444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
The Angola agriculture market represents a cornerstone of the nation’s economic diversification strategy, moving beyond oil dependency toward sustainable agricultural development. Angola’s agricultural sector encompasses vast fertile lands spanning approximately 35 million hectares of arable territory, positioning the country as a significant player in sub-Saharan African agriculture. The market demonstrates remarkable potential with agricultural productivity showing consistent improvement trends across multiple crop categories including cassava, maize, coffee, and cotton production.
Market dynamics indicate substantial growth opportunities driven by government initiatives, international partnerships, and modernization efforts. The sector contributes approximately 8.2% to Angola’s GDP, with projections suggesting increased contribution as infrastructure development accelerates. Agricultural modernization programs have introduced advanced farming techniques, irrigation systems, and mechanization processes that enhance productivity and crop yields across various regions.
Regional distribution shows concentrated agricultural activity in the central highlands, coastal plains, and northern provinces, where favorable climatic conditions support diverse crop cultivation. The market encompasses both subsistence farming and commercial agriculture, with smallholder farmers representing approximately 85% of agricultural producers while contributing significantly to food security and rural employment generation.
The Angola agriculture market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of agricultural production, processing, distribution, and trade activities within Angola’s territorial boundaries. This market encompasses crop cultivation, livestock farming, fisheries, forestry, and related agribusiness operations that contribute to food security, economic development, and rural livelihoods across the nation.
Agricultural market scope includes traditional subsistence farming practices alongside modern commercial agriculture operations, incorporating both domestic consumption and export-oriented production systems. The market integrates various stakeholders including smallholder farmers, commercial producers, agricultural cooperatives, processing facilities, distributors, and government agencies working collectively to enhance agricultural productivity and market access.
Market definition extends beyond primary production to encompass value-added activities such as food processing, packaging, storage, transportation, and marketing services that connect rural producers with urban consumers and international markets. This comprehensive approach recognizes agriculture’s multifaceted role in economic diversification, employment creation, and sustainable development initiatives.
Angola’s agricultural transformation represents a strategic pivot from oil-dependent economics toward diversified agricultural development, creating substantial opportunities for sustainable growth and food security enhancement. The market demonstrates robust potential with agricultural growth rates projected at 6.5% annually through comprehensive modernization programs and infrastructure investments.
Key market drivers include government policy support, international development partnerships, climate-smart agriculture adoption, and increasing domestic food demand. The sector benefits from abundant natural resources including fertile soils, favorable climate conditions, and extensive water resources that support diverse agricultural production systems across multiple agroecological zones.
Strategic initiatives focus on productivity enhancement, value chain development, market access improvement, and technology adoption to transform traditional farming practices into modern agricultural enterprises. The market shows particular strength in staple crop production with cassava, maize, and sweet potato cultivation experiencing significant yield improvements through improved seed varieties and farming techniques.
Investment opportunities span across mechanization, irrigation infrastructure, processing facilities, storage systems, and distribution networks that address critical gaps in agricultural value chains. The market attracts both domestic and international investors seeking to capitalize on Angola’s agricultural potential while contributing to economic diversification objectives.
Market intelligence reveals several critical insights that shape Angola’s agricultural landscape and future development trajectory:
Government policy support serves as the primary catalyst driving Angola’s agricultural market transformation through comprehensive development programs, subsidies, and institutional reforms. The National Development Plan prioritizes agricultural modernization with substantial budget allocations for infrastructure development, technology transfer, and farmer capacity building initiatives that enhance productivity and market competitiveness.
Economic diversification imperatives create strong momentum for agricultural development as Angola seeks to reduce oil dependency and build resilient economic foundations. The government’s commitment to import substitution drives domestic production expansion, particularly in staple foods, creating protected market opportunities for local producers while reducing foreign exchange pressures.
Infrastructure development accelerates market growth through improved road networks, irrigation systems, storage facilities, and processing plants that connect rural producers with urban markets. Transportation improvements reduce logistics costs and post-harvest losses while enabling farmers to access better prices for their products in distant markets.
