444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
The US fixed-tilt solar PV market represents a cornerstone of America’s renewable energy transformation, establishing itself as the dominant photovoltaic installation methodology across residential, commercial, and utility-scale applications. Fixed-tilt solar systems maintain a stationary position throughout the day, typically oriented toward the south at an optimal angle to maximize solar energy capture while minimizing installation and maintenance costs.
Market dynamics indicate robust expansion driven by declining solar panel costs, favorable federal and state incentives, and increasing corporate sustainability commitments. The technology’s simplicity and reliability have made it the preferred choice for approximately 85% of all solar installations nationwide, demonstrating its market dominance over tracking systems and other alternatives.
Geographic distribution shows concentrated growth in sun-rich states including California, Texas, Florida, and North Carolina, where optimal solar irradiance conditions combine with supportive regulatory frameworks. The market benefits from mature supply chains, experienced installation workforce, and standardized mounting solutions that reduce project complexity and timeline.
Technology advancement continues to enhance system efficiency through improved panel designs, optimized mounting structures, and advanced inverter technologies. These innovations enable fixed-tilt systems to achieve performance ratios exceeding 80% in optimal conditions, making them increasingly competitive with more complex tracking alternatives.
The US fixed-tilt solar PV market refers to the segment of photovoltaic installations that utilize stationary mounting systems positioned at a predetermined angle to optimize solar energy collection throughout the year without mechanical tracking mechanisms.
Fixed-tilt systems represent the most straightforward approach to solar energy harvesting, where photovoltaic panels are permanently mounted at an angle typically ranging from 15 to 45 degrees, depending on geographic latitude and local solar conditions. This methodology contrasts with tracking systems that follow the sun’s movement throughout the day.
System components include photovoltaic modules, mounting rails, clamps, grounding equipment, and structural foundations designed to withstand local wind and snow loads. The fixed orientation eliminates moving parts, reducing maintenance requirements and potential failure points while maintaining consistent energy production patterns.
Market applications span residential rooftop installations, commercial building-mounted systems, and large-scale utility solar farms. Each application category utilizes different mounting approaches, from roof-penetrating attachments to ground-mounted racking systems, all maintaining the fixed-tilt principle for optimal cost-effectiveness and reliability.
Strategic positioning of the US fixed-tilt solar PV market reflects its role as the foundation of America’s solar energy expansion, driven by cost advantages, proven reliability, and widespread industry adoption. The market continues to capture the majority of new solar installations due to its optimal balance of performance and economic efficiency.
Growth trajectory remains strong with annual installation growth rates averaging 12-15% across different market segments, supported by federal investment tax credits, state renewable portfolio standards, and declining equipment costs. Utility-scale projects represent the largest growth driver, while residential installations maintain steady expansion.
Competitive landscape features established manufacturers, experienced installers, and mature supply chains that enable rapid project deployment and cost optimization. Market consolidation among installation companies has improved service quality while maintaining competitive pricing structures.
Technology evolution focuses on efficiency improvements, durability enhancements, and installation process optimization rather than fundamental system redesign. These incremental advances maintain fixed-tilt systems’ competitive position against more complex alternatives while reducing overall project costs.
Future outlook indicates continued market expansion supported by corporate renewable energy procurement, grid modernization initiatives, and energy storage integration opportunities. The market’s maturity provides stability for long-term investment planning and project financing.
Market penetration analysis reveals fixed-tilt solar PV systems’ dominant position across all installation categories, with particular strength in utility-scale developments where cost optimization takes precedence over maximum energy yield. The technology’s proven track record supports investor confidence and project financing accessibility.
Economic incentives continue to propel market expansion through federal investment tax credits, state-level renewable energy certificates, and net metering policies that improve project economics. The 30% federal investment tax credit extension through 2032 provides long-term market stability and investment certainty for developers and customers.
