444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
The France data center processor market represents a critical component of the nation’s digital infrastructure ecosystem, experiencing unprecedented growth driven by cloud computing adoption, artificial intelligence deployment, and edge computing requirements. French enterprises are increasingly investing in high-performance processors to support their digital transformation initiatives, creating substantial demand for advanced semiconductor solutions across various data center applications.
Market dynamics indicate that France’s strategic position as a European technology hub has accelerated processor adoption rates, with cloud service providers and enterprise data centers leading the demand surge. The market encompasses various processor types including central processing units (CPUs), graphics processing units (GPUs), and specialized artificial intelligence processors, each serving distinct computational requirements within modern data center environments.
Growth trajectories suggest the market is expanding at a compound annual growth rate of 8.2%, fueled by increasing data generation, stringent data sovereignty requirements, and the proliferation of edge computing applications. French organizations across sectors including finance, telecommunications, healthcare, and manufacturing are driving processor demand through their digital modernization efforts and compliance with European data protection regulations.
Regional positioning within the broader European market shows France commanding approximately 18% market share in data center processor adoption, reflecting the country’s robust technology infrastructure and favorable government policies supporting digital innovation. The market benefits from strong partnerships between international processor manufacturers and French system integrators, creating a comprehensive ecosystem for advanced computing solutions.
The France data center processor market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of semiconductor processing units deployed within French data center facilities to handle computational workloads, data processing tasks, and application hosting requirements across various industries and use cases.
Data center processors encompass multiple categories of specialized chips designed to optimize performance for specific computational tasks. Central processing units serve as the primary computational engines handling general-purpose processing tasks, while graphics processing units excel in parallel processing applications such as machine learning, artificial intelligence, and high-performance computing workloads.
Market scope includes processors deployed across various data center types, from large-scale hyperscale facilities operated by cloud service providers to smaller enterprise data centers and emerging edge computing locations. The market encompasses both new processor installations and upgrade cycles as organizations modernize their computational infrastructure to meet evolving performance requirements.
Technological evolution within the market reflects broader trends toward specialized processing architectures, including artificial intelligence accelerators, field-programmable gate arrays, and application-specific integrated circuits designed to optimize specific workload types while improving energy efficiency and computational density within data center environments.
Strategic positioning of the France data center processor market demonstrates robust growth potential driven by accelerating digital transformation initiatives, cloud migration strategies, and emerging technologies requiring advanced computational capabilities. Market participants are witnessing increased demand across multiple processor categories as French organizations modernize their IT infrastructure to support evolving business requirements.
Key growth drivers include the expansion of cloud service providers establishing local presence to meet data sovereignty requirements, increasing adoption of artificial intelligence applications across industries, and the proliferation of edge computing deployments supporting Internet of Things initiatives and real-time processing requirements.
Competitive landscape features established semiconductor manufacturers competing alongside emerging specialized processor developers, creating a dynamic market environment characterized by rapid technological innovation and evolving customer requirements. French enterprises are increasingly prioritizing processor solutions that deliver optimal performance-per-watt ratios while supporting sustainability objectives.
Market segmentation reveals diverse application areas driving processor demand, with cloud computing workloads representing approximately 42% of total demand, followed by enterprise applications and emerging artificial intelligence implementations. The market benefits from strong government support for digital infrastructure development and favorable regulatory frameworks encouraging technology investment.
Primary market insights reveal several critical factors shaping the France data center processor landscape:
Digital transformation initiatives across French enterprises represent the primary driver of data center processor demand, as organizations modernize their IT infrastructure to support cloud-native applications, artificial intelligence implementations, and data-driven business processes. Government digitalization programs and industry-specific modernization requirements are accelerating processor adoption rates across multiple sectors.
Cloud computing expansion continues driving substantial processor demand as hyperscale cloud providers establish local presence in France to serve European markets while complying with data sovereignty requirements. Multi-cloud strategies adopted by French enterprises are creating demand for processors capable of supporting diverse cloud platforms and hybrid deployment models.
Artificial intelligence proliferation across industries is generating significant demand for specialized processors optimized for machine learning workloads, deep learning applications, and real-time inference processing. French organizations in sectors including automotive, healthcare, finance, and manufacturing are implementing AI-driven solutions requiring advanced computational capabilities.