International partnerships provide technical assistance, financing, and market access opportunities that support agricultural modernization efforts. Development organizations, bilateral agreements, and private sector collaborations introduce advanced technologies, best practices, and export market connections that enhance sector competitiveness and sustainability.
Climate advantages position Angola favorably for agricultural production with diverse agroecological zones supporting year-round cultivation of various crops. The country’s tropical climate and abundant water resources create natural competitive advantages for agricultural development, particularly in regions with reliable rainfall patterns and fertile soils.
Infrastructure deficits represent significant constraints limiting agricultural market development, particularly inadequate rural road networks that isolate farming communities from markets and increase transportation costs. Limited storage facilities and processing capacity create bottlenecks that result in substantial post-harvest losses and reduced farmer incomes, undermining production incentives and market efficiency.
Access to finance remains a critical challenge for smallholder farmers who lack collateral and credit history required by formal financial institutions. High interest rates and complex lending procedures limit farmers’ ability to invest in improved seeds, fertilizers, equipment, and other productivity-enhancing inputs essential for competitive agricultural production.
Limited mechanization constrains productivity and scale of operations, with most farmers relying on manual labor and traditional farming methods that limit output potential. Equipment availability and maintenance services remain inadequate, particularly in remote rural areas where agricultural machinery and spare parts are scarce or prohibitively expensive.
Market information gaps prevent farmers from making informed production and marketing decisions, resulting in oversupply of certain crops and missed opportunities in high-value markets. Price volatility and lack of transparent market mechanisms create uncertainty that discourages investment in agricultural production and value addition activities.
Climate variability poses increasing risks to agricultural production with irregular rainfall patterns, droughts, and extreme weather events affecting crop yields and livestock productivity. Limited irrigation infrastructure makes agriculture heavily dependent on rainfall, creating vulnerability to climate shocks that can devastate entire harvests and farmer livelihoods.
Value chain development presents substantial opportunities for creating integrated agricultural systems that connect producers with processors, distributors, and end markets through coordinated supply chain management. Agro-processing investments can transform raw agricultural products into higher-value goods, creating employment opportunities and increasing farmer incomes while meeting growing consumer demand for processed foods.
Export market expansion offers significant potential, particularly for specialty crops like coffee, cotton, and tropical fruits that can command premium prices in international markets. Organic certification and sustainable production practices create opportunities to access high-value niche markets in Europe and North America where consumers pay premium prices for environmentally responsible products.
Technology integration enables precision agriculture, digital marketing platforms, and mobile financial services that can revolutionize farming practices and market access. Drone technology for crop monitoring, GPS-guided equipment, and satellite imagery provide opportunities for optimizing resource use and maximizing yields while reducing environmental impact.
Cooperative development creates opportunities for smallholder farmers to achieve economies of scale, access better prices, and invest collectively in processing equipment and storage facilities. Farmer organizations can negotiate better terms with input suppliers, access credit more easily, and develop direct relationships with buyers that bypass intermediaries and increase profit margins.
Climate-smart agriculture presents opportunities to develop resilient farming systems that adapt to changing environmental conditions while maintaining productivity. Conservation agriculture techniques, drought-resistant varieties, and integrated pest management systems offer pathways to sustainable intensification that protects natural resources while increasing agricultural output.
Supply-demand dynamics in Angola’s agricultural market reflect the complex interplay between growing domestic food requirements and evolving production capabilities. Population growth and urbanization drive increasing demand for diverse food products, creating market opportunities for farmers who can adapt production to changing consumer preferences and dietary patterns.
Seasonal variations significantly influence market dynamics with distinct planting and harvesting cycles affecting product availability and pricing throughout the year. Storage limitations exacerbate seasonal price fluctuations, creating opportunities for investors in post-harvest infrastructure while challenging farmers to optimize timing of sales and production decisions.
Regional market integration evolves as transportation infrastructure improves, enabling producers in different provinces to access broader markets and consumers to benefit from increased product variety and competitive pricing. Cross-border trade with neighboring countries creates additional market opportunities while introducing competitive pressures that drive efficiency improvements.
Technology adoption rates vary significantly across different farmer categories and regions, creating a dynamic landscape where early adopters gain competitive advantages while traditional farmers face increasing pressure to modernize. Knowledge transfer mechanisms play crucial roles in accelerating technology diffusion and ensuring broad-based agricultural development.