Cost competitiveness has reached grid parity in most US markets, making fixed-tilt solar installations economically attractive without subsidies. Declining module prices, improved installation efficiency, and economies of scale in manufacturing contribute to ongoing cost reductions that expand market accessibility.
Corporate sustainability initiatives drive significant demand from commercial and industrial customers seeking to reduce carbon footprints and achieve renewable energy targets. Fortune 500 companies increasingly prioritize solar procurement as part of comprehensive environmental, social, and governance strategies.
Grid modernization efforts create opportunities for distributed solar integration, with fixed-tilt systems providing stable, predictable generation profiles that support grid stability and planning. Utility companies recognize solar energy’s role in meeting peak demand periods and reducing transmission losses.
Energy independence goals at federal and state levels promote domestic renewable energy development, with fixed-tilt solar systems offering proven technology for rapid capacity deployment. National security considerations increasingly favor domestic energy production over fossil fuel imports.
Technological reliability attracts risk-averse investors and customers who prioritize proven performance over maximum energy yield. The absence of tracking mechanisms eliminates potential failure points while maintaining predictable maintenance schedules and operational costs.
Land availability constraints limit utility-scale project development in densely populated regions, requiring developers to secure suitable sites with appropriate solar resources, transmission access, and permitting feasibility. Competition for prime development sites increases land costs and project complexity.
Grid interconnection challenges create bottlenecks for large-scale solar deployment, with transmission capacity limitations and lengthy interconnection queues delaying project completion. Aging grid infrastructure requires substantial upgrades to accommodate increased renewable energy penetration.
Policy uncertainty regarding long-term incentive structures and regulatory frameworks creates investment hesitation among developers and financiers. Potential changes to net metering policies, renewable energy standards, and tax credit programs introduce market volatility.
Supply chain disruptions periodically impact component availability and pricing, particularly for imported solar panels and specialized mounting hardware. Trade policy changes and international manufacturing constraints can affect project timelines and costs.
Skilled workforce limitations constrain installation capacity in rapidly growing markets, with certified installers and project managers in high demand. Training program capacity and workforce development initiatives struggle to keep pace with market expansion.
Permitting complexities vary significantly across jurisdictions, creating administrative burdens and timeline uncertainties for project development. Inconsistent local regulations and approval processes increase soft costs and development risks.
Energy storage integration presents significant growth opportunities as battery costs decline and grid services markets develop. Fixed-tilt solar systems paired with storage solutions can provide dispatchable renewable energy and participate in ancillary services markets, enhancing project economics.
Agrivoltaics applications enable dual land use for solar energy generation and agricultural production, addressing land use concerns while creating additional revenue streams for farmers. This innovative approach expands available development sites and improves community acceptance.
Floating solar installations on reservoirs, retention ponds, and other water bodies offer new deployment opportunities while reducing water evaporation and algae growth. These installations avoid land use conflicts while maintaining fixed-tilt system advantages.
Community solar programs expand market access to customers unable to install rooftop systems, including renters, condominium owners, and businesses with unsuitable roof conditions. Shared solar facilities democratize renewable energy access while maintaining economies of scale.
Industrial process integration creates opportunities for on-site solar generation to power manufacturing operations, data centers, and other energy-intensive facilities. Direct consumption reduces transmission costs and improves energy security for industrial customers.
Electric vehicle charging infrastructure integration with solar canopies and parking structures provides clean transportation energy while generating additional revenue streams. The convergence of solar and EV markets creates synergistic growth opportunities.
Supply and demand equilibrium in the US fixed-tilt solar PV market reflects mature industry dynamics with established manufacturing capacity, experienced installation workforce, and predictable customer demand patterns. Market stability enables long-term planning and investment commitments from industry participants.
Price competition among system integrators and equipment suppliers drives continuous cost reductions while maintaining quality standards. Competitive bidding processes for utility-scale projects and residential market competition ensure customers benefit from ongoing price improvements.
