444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
The US diabetes devices market represents one of the most dynamic and rapidly evolving healthcare technology sectors in North America. With diabetes affecting millions of Americans, the demand for innovative medical devices continues to surge, driven by technological advancements and increasing patient awareness. Market dynamics indicate substantial growth potential, with the sector experiencing a robust 8.2% CAGR as healthcare providers and patients increasingly adopt sophisticated monitoring and management solutions.
Healthcare transformation has positioned diabetes devices as essential tools in modern medical practice. The market encompasses a comprehensive range of products including continuous glucose monitors, insulin pumps, blood glucose meters, and emerging smart insulin delivery systems. Patient-centric care models have accelerated adoption rates, with approximately 72% of diabetes patients now utilizing some form of digital health monitoring device.
Technological innovation continues to reshape the landscape, with artificial intelligence integration and smartphone connectivity becoming standard features. The convergence of healthcare and technology has created unprecedented opportunities for device manufacturers, healthcare providers, and patients seeking improved diabetes management outcomes.
The US diabetes devices market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of medical technologies, equipment, and digital solutions specifically designed for the diagnosis, monitoring, and management of diabetes mellitus in the United States healthcare system. This market encompasses both traditional and innovative devices that enable patients and healthcare professionals to effectively monitor blood glucose levels, deliver insulin therapy, and maintain optimal glycemic control.
Device categories within this market include glucose monitoring systems, insulin delivery devices, diabetes management software, and integrated digital health platforms. These technologies serve the critical function of empowering patients with real-time health data while enabling healthcare providers to make informed treatment decisions based on comprehensive patient monitoring information.
Strategic market analysis reveals the US diabetes devices sector as a cornerstone of modern healthcare technology, characterized by rapid innovation cycles and increasing patient adoption. The market demonstrates exceptional resilience and growth potential, supported by favorable regulatory environments and expanding insurance coverage for diabetes management technologies.
Key market drivers include the rising prevalence of diabetes, technological advancement in continuous monitoring systems, and growing emphasis on preventive healthcare. Approximately 85% of healthcare providers now recommend digital diabetes management tools to their patients, reflecting the mainstream acceptance of these technologies in clinical practice.
Competitive dynamics showcase established medical device manufacturers alongside innovative technology companies, creating a diverse ecosystem of solutions. The market benefits from strong research and development investments, with companies allocating significant resources to next-generation device development and artificial intelligence integration.

Market intelligence reveals several critical insights shaping the US diabetes devices landscape:
Market segmentation analysis indicates continuous glucose monitors represent the fastest-growing category, with adoption rates increasing by 15% annually among Type 1 diabetes patients. This growth trajectory reflects the superior clinical benefits and improved quality of life these devices provide compared to traditional monitoring methods.
Primary growth catalysts propelling the US diabetes devices market include demographic trends, technological innovation, and evolving healthcare delivery models. The increasing prevalence of diabetes across all age groups creates sustained demand for effective management solutions, while aging populations require more sophisticated monitoring capabilities.
Technological advancement serves as a fundamental driver, with continuous glucose monitoring systems offering real-time data transmission and predictive analytics. These innovations enable proactive diabetes management, reducing the risk of complications and improving long-term health outcomes for patients.
Healthcare policy initiatives supporting preventive care and chronic disease management create favorable market conditions. Government programs and insurance providers increasingly recognize the cost-effectiveness of diabetes devices in preventing expensive complications and hospitalizations.
Market challenges facing the US diabetes devices sector include cost considerations, technological complexity, and regulatory compliance requirements. High device costs can limit patient access, particularly for uninsured or underinsured populations, creating barriers to widespread adoption.
Technical limitations in some devices, including accuracy concerns and user interface complexity, may impact patient satisfaction and long-term adherence. Additionally, the need for regular calibration and maintenance can create ongoing challenges for some users.
Regulatory compliance requirements, while ensuring safety and efficacy, can extend development timelines and increase costs for manufacturers. The complex approval process may delay the introduction of innovative technologies to the market.
Emerging opportunities within the US diabetes devices market span technological innovation, market expansion, and strategic partnerships. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities presents significant potential for next-generation diabetes management solutions.