Policy evolution continues shaping market dynamics through regulatory changes, subsidy programs, and institutional reforms that influence farmer behavior, investment decisions, and market structure. Stakeholder coordination between government agencies, private sector actors, and development partners creates synergies that amplify positive market impacts while addressing systemic challenges.
Comprehensive data collection methodologies combine primary research through farmer surveys, stakeholder interviews, and field observations with secondary data analysis from government statistics, international organizations, and academic publications. Multi-source triangulation ensures data reliability and provides comprehensive insights into market conditions, trends, and development opportunities across Angola’s diverse agricultural landscape.
Quantitative analysis employs statistical techniques to identify trends, correlations, and patterns in agricultural production, market prices, and trade flows. Time series analysis reveals seasonal patterns and long-term trends while cross-sectional comparisons highlight regional variations and performance differences across different agricultural systems and farmer categories.
Qualitative research methods include focus group discussions, key informant interviews, and participatory rural appraisal techniques that capture farmer perspectives, market constraints, and development priorities. Stakeholder mapping identifies key actors, relationships, and influence patterns that shape agricultural market dynamics and policy implementation effectiveness.
Geographic information systems integrate spatial data on climate, soils, infrastructure, and production patterns to analyze agricultural potential and identify optimal locations for development interventions. Remote sensing data provides objective measures of crop performance, land use changes, and environmental conditions that complement ground-based observations and farmer reports.
Market analysis frameworks examine value chains, competitive dynamics, and institutional arrangements that influence agricultural market performance. SWOT analysis and stakeholder analysis provide structured approaches for identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats while understanding complex relationships between different market actors and institutions.
Northern provinces including Uíge, Zaire, and Cabinda demonstrate strong agricultural potential with favorable rainfall patterns and fertile soils supporting diverse crop production. Coffee cultivation remains particularly significant in these regions, with quality improvements positioning local producers for premium export markets while smallholder farmers benefit from cooperative marketing arrangements and technical assistance programs.
Central highlands encompassing Huambo, Bié, and parts of Huíla provinces represent Angola’s agricultural heartland with maize and bean production dominating farming systems. These regions benefit from cooler temperatures and reliable rainfall that support year-round cultivation while elevation provides natural advantages for certain crop varieties and livestock production systems.
Coastal regions along the Atlantic Ocean offer opportunities for irrigated agriculture and aquaculture development, with proximity to urban markets providing competitive advantages for perishable crops and fresh produce. Luanda province serves as the primary market destination, creating strong demand for vegetables, fruits, and dairy products from surrounding agricultural areas.
Eastern provinces including Moxico and Cuando Cubango feature extensive grazing lands suitable for livestock development while river systems provide irrigation potential for crop production. These regions show particular promise for cattle ranching and mixed farming systems that integrate crop and livestock production for improved sustainability and profitability.
Southern provinces such as Namibe and Cunene face greater climate challenges but offer opportunities for drought-resistant crops and specialized production systems adapted to semi-arid conditions. Irrigation development along major rivers creates oases of intensive agriculture while traditional pastoralism remains important for rural livelihoods and cultural preservation.
Market structure in Angola’s agricultural sector reflects a diverse ecosystem of producers ranging from smallholder farmers to large commercial operations, each playing distinct roles in meeting domestic food requirements and export opportunities. Competitive dynamics evolve as modernization programs introduce new technologies, market channels, and business models that reshape traditional agricultural practices.
Leading agricultural enterprises include both domestic companies and international investors who bring capital, technology, and market access to Angola’s agricultural development:
Competitive advantages vary across different market segments, with large commercial operations benefiting from economies of scale and advanced technology while smallholder farmers maintain advantages in labor-intensive crops and local market knowledge. Market positioning strategies increasingly focus on quality differentiation, sustainability credentials, and direct market relationships that bypass traditional intermediaries.
Strategic partnerships between domestic and international companies create synergies that combine local knowledge with global expertise, technology, and market access. Joint ventures and technical cooperation agreements enable knowledge transfer while building local capacity for sustainable agricultural development and competitive market participation.