Technology convergence with energy storage, smart inverters, and grid management systems creates integrated solutions that enhance fixed-tilt solar value propositions. These combinations address intermittency concerns while providing additional grid services and revenue opportunities.
Regulatory evolution continues to shape market conditions through updated building codes, electrical standards, and interconnection requirements. Industry collaboration with regulatory bodies ensures standards keep pace with technology advancement while maintaining safety and reliability.
Financial innovation in project financing, including green bonds, tax equity partnerships, and power purchase agreements, expands capital availability for solar development. Sophisticated financing structures reduce customer barriers and enable larger project scales.
Market consolidation among installation companies and equipment manufacturers creates larger, more capable organizations while maintaining competitive market conditions. Strategic partnerships and vertical integration improve supply chain efficiency and customer service capabilities.
Primary research encompasses comprehensive interviews with industry executives, technology developers, installation companies, and end-users across residential, commercial, and utility market segments. Direct engagement with market participants provides insights into current trends, challenges, and future opportunities.
Secondary analysis incorporates government databases, industry association reports, and regulatory filings to establish market sizing, growth trends, and competitive positioning. Official statistics from the Energy Information Administration and state public utility commissions provide authoritative market data.
Technology assessment evaluates current and emerging fixed-tilt solar technologies through laboratory testing data, field performance studies, and manufacturer specifications. Performance analysis includes efficiency measurements, durability testing, and long-term degradation studies.
Economic modeling analyzes project costs, financing structures, and revenue projections across different market segments and geographic regions. Levelized cost of energy calculations and financial return analysis inform market attractiveness assessments.
Regulatory analysis examines federal, state, and local policies affecting solar market development, including incentive programs, interconnection standards, and permitting requirements. Policy impact assessment quantifies regulatory influence on market growth and investment decisions.
Competitive intelligence monitors company strategies, product developments, and market positioning through public disclosures, patent filings, and industry announcements. Strategic analysis identifies market leaders and emerging competitive threats.
California market leadership continues with the state maintaining approximately 35% of national installed capacity, driven by aggressive renewable energy standards, favorable net metering policies, and strong solar resources. The mature market features sophisticated financing options and experienced installation workforce supporting continued growth.
Texas expansion represents the fastest-growing regional market, with utility-scale fixed-tilt installations driving capacity additions. Competitive electricity markets and abundant land availability create favorable conditions for large-scale solar development, while corporate renewable energy procurement supports market growth.
Southeast emergence includes Florida, North Carolina, and Georgia as rapidly developing markets with improving solar resources recognition and supportive state policies. Utility-scale projects dominate regional growth, with fixed-tilt systems preferred for their cost-effectiveness and reliability.
Northeast markets focus on distributed generation applications, with fixed-tilt systems adapted for challenging installation conditions including steep roofs and limited space. Community solar programs and virtual net metering expand market access beyond traditional rooftop installations.
Mountain West development benefits from excellent solar resources and available land for utility-scale projects. States including Nevada, Arizona, and Colorado leverage natural advantages and supportive policies to attract solar investment and development.
Midwest growth accelerates through corporate renewable energy procurement and improving state policies. Fixed-tilt systems prove particularly suitable for agricultural land dual-use applications and industrial facility installations across the region.
Market leadership in the US fixed-tilt solar PV sector encompasses established manufacturers, experienced installers, and integrated solution providers who have built comprehensive capabilities across the solar value chain. Competition focuses on cost optimization, installation quality, and customer service excellence.
Strategic positioning varies among competitors, with some focusing on technology innovation, others emphasizing cost leadership, and many pursuing vertical integration to control more of the value chain. Market consolidation continues as companies seek scale advantages and operational efficiency.
By Application:
By Mounting Type:
By Technology:
Residential segment demonstrates steady growth driven by declining system costs, improved financing options, and increasing environmental awareness among homeowners. Fixed-tilt rooftop installations dominate due to space constraints and cost optimization priorities, with average system sizes increasing 8-10% annually as panel efficiency improves.