Telehealth integration creates new avenues for remote patient monitoring and virtual care delivery, particularly relevant in post-pandemic healthcare environments. This trend opens opportunities for device manufacturers to develop comprehensive digital health ecosystems.
Pediatric market segments represent substantial growth potential, as younger patients increasingly require sophisticated diabetes management tools. The development of age-appropriate devices and interfaces could capture this expanding demographic.
Market forces shaping the US diabetes devices landscape include competitive pressures, technological convergence, and evolving patient expectations. The interplay between established medical device companies and innovative technology startups creates a dynamic competitive environment fostering continuous innovation.
Supply chain considerations have gained prominence, with manufacturers focusing on resilient production networks and strategic component sourcing. The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the importance of supply chain diversification and domestic manufacturing capabilities.
Regulatory evolution continues to influence market dynamics, with agencies adapting approval processes to accommodate innovative technologies while maintaining safety standards. MarkWide Research analysis indicates that streamlined regulatory pathways have reduced average approval times by 23% for qualifying diabetes devices.
Partnership strategies between device manufacturers, healthcare providers, and technology companies create synergistic opportunities for market expansion and improved patient outcomes. These collaborations often result in integrated solutions that address multiple aspects of diabetes management.
Comprehensive market analysis employs multiple research methodologies to ensure accurate and reliable insights into the US diabetes devices market. Primary research includes extensive interviews with healthcare professionals, device manufacturers, and patient advocacy groups to capture diverse perspectives on market trends and challenges.
Secondary research encompasses analysis of clinical studies, regulatory filings, patent applications, and industry publications to identify emerging technologies and market opportunities. This approach provides a holistic view of the market landscape and competitive dynamics.
Data validation processes include cross-referencing multiple sources and expert review to ensure accuracy and reliability of market insights. Quantitative analysis focuses on adoption rates, growth trends, and market share dynamics across different device categories and patient segments.
Geographic distribution within the US diabetes devices market reveals significant regional variations in adoption rates, healthcare infrastructure, and patient demographics. The Northeast and West Coast regions demonstrate higher adoption rates for advanced diabetes technologies, reflecting greater healthcare spending and technology acceptance.
Urban versus rural market dynamics present distinct challenges and opportunities. Urban areas typically show faster adoption of new technologies and better access to specialized healthcare providers, while rural regions may face challenges related to healthcare access and technology infrastructure.
State-level analysis indicates that California, Texas, and Florida represent the largest markets by patient population, collectively accounting for approximately 35% of total market demand. These states benefit from large healthcare systems, research institutions, and favorable reimbursement environments.
Market leadership in the US diabetes devices sector is characterized by a mix of established medical device manufacturers and innovative technology companies. The competitive environment fosters continuous innovation and drives improvements in device functionality, user experience, and clinical outcomes.
Key market participants include:
Competitive strategies focus on product differentiation, clinical evidence generation, and strategic partnerships with healthcare providers. Companies invest heavily in research and development to maintain technological leadership and expand market share.
Market segmentation analysis reveals distinct categories within the US diabetes devices market, each serving specific patient needs and clinical applications. Understanding these segments is crucial for manufacturers, healthcare providers, and investors seeking to capitalize on market opportunities.
By Device Type:
By Patient Type:
Continuous Glucose Monitors represent the fastest-growing segment, driven by superior clinical outcomes and improved patient quality of life. These devices offer real-time glucose data, trend arrows, and customizable alerts, enabling proactive diabetes management and reducing the risk of dangerous glucose excursions.
Insulin pump technology continues to evolve with advanced automation features, including predictive low glucose suspend and automated insulin delivery systems. These innovations represent significant progress toward artificial pancreas systems and improved glycemic control.
Smart insulin pens emerge as a bridge technology, combining the familiarity of traditional injection methods with digital connectivity and dose tracking capabilities. This category appeals to patients seeking moderate technology integration without the complexity of pump therapy.
Integration platforms that combine multiple device types and data sources are gaining traction, offering comprehensive diabetes management ecosystems. These solutions provide healthcare providers with holistic patient views and enable more informed treatment decisions.