Crop-based segmentation reveals distinct market dynamics across different agricultural products, each with unique production requirements, market channels, and development opportunities:
By Crop Type:
By Farm Size:
By Production System:
Staple food production remains the foundation of Angola’s agricultural sector with cassava leading as the most important crop, providing food security for millions of rural and urban consumers. Cassava cultivation benefits from drought tolerance and minimal input requirements while offering opportunities for processing into flour, starch, and other value-added products that extend shelf life and market reach.
Maize production shows significant potential for expansion and productivity improvement through hybrid seed varieties, proper fertilization, and mechanization. Market demand for maize continues growing due to population increase and changing dietary preferences, while processing opportunities include animal feed, brewing, and food products that create additional value for producers.
Coffee cultivation represents Angola’s most promising export crop with historical reputation for quality and growing international recognition. Arabica varieties grown in highland regions command premium prices while rehabilitation of abandoned plantations and introduction of modern processing techniques enhance product quality and market competitiveness.
Horticultural development responds to increasing urban demand for fresh vegetables and fruits, creating opportunities for peri-urban agriculture and greenhouse production. Cold chain infrastructure development enables longer storage and transportation of perishable products while organic production methods access premium market segments with higher profit margins.
Livestock integration provides opportunities for sustainable intensification through improved breeds, better feeding practices, and disease management programs. Dairy production shows particular potential near urban centers while beef cattle and small ruminants contribute to rural livelihoods and protein supply in areas with limited crop production potential.
Farmers benefit from agricultural market development through increased income opportunities, improved access to inputs and technology, and enhanced food security for their families. Productivity improvements enable farmers to produce more food on the same land area while reducing labor requirements and production costs through mechanization and efficient farming practices.
Agribusiness companies gain access to growing domestic markets and export opportunities while contributing to economic development and job creation. Value chain integration enables companies to capture additional margins through processing, packaging, and marketing activities while building long-term relationships with producer communities and consumer markets.
Government stakeholders achieve multiple policy objectives including economic diversification, rural development, food security, and foreign exchange generation through agricultural exports. Tax revenue from agricultural activities and related businesses contributes to public finances while rural employment reduces urban migration pressures and social tensions.
Development partners see tangible results from their investments in agricultural development through improved livelihoods, environmental sustainability, and economic growth. Poverty reduction outcomes align with international development goals while building local capacity for continued progress and self-reliance in agricultural development.
Consumers benefit from increased food availability, improved quality, and competitive pricing as agricultural markets become more efficient and productive. Nutritional diversity improves as farmers produce wider varieties of crops while food safety standards enhance consumer confidence and public health outcomes.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Digital transformation emerges as a dominant trend with mobile technology, satellite imagery, and data analytics revolutionizing farming practices and market access. Precision agriculture applications enable farmers to optimize input use, monitor crop performance, and make data-driven decisions that improve productivity while reducing environmental impact and production costs.
Sustainable agriculture practices gain momentum as environmental awareness increases and market demand grows for responsibly produced food products. Conservation agriculture techniques, integrated pest management, and organic farming methods attract both domestic and international consumers willing to pay premium prices for environmentally friendly products.
Value chain integration accelerates as stakeholders recognize benefits of coordinated supply chain management from production through processing to final markets. Contract farming arrangements provide farmers with guaranteed markets and technical support while ensuring processors reliable supply of quality raw materials for their operations.
Climate-smart agriculture adoption increases in response to changing weather patterns and environmental challenges. Drought-resistant varieties, water-efficient irrigation systems, and diversified cropping systems help farmers adapt to climate variability while maintaining productivity and profitability.
Youth engagement in agriculture grows through entrepreneurship programs, technology adoption, and modern farming approaches that make agriculture attractive to younger generations. Agribusiness startups introduce innovative solutions for input supply, market access, and financial services that address traditional constraints facing agricultural development.
Infrastructure investments accelerate with major road construction projects, irrigation system development, and storage facility construction improving agricultural market access and reducing post-harvest losses. Rural electrification programs enable mechanization, processing activities, and cold storage systems that enhance agricultural productivity and value addition capabilities.