Edge computing deployment is creating new demand patterns for processors optimized for distributed computing environments, supporting applications requiring low-latency processing and real-time decision-making capabilities. Internet of Things expansion and Industry 4.0 initiatives are driving edge processor requirements across manufacturing, logistics, and smart city applications.
Regulatory compliance requirements including GDPR and emerging European digital sovereignty initiatives are driving demand for processors deployed within French data centers to ensure data processing occurs within approved jurisdictions while maintaining high performance standards.
High capital investment requirements for advanced processor technologies create barriers for smaller organizations seeking to modernize their data center infrastructure. Budget constraints and lengthy procurement cycles can delay processor upgrades, particularly for specialized AI and high-performance computing applications requiring significant financial commitments.
Technical complexity associated with implementing advanced processor architectures presents challenges for organizations lacking specialized expertise in modern data center technologies. Integration difficulties between new processors and existing infrastructure can create deployment delays and increase implementation costs.
Supply chain vulnerabilities affecting global semiconductor markets impact processor availability and pricing in the French market. Geopolitical tensions and trade restrictions can create uncertainty around processor sourcing and long-term technology roadmaps, affecting strategic planning for data center investments.
Energy consumption concerns related to high-performance processors create challenges for organizations prioritizing sustainability objectives and managing operational costs. Power infrastructure limitations in some data center facilities may restrict deployment of the most advanced processor technologies requiring substantial electrical capacity.
Skills shortage in specialized areas such as AI processor optimization, high-performance computing, and advanced data center management creates implementation challenges and increases operational costs for organizations deploying cutting-edge processor technologies.
Emerging technology adoption presents substantial opportunities for processor vendors targeting French data centers implementing artificial intelligence, machine learning, and advanced analytics applications. Industry 4.0 initiatives across manufacturing sectors create demand for specialized processors supporting real-time processing and edge computing requirements.
Sustainability initiatives drive opportunities for energy-efficient processor technologies that deliver superior performance-per-watt ratios while supporting corporate environmental objectives. Green data center implementations create demand for processors optimized for renewable energy integration and reduced carbon footprint operations.
5G network deployment across France creates opportunities for network processing units and specialized communication processors supporting next-generation telecommunications infrastructure. Edge computing expansion driven by 5G capabilities opens new market segments for compact, efficient processors optimized for distributed deployment scenarios.
Government digitalization programs and smart city initiatives create opportunities for processor vendors supporting public sector digital transformation projects. Healthcare digitalization and financial services modernization present sector-specific opportunities for specialized processor solutions addressing regulatory compliance and performance requirements.
Hybrid cloud adoption creates opportunities for processors optimized for seamless integration between on-premises and cloud environments, supporting organizations implementing flexible IT strategies that balance performance, security, and cost considerations.
Competitive dynamics within the France data center processor market reflect intense competition between established semiconductor manufacturers and emerging specialized processor developers. Innovation cycles are accelerating as companies compete to deliver processors with superior performance, energy efficiency, and specialized capabilities for emerging applications.
Technology evolution is driving market dynamics toward specialized processor architectures optimized for specific workload types, including AI accelerators, quantum processing units, and neuromorphic processors. Performance improvements of approximately 25-30% annually in key processor categories are creating upgrade cycles and driving market expansion.
Customer requirements are evolving toward processors that deliver optimal total cost of ownership through improved energy efficiency, reduced cooling requirements, and enhanced computational density. French organizations are increasingly prioritizing processors that support sustainability objectives while delivering required performance levels.
Partnership strategies between processor manufacturers, system integrators, and cloud service providers are shaping market dynamics through collaborative development of optimized solutions for French market requirements. Ecosystem development around specialized processor technologies is creating competitive advantages for companies offering comprehensive solution portfolios.
Pricing pressures from competitive market conditions are balanced by increasing demand for advanced processor capabilities, creating opportunities for vendors offering differentiated value propositions through superior performance, energy efficiency, or specialized features addressing specific market segments.
Comprehensive market analysis methodology employed for evaluating the France data center processor market incorporates multiple research approaches to ensure accurate and reliable insights. Primary research activities include extensive interviews with industry executives, technology decision-makers, and procurement specialists across various sectors utilizing data center processors.
Secondary research components encompass analysis of industry reports, government publications, technology vendor documentation, and academic research related to processor technologies and data center trends. Market sizing methodologies utilize bottom-up and top-down approaches to validate market scope and growth projections across different processor categories and application segments.