Commercial applications show strong expansion as businesses pursue sustainability goals and energy cost reduction strategies. Fixed-tilt systems prove ideal for large commercial rooftops and industrial facilities where space availability allows optimal system sizing and orientation for maximum economic benefit.
Utility-scale development represents the largest market segment by capacity, with fixed-tilt installations preferred for their cost-effectiveness and operational simplicity. Project sizes continue growing as developers achieve greater economies of scale and transmission infrastructure accommodates larger installations.
Community solar programs expand market access to underserved customer segments while maintaining fixed-tilt system advantages. These shared installations enable economies of scale while providing renewable energy access to renters, condominium owners, and customers with unsuitable rooftop conditions.
Technology integration with energy storage systems creates enhanced value propositions across all market segments. Fixed-tilt solar paired with batteries provides dispatchable renewable energy and grid services capabilities that improve project economics and customer benefits.
Geographic expansion continues into previously underserved markets as solar economics improve and state policies become more supportive. Fixed-tilt systems’ proven reliability and cost-effectiveness facilitate market entry in regions with developing solar industries.
For Customers:
For Installers:
For Utilities:
For Policymakers:
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Bifacial technology adoption accelerates as manufacturers develop specialized mounting solutions that maximize rear-side energy capture while maintaining fixed-tilt system simplicity. These advanced panels can increase energy yield by 10-20% in optimal conditions without significantly increasing installation complexity or costs.
Smart inverter integration enables fixed-tilt solar systems to provide grid services including voltage regulation, frequency response, and reactive power support. These capabilities create additional revenue opportunities while supporting grid stability as renewable energy penetration increases.
Agrivoltaics expansion demonstrates dual land use potential, with specialized mounting systems allowing continued agricultural activities beneath elevated solar panels. This approach addresses land use concerns while creating additional income streams for farmers and expanding available development sites.
Community solar growth democratizes renewable energy access through shared installations serving multiple customers. Fixed-tilt systems prove ideal for these applications due to their cost-effectiveness and operational simplicity, enabling broader market participation.
Energy storage pairing becomes increasingly common as battery costs decline and grid services markets develop. Solar-plus-storage installations provide dispatchable renewable energy and can participate in capacity markets, enhancing project economics and customer value.
Floating solar development expands installation opportunities on water bodies while maintaining fixed-tilt advantages. These installations avoid land use conflicts and can reduce water evaporation while providing clean energy generation.
Direct corporate procurement grows as large energy users seek long-term renewable energy contracts. Fixed-tilt utility-scale projects provide cost-effective solutions for corporate sustainability goals while offering predictable pricing over extended contract terms.
Technology advancement continues with next-generation solar panels achieving higher efficiencies and improved durability for fixed-tilt applications. Recent developments include passivated emitter and rear cell technology, heterojunction cells, and advanced anti-reflective coatings that enhance energy capture.
Manufacturing expansion in the United States reduces supply chain risks and supports domestic job creation. New production facilities for solar panels, inverters, and mounting systems improve supply security while reducing transportation costs and delivery times.
Regulatory updates streamline permitting processes and standardize interconnection requirements across jurisdictions. Model codes and standardized approval processes reduce soft costs and project timelines while maintaining safety and reliability standards.
Financing innovation includes green bonds, securitization programs, and community investment funds that expand capital availability for solar projects. These financial instruments reduce borrowing costs and enable larger project scales while attracting institutional investment.
Grid modernization initiatives improve renewable energy integration capabilities through advanced metering infrastructure, distribution automation, and energy storage deployment. These upgrades support higher solar penetration levels while maintaining grid reliability and power quality.
Workforce development programs expand training capacity for solar installers, electricians, and project managers. Industry partnerships with educational institutions and labor organizations ensure skilled workforce availability to support continued market growth.
Research and development focuses on next-generation technologies including perovskite tandem cells, advanced materials, and manufacturing process improvements. MarkWide Research analysis indicates these innovations could further reduce costs while improving performance and durability.