Technology partnerships between government agencies, international organizations, and private companies introduce advanced agricultural technologies including GPS-guided equipment, drone applications, and mobile-based extension services. Research collaborations with international agricultural research centers develop improved crop varieties and farming practices adapted to local conditions.
Financial sector innovations include mobile money services, agricultural insurance products, and specialized lending programs designed to address farmers’ unique financial needs. Microfinance institutions expand rural coverage while commercial banks develop agricultural lending expertise and risk management capabilities.
Market infrastructure development includes construction of modern wholesale markets, processing facilities, and export terminals that improve market efficiency and access to international markets. Quality standards implementation ensures food safety and enables access to premium markets with higher prices and stable demand.
Policy reforms streamline land tenure systems, simplify business registration procedures, and establish agricultural development zones with special incentives for investors. Institutional strengthening improves extension services, research capacity, and regulatory frameworks that support sustainable agricultural development and market competitiveness.
MarkWide Research analysis indicates that strategic focus on infrastructure development should prioritize rural road networks and storage facilities that address critical bottlenecks limiting market access and causing post-harvest losses. Investment coordination between government agencies and development partners can maximize impact while avoiding duplication of efforts and ensuring sustainable maintenance of infrastructure investments.
Technology adoption strategies should emphasize appropriate technologies that match farmer capabilities and economic conditions rather than pursuing high-tech solutions that may not be sustainable in rural contexts. Extension service strengthening through training programs, demonstration plots, and farmer-to-farmer learning networks can accelerate technology diffusion and ensure effective implementation of improved practices.
Value chain development requires coordinated interventions that address multiple constraints simultaneously rather than focusing on single components in isolation. Stakeholder platforms bringing together farmers, processors, traders, and support service providers can identify synergies and develop collaborative solutions that benefit all participants.
Financial sector development should include risk management instruments such as crop insurance and weather-based index insurance that protect farmers against production risks while encouraging investment in productivity improvements. Collateral alternatives including warehouse receipts and group lending mechanisms can expand credit access for smallholder farmers without traditional collateral.
Market diversification strategies should balance domestic food security objectives with export market development, ensuring that increased commercial production does not compromise local food availability or affordability. Regional market integration offers opportunities for economies of scale while reducing dependence on distant international markets with higher transaction costs and greater volatility.
Long-term prospects for Angola’s agricultural market remain highly positive with projected growth rates of 7.2% annually over the next decade driven by continued government investment, technology adoption, and market development initiatives. Structural transformation will gradually shift the sector from subsistence-oriented production toward commercial agriculture with improved productivity, quality, and market integration.
Technology integration will accelerate with digital adoption rates expected to reach 45% of commercial farmers by 2030, enabling precision agriculture, automated systems, and data-driven decision making that optimize resource use and maximize yields. Artificial intelligence and machine learning applications will provide predictive analytics for weather, pest management, and market forecasting that enhance farm management capabilities.
Market expansion will create new opportunities as processing capacity increases and export infrastructure develops, enabling Angola to compete effectively in regional and international markets. Brand development for Angolan agricultural products will build on quality improvements and sustainable production practices to command premium prices in specialty market segments.
Climate adaptation will become increasingly important with resilient farming systems incorporating drought-tolerant varieties, efficient irrigation, and diversified production strategies that maintain productivity under changing environmental conditions. Carbon markets may provide additional revenue streams for farmers adopting climate-smart practices that sequester carbon and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Investment flows will continue increasing as MWR projections indicate growing confidence in Angola’s agricultural potential among both domestic and international investors. Public-private partnerships will play crucial roles in financing large-scale infrastructure projects while ensuring sustainable development outcomes that benefit all stakeholders in the agricultural value chain.
Angola’s agriculture market stands at a transformative juncture with unprecedented opportunities for sustainable development, economic diversification, and improved livelihoods across rural communities. The convergence of government commitment, international support, natural resource advantages, and growing market demand creates a favorable environment for agricultural sector transformation that can drive broader economic development and poverty reduction.