Healthcare providers benefit from improved patient outcomes, enhanced clinical decision-making capabilities, and streamlined workflow integration. Diabetes devices provide comprehensive patient data, enabling evidence-based treatment adjustments and proactive intervention strategies.
Patients experience significant improvements in quality of life, reduced disease burden, and greater confidence in diabetes management. Advanced devices offer convenience, accuracy, and peace of mind through continuous monitoring and automated features.
Payers and insurance companies realize cost savings through reduced hospitalizations, emergency interventions, and long-term complications. The preventive nature of effective diabetes management translates to substantial healthcare cost reductions over time.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Digital health integration represents a dominant trend, with diabetes devices increasingly connecting to smartphone applications, electronic health records, and telehealth platforms. This connectivity enables comprehensive data sharing and improved care coordination between patients and healthcare providers.
Artificial intelligence adoption is accelerating across device categories, with machine learning algorithms providing predictive insights, personalized recommendations, and automated adjustments. MWR research indicates that AI-enabled devices show 28% better glycemic outcomes compared to traditional monitoring methods.
Miniaturization trends continue to drive device development, with manufacturers focusing on smaller, more discreet devices that integrate seamlessly into patients’ daily lives. This trend particularly appeals to younger patients and those seeking minimal lifestyle impact.
Recent innovations in the US diabetes devices market include breakthrough technologies and strategic partnerships that reshape the competitive landscape. Major manufacturers continue to invest in next-generation solutions that address unmet patient needs and clinical challenges.
Regulatory milestones include FDA approvals for advanced continuous glucose monitors with extended wear times and improved accuracy. These approvals enable broader patient access to cutting-edge monitoring technologies and support market expansion.
Strategic acquisitions and partnerships between established medical device companies and innovative technology firms create synergistic opportunities for product development and market expansion. These collaborations often result in integrated solutions that combine hardware expertise with software innovation.
Clinical study results continue to demonstrate the effectiveness of advanced diabetes devices in improving patient outcomes and reducing healthcare costs. These evidence-based findings support broader adoption and insurance coverage expansion.
Strategic recommendations for market participants include focusing on user experience optimization, expanding insurance coverage partnerships, and investing in artificial intelligence capabilities. Companies should prioritize patient-centric design approaches that simplify device operation while maintaining clinical effectiveness.
Market entry strategies should emphasize differentiation through unique value propositions, whether through superior accuracy, enhanced connectivity, or improved user interfaces. New entrants should consider niche market segments or underserved patient populations as initial target markets.
Partnership opportunities with healthcare systems, technology companies, and research institutions can accelerate innovation and market penetration. Collaborative approaches often yield superior solutions and shared risk profiles for complex development projects.
Long-term projections for the US diabetes devices market indicate sustained growth driven by technological advancement, expanding patient populations, and evolving healthcare delivery models. The market is expected to maintain robust growth rates exceeding 7% annually through the next decade.
Technological evolution will likely focus on artificial intelligence integration, predictive analytics, and automated treatment delivery systems. The convergence of diabetes devices with broader digital health ecosystems will create comprehensive patient management platforms.
Market maturation may lead to increased consolidation among smaller players while creating opportunities for specialized niche providers. The competitive landscape will likely favor companies that successfully integrate hardware innovation with software capabilities and clinical evidence.
Regulatory developments are expected to continue supporting innovation while maintaining safety standards. Streamlined approval processes for breakthrough technologies may accelerate market introduction of next-generation devices and treatment approaches.
The US diabetes devices market stands as a testament to the power of medical technology innovation in addressing critical healthcare challenges. With robust growth prospects, continuous technological advancement, and expanding patient access, the market represents significant opportunities for stakeholders across the healthcare ecosystem.
Market dynamics favor continued expansion, supported by favorable demographics, regulatory environments, and clinical evidence demonstrating the value of advanced diabetes management technologies. The integration of artificial intelligence, connectivity features, and personalized medicine approaches positions the market for sustained growth and innovation.