Market participants should focus on operational excellence and cost optimization as the industry matures and competition intensifies. Companies that achieve superior installation quality, customer service, and project execution will maintain competitive advantages in increasingly price-sensitive markets.
Technology integration opportunities with energy storage, smart grid systems, and electric vehicle charging infrastructure should be prioritized for long-term growth. These convergent technologies create enhanced value propositions and new revenue streams beyond traditional solar generation.
Geographic diversification into emerging markets provides growth opportunities as solar economics improve nationwide. Early market entry in developing regions can establish competitive positions before markets mature and competition intensifies.
Supply chain optimization through vertical integration or strategic partnerships reduces costs and improves delivery reliability. Companies should evaluate make-versus-buy decisions for critical components while maintaining flexibility for technology evolution.
Customer segmentation strategies should address distinct needs across residential, commercial, and utility markets. Specialized solutions, financing options, and service models for each segment can improve customer satisfaction and market penetration.
Policy engagement remains critical as regulatory frameworks continue evolving. Active participation in policy development ensures industry perspectives are considered while building relationships with key stakeholders and decision-makers.
Workforce investment in training and development programs supports quality installations while building industry capacity. Companies that invest in employee skills and safety training will achieve better project outcomes and customer satisfaction.
Market expansion will continue driven by improving economics, supportive policies, and growing environmental awareness. MarkWide Research projects sustained growth across all market segments, with utility-scale installations leading capacity additions while residential and commercial markets maintain steady expansion.
Technology evolution focuses on incremental improvements rather than revolutionary changes, with efficiency gains, durability enhancements, and cost reductions maintaining fixed-tilt systems’ competitive position. Advanced materials and manufacturing processes will drive continued performance improvements.
Grid integration capabilities will expand through smart inverter deployment and energy storage pairing, enabling solar systems to provide valuable grid services beyond energy generation. These capabilities create additional revenue opportunities and support higher renewable energy penetration.
Market maturation will bring increased standardization, improved installation practices, and enhanced customer experiences. Industry consolidation may continue as companies seek scale advantages, but competitive market conditions should persist.
Geographic expansion into previously underserved markets will accelerate as solar economics improve and state policies become more supportive. Fixed-tilt systems’ proven reliability and cost-effectiveness facilitate market development in emerging regions.
Innovation focus will shift toward system integration, installation efficiency, and customer experience rather than fundamental technology changes. Digital tools, automated processes, and enhanced monitoring capabilities will improve project outcomes and operational performance.
Long-term growth prospects remain strong with projected annual growth rates of 10-15% over the next decade, supported by continued cost reductions, policy support, and increasing corporate renewable energy procurement. The market’s maturity provides stability for long-term planning and investment.
The US fixed-tilt solar PV market represents a cornerstone of America’s renewable energy transformation, demonstrating remarkable growth and technological maturation over the past decade. With its proven reliability, cost-effectiveness, and broad applicability across residential, commercial, and utility-scale applications, fixed-tilt solar technology has established itself as the dominant photovoltaic installation methodology nationwide.
Market fundamentals remain strong, supported by declining costs, favorable policies, and increasing environmental awareness among consumers and businesses. The technology’s simplicity and reliability continue to attract risk-averse investors while providing predictable energy generation and maintenance requirements that facilitate project financing and long-term planning.
Future prospects indicate sustained expansion across all market segments, with utility-scale installations driving capacity growth while residential and commercial markets maintain steady development. Technology integration opportunities with energy storage, smart grid systems, and electric vehicle infrastructure create additional value propositions and revenue streams beyond traditional solar generation.
The market’s maturity, combined with ongoing innovation and supportive policy frameworks, positions fixed-tilt solar PV systems as a critical component of America’s clean energy future, offering reliable, cost-effective renewable electricity generation for decades to come.
What is Fixed-tilt Solar PV?