Strategic investments in infrastructure, technology, and human capital development will determine the pace and sustainability of agricultural transformation while ensuring that benefits reach smallholder farmers who comprise the majority of agricultural producers. Coordinated approaches that address multiple constraints simultaneously while building on existing strengths offer the greatest potential for achieving transformational change in Angola’s agricultural sector.
Market development success will depend on maintaining balance between commercial objectives and social development goals, ensuring that agricultural modernization contributes to food security, rural employment, and environmental sustainability. The Angola agriculture market represents not just an economic opportunity but a pathway toward inclusive development that can improve lives while building a more resilient and diversified national economy for future generations.
What is Angola Agriculture?
Angola Agriculture refers to the sector involved in the cultivation of crops, livestock production, and related activities in Angola. It plays a crucial role in the country’s economy and food security.
What are the key players in the Angola Agriculture Market?
Key players in the Angola Agriculture Market include companies like Agropecuária do Lobito, Sodepac, and Cotonang, which are involved in various agricultural activities such as crop production and livestock farming, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the Angola Agriculture Market?
The Angola Agriculture Market is driven by factors such as increasing demand for food due to population growth, government initiatives to boost agricultural productivity, and investment in modern farming technologies.
What challenges does the Angola Agriculture Market face?
Challenges in the Angola Agriculture Market include limited access to financing for farmers, inadequate infrastructure, and the impact of climate change on crop yields and livestock health.
What opportunities exist in the Angola Agriculture Market?
Opportunities in the Angola Agriculture Market include the potential for organic farming, expansion of export markets for agricultural products, and the adoption of sustainable farming practices to enhance productivity.
What trends are shaping the Angola Agriculture Market?
Trends in the Angola Agriculture Market include the increasing use of technology in farming, a shift towards sustainable agricultural practices, and the growing interest in agro-tourism as a complementary income source for farmers.
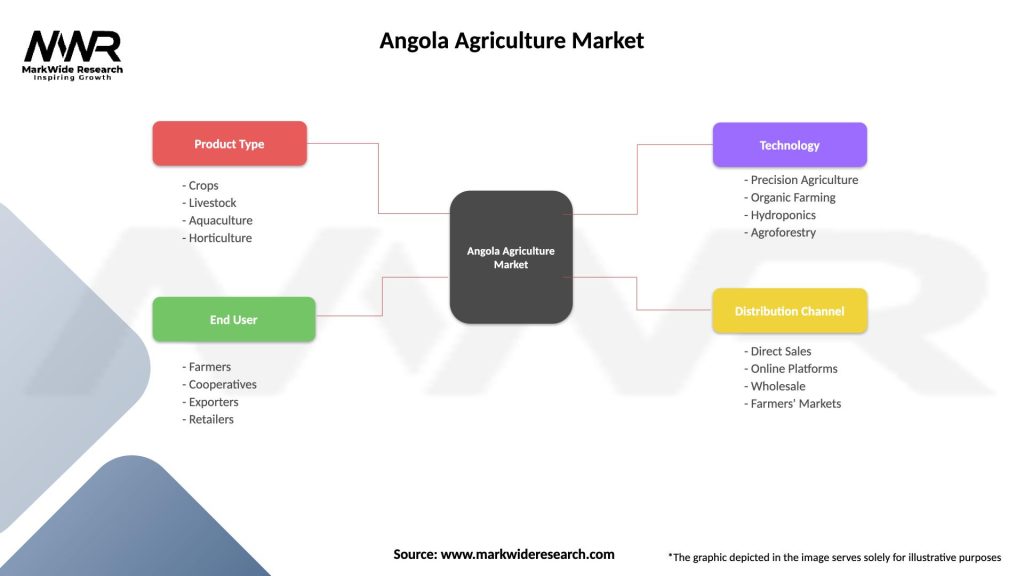
Angola Agriculture Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Crops, Livestock, Aquaculture, Horticulture |
| End User | Farmers, Cooperatives, Exporters, Retailers |
| Technology | Precision Agriculture, Organic Farming, Hydroponics, Agroforestry |
| Distribution Channel | Direct Sales, Online Platforms, Wholesale, Farmers’ Markets |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the Angola Agriculture Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at