable connectivity and digital services facilitate e-commerce, remote work, and global business operations.
Government entities benefit from enhanced digital governance capabilities, improved public service delivery, and economic development opportunities. Telecommunications infrastructure supports smart city initiatives, e-government services, and digital inclusion programs.
Technology vendors find expanding market opportunities for equipment, software, and services as operators invest in network modernization and service enhancement. The 5G rollout and digital transformation initiatives create substantial demand for advanced technology solutions.
Investors can capitalize on market growth potential, infrastructure development opportunities, and the expanding digital economy. The telecommunications sector offers attractive investment prospects with stable cash flows and growth potential.
Economic development benefits from improved connectivity, digital inclusion, and technology adoption across various sectors. Telecommunications infrastructure serves as an enabler for economic growth, innovation, and competitiveness in the global market.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Network virtualization is transforming telecommunications infrastructure, with software-defined networking and network function virtualization enabling more flexible, efficient, and cost-effective network operations. This trend allows operators to rapidly deploy new services and optimize network performance.
Artificial intelligence integration is becoming increasingly prevalent in network management, customer service, and predictive maintenance applications. AI-powered solutions help optimize network performance, reduce operational costs, and enhance customer experiences through personalized services.
Sustainability initiatives are gaining prominence as operators focus on reducing environmental impact through energy-efficient technologies, renewable energy adoption, and green infrastructure solutions. Environmental considerations are becoming important factors in investment decisions and operational strategies.
Open RAN adoption is emerging as a significant trend, promoting vendor diversity, reducing costs, and enabling innovation in network infrastructure. This approach allows operators to mix and match equipment from different vendors while maintaining interoperability.
Edge computing deployment is accelerating as applications require low-latency processing capabilities. Telecommunications providers are establishing edge computing facilities to support real-time applications, reduce network congestion, and enable new service offerings.
Digital service integration continues to expand as operators evolve beyond traditional connectivity services to offer comprehensive digital solutions including cloud services, cybersecurity, and industry-specific applications.
Private network solutions are gaining traction among enterprises seeking dedicated, secure, and high-performance connectivity for specific applications such as manufacturing automation, logistics, and smart building management.
5G network launches have marked significant milestones in the Philippines telecommunications industry, with major operators successfully deploying commercial 5G services in key urban areas. These launches demonstrate the industry’s commitment to technological advancement and future-ready infrastructure development.
Submarine cable investments have enhanced international connectivity, with new cable systems improving bandwidth capacity, reducing latency, and strengthening the Philippines’ position as a regional telecommunications hub. These investments support growing demand for international communications and data services.
Fiber infrastructure expansion has accelerated dramatically, with operators investing heavily in fiber-to-the-home networks to meet growing broadband demand. According to MarkWide Research analysis, fiber network coverage has expanded significantly across major urban centers and is increasingly reaching suburban and rural areas.
Regulatory reforms have introduced new policies promoting competition, infrastructure sharing, and foreign investment. Recent regulatory changes have streamlined approval processes, encouraged new market entrants, and established frameworks for emerging technologies.
Strategic partnerships between telecommunications operators and technology companies have accelerated innovation and service development. These collaborations focus on areas such as cloud computing, cybersecurity, IoT solutions, and digital transformation services.
Merger and acquisition activities have reshaped the competitive landscape, with companies pursuing strategic consolidation to achieve economies of scale, expand geographical coverage, and enhance technological capabilities.
Digital payment integration has transformed telecommunications services, with operators launching mobile wallet solutions and financial services that leverage their customer base and network infrastructure to capture additional revenue streams.
Infrastructure investment priorities should focus on fiber optic network expansion, particularly in underserved rural areas where government support and international funding can help bridge the digital divide. Operators should leverage public-private partnerships to accelerate deployment while managing investment risks.
Service diversification strategies should emphasize digital transformation solutions for enterprise customers, including cloud services, cybersecurity, and industry-specific applications. This approach can generate higher-margin revenues while reducing dependence on traditional voice and messaging services.
Technology adoption roadmaps should prioritize 5G deployment in high-value areas while maintaining 4G network quality and coverage. Operators should develop clear migration strategies that balance investment requirements with revenue generation potential.
Customer experience enhancement should remain a top priority, with investments in network quality, customer service capabilities, and digital service platforms. Superior customer experience can serve as a key differentiator in the competitive market environment.
Partnership development should focus on strategic alliances with technology providers, content creators, and international operators to enhance service offerings and expand market reach. These partnerships can provide access to new technologies and markets while sharing investment risks.
Regulatory engagement should be proactive, with operators working closely with government agencies to shape policies that promote industry growth while ensuring consumer protection and national security considerations.
Sustainability integration should become a core component of business strategies, with investments in energy-efficient technologies, renewable energy adoption, and environmental impact reduction initiatives that align with global sustainability trends.
Market growth prospects remain robust for the Philippines telecommunication industry, with continued expansion expected across all service segments. The digital transformation trend, government digitalization initiatives, and increasing consumer demand for high-speed connectivity will drive sustained growth over the forecast period.
5G technology adoption is projected to accelerate significantly, with network coverage expanding beyond major urban centers to include secondary cities and industrial zones. The technology will enable new applications and services, creating additional revenue opportunities for operators while supporting economic development initiatives.
Fiber infrastructure development will continue at an accelerated pace, with MWR projecting substantial growth in fiber-to-the-home connections as operators compete to provide high-speed broadband services. This infrastructure investment will support the growing demand for remote work, online education, and digital entertainment services.