Success factors for market participants include maintaining focus on patient outcomes, investing in research and development, and building strategic partnerships that enhance market reach and clinical capabilities. As the market evolves, companies that prioritize user experience, clinical effectiveness, and accessibility will likely achieve the strongest competitive positions in this dynamic and essential healthcare technology sector.
What is Diabetes Devices?
Diabetes devices refer to medical tools and technologies used to manage diabetes, including blood glucose monitors, insulin pumps, and continuous glucose monitoring systems. These devices help patients track their blood sugar levels and administer insulin as needed.
What are the key players in the US Diabetes Devices Market?
Key players in the US Diabetes Devices Market include Medtronic, Abbott Laboratories, and Dexcom, among others. These companies are known for their innovative products and technologies that enhance diabetes management.
What are the main drivers of growth in the US Diabetes Devices Market?
The main drivers of growth in the US Diabetes Devices Market include the increasing prevalence of diabetes, advancements in technology, and rising awareness about diabetes management. Additionally, the demand for personalized healthcare solutions is contributing to market expansion.
What challenges does the US Diabetes Devices Market face?
The US Diabetes Devices Market faces challenges such as regulatory hurdles, high costs of advanced devices, and the need for continuous innovation. Additionally, patient adherence to device usage can be a significant barrier to effective diabetes management.
What opportunities exist in the US Diabetes Devices Market?
Opportunities in the US Diabetes Devices Market include the development of smart devices that integrate with mobile applications, the potential for telehealth solutions, and the growing focus on preventive healthcare. These trends can lead to improved patient outcomes and increased market penetration.
What trends are shaping the US Diabetes Devices Market?
Trends shaping the US Diabetes Devices Market include the rise of wearable technology, the integration of artificial intelligence in diabetes management, and the increasing popularity of remote monitoring solutions. These innovations are enhancing the way patients manage their diabetes.
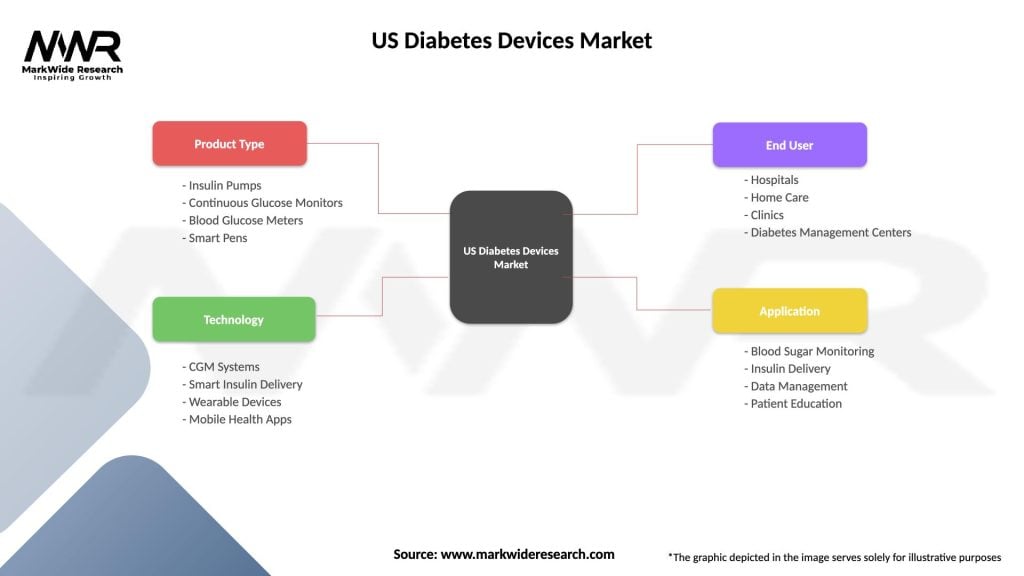
US Diabetes Devices Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Insulin Pumps, Continuous Glucose Monitors, Blood Glucose Meters, Smart Pens |
| Technology | CGM Systems, Smart Insulin Delivery, Wearable Devices, Mobile Health Apps |
| End User | Hospitals, Home Care, Clinics, Diabetes Management Centers |
| Application | Blood Sugar Monitoring, Insulin Delivery, Data Management, Patient Education |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the US Diabetes Devices Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at