Fixed-tilt Solar PV refers to solar photovoltaic systems that are mounted at a fixed angle to capture sunlight. These systems are commonly used in residential, commercial, and utility-scale applications due to their simplicity and cost-effectiveness.
What are the key players in the US Fixed-tilt Solar PV Market?
Key players in the US Fixed-tilt Solar PV Market include First Solar, SunPower, and Canadian Solar, among others. These companies are involved in manufacturing solar panels, providing installation services, and developing solar projects.
What are the growth factors driving the US Fixed-tilt Solar PV Market?
The growth of the US Fixed-tilt Solar PV Market is driven by increasing demand for renewable energy, government incentives for solar installations, and advancements in solar technology. Additionally, the rising awareness of environmental sustainability contributes to market expansion.
What challenges does the US Fixed-tilt Solar PV Market face?
The US Fixed-tilt Solar PV Market faces challenges such as regulatory hurdles, competition from alternative energy sources, and fluctuations in material costs. These factors can impact project feasibility and profitability.
What opportunities exist in the US Fixed-tilt Solar PV Market?
Opportunities in the US Fixed-tilt Solar PV Market include the potential for technological innovations, such as improved efficiency in solar panels, and the expansion of solar farms. Additionally, increasing corporate sustainability initiatives are driving demand for solar energy solutions.
What trends are shaping the US Fixed-tilt Solar PV Market?
Trends in the US Fixed-tilt Solar PV Market include the growing adoption of energy storage solutions, the integration of smart technology in solar systems, and a shift towards larger-scale installations. These trends are enhancing the efficiency and reliability of solar energy generation.
US Fixed-tilt Solar PV Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
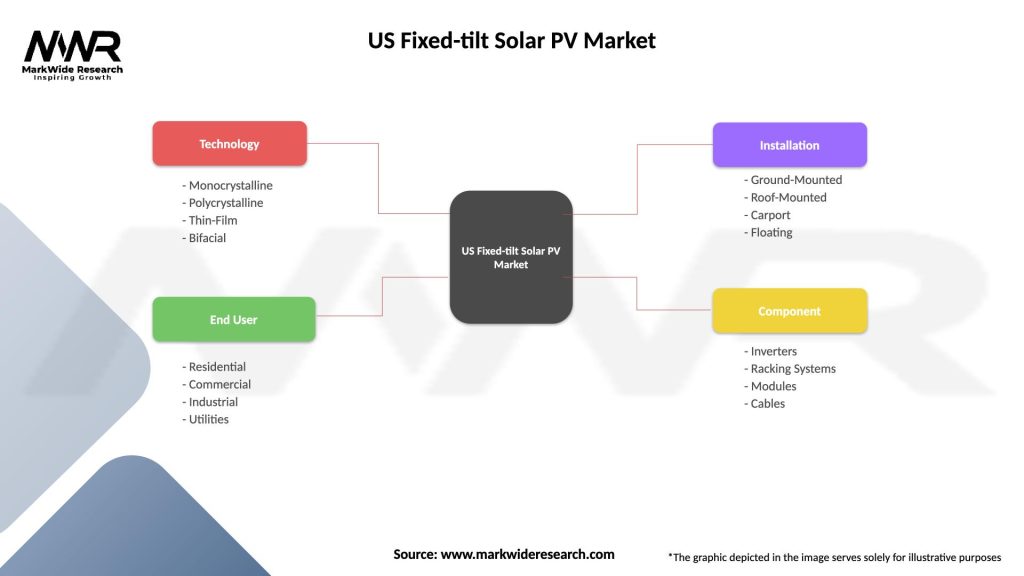
| Technology | Monocrystalline, Polycrystalline, Thin-Film, Bifacial |
| End User | Residential, Commercial, Industrial, Utilities |
| Installation | Ground-Mounted, Roof-Mounted, Carport, Floating |
| Component | Inverters, Racking Systems, Modules, Cables |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the US Fixed-tilt Solar PV Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at