Enterprise market expansion is expected to drive significant revenue growth as businesses across various industries undergo digital transformation. Cloud migration, cybersecurity services, and IoT applications will create substantial opportunities for telecommunications providers to expand beyond traditional connectivity services.
Rural connectivity improvements will gain momentum through government initiatives, international funding, and innovative technology solutions. Satellite communications, wireless technologies, and infrastructure sharing arrangements will help bridge the digital divide and expand market reach.
International connectivity enhancement will strengthen the Philippines’ position as a regional telecommunications hub, with new submarine cable investments and improved international gateway facilities supporting growing demand for global communications and data services.
Technology convergence will continue to blur traditional industry boundaries, with telecommunications operators evolving into comprehensive digital service providers offering integrated solutions spanning connectivity, content, applications, and emerging technologies.
The Philippines telecommunication industry represents a dynamic and rapidly evolving market with substantial growth potential driven by digital transformation initiatives, technological advancement, and increasing consumer demand for high-speed connectivity. The market demonstrates strong fundamentals with intense competition fostering innovation, service improvements, and competitive pricing that benefits all stakeholders.
Key success factors for market participants include strategic infrastructure investments, service diversification, customer experience enhancement, and technology adoption. The industry’s evolution from traditional telecommunications services to comprehensive digital solutions creates new opportunities while requiring continuous adaptation to changing market conditions and consumer preferences.
Future growth prospects remain positive, with 5G deployment, fiber infrastructure expansion, and enterprise digital transformation driving sustained market development. The government’s supportive regulatory environment, combined with increasing foreign investment and strategic partnerships, creates favorable conditions for continued industry growth and technological advancement across the Philippine archipelago.
What is the Philippines Telecommunication Industry?
The Philippines Telecommunication Industry encompasses the various services and technologies that facilitate communication over distances, including mobile and fixed-line services, internet access, and broadcasting. It plays a crucial role in connecting individuals and businesses across the archipelago.
Who are the major players in the Philippines Telecommunication Industry Market?
Major players in the Philippines Telecommunication Industry Market include PLDT, Globe Telecom, and DITO Telecommunity. These companies provide a range of services from mobile communications to broadband internet, competing to enhance connectivity and customer experience.
What are the key drivers of growth in the Philippines Telecommunication Industry Market?
Key drivers of growth in the Philippines Telecommunication Industry Market include the increasing demand for mobile data services, the expansion of internet infrastructure, and the rise of digital services such as e-commerce and online education. These factors are pushing companies to innovate and improve their offerings.
What challenges does the Philippines Telecommunication Industry Market face?
The Philippines Telecommunication Industry Market faces challenges such as regulatory hurdles, infrastructure limitations, and intense competition among service providers. These issues can hinder the ability to deliver consistent and high-quality services to consumers.
What opportunities exist in the Philippines Telecommunication Industry Market?
Opportunities in the Philippines Telecommunication Industry Market include the potential for expanding fiber-optic networks, the growth of mobile payment systems, and the increasing adoption of smart technologies. These trends can lead to enhanced service offerings and improved customer engagement.
What trends are shaping the Philippines Telecommunication Industry Market?
Trends shaping the Philippines Telecommunication Industry Market include the shift towards digital transformation, the rise of 5G technology, and the growing importance of cybersecurity. These trends are influencing how companies operate and deliver services to meet evolving consumer needs.
the Philippines Telecommunication Industry Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
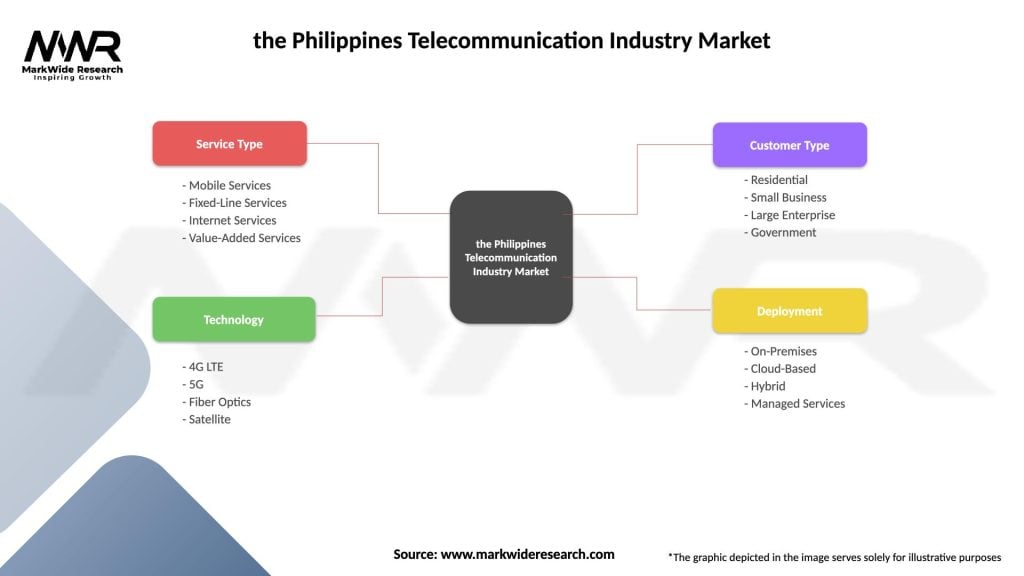
| Service Type | Mobile Services, Fixed-Line Services, Internet Services, Value-Added Services |
| Technology | 4G LTE, 5G, Fiber Optics, Satellite |
| Customer Type | Residential, Small Business, Large Enterprise, Government |
| Deployment | On-Premises, Cloud-Based, Hybrid, Managed Services |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the the Philippines Telecommunication Industry Market
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at