Data validation processes include cross-referencing information from multiple sources, conducting expert interviews to verify market trends, and analyzing historical data patterns to ensure accuracy of growth projections and market dynamics assessments. Quantitative analysis incorporates statistical modeling to identify correlations between market drivers and adoption patterns.
Regional analysis methodology examines France-specific factors including regulatory environment, technology adoption patterns, competitive landscape characteristics, and economic conditions affecting processor market development. Segmentation analysis evaluates market dynamics across processor types, application areas, and end-user sectors to provide comprehensive market understanding.
Île-de-France region dominates the French data center processor market, accounting for approximately 45% of total demand due to the concentration of major enterprises, financial institutions, and technology companies in the Paris metropolitan area. Data center clusters in this region support both domestic and international organizations requiring high-performance processing capabilities.
Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region represents a significant market segment driven by manufacturing industries, research institutions, and emerging technology companies implementing advanced computing solutions. Lyon and Grenoble serve as key technology hubs driving processor demand for industrial applications and research computing requirements.
Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur region benefits from its position as a Mediterranean technology corridor, with Nice and Marseille hosting data centers supporting telecommunications, logistics, and international business operations. Connectivity advantages to European and African markets drive processor demand for global service delivery.
Grand Est region leverages its strategic location bordering Germany and other European markets to attract data center investments requiring advanced processor technologies. Cross-border business operations and European Union institutional requirements drive demand for high-performance computing solutions.
Regional distribution patterns show approximately 35% of processor deployments concentrated in hyperscale data centers, 40% in enterprise facilities, and 25% in edge computing locations across various French regions, reflecting diverse application requirements and deployment strategies.
Market leadership in the France data center processor market is characterized by intense competition among established semiconductor manufacturers and emerging specialized technology providers. Key market participants include:
Competitive strategies focus on delivering processors with superior performance-per-watt ratios, specialized capabilities for emerging applications, and comprehensive ecosystem support including software tools, development platforms, and technical services.
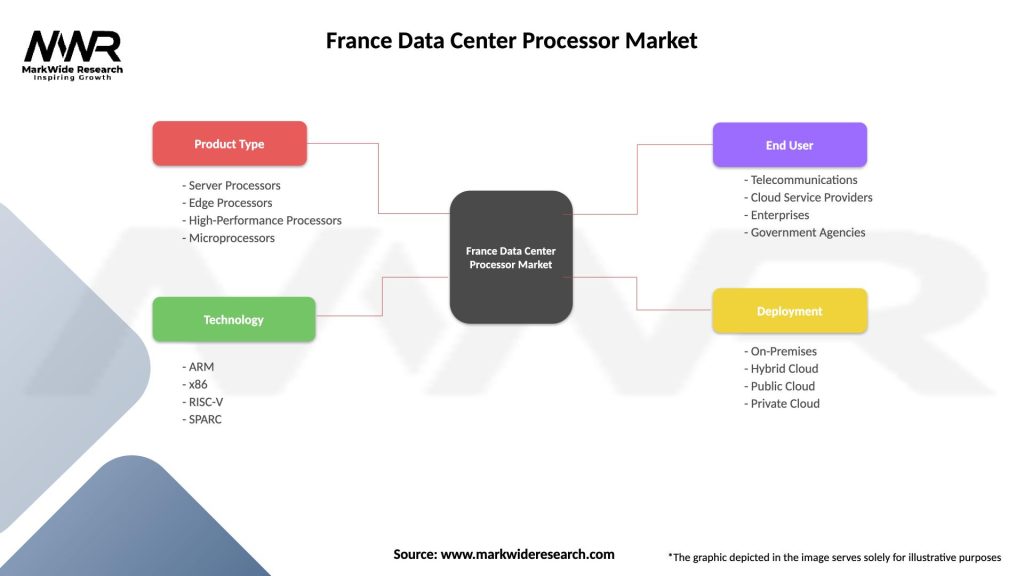
By Processor Type:
By Application:
By End-User Sector:
CPU Category Analysis reveals continued dominance in general-purpose computing applications, with x86 architecture maintaining strong market position while ARM-based processors gain traction in energy-efficient deployments. Performance improvements focus on core count increases, enhanced instruction sets, and improved memory bandwidth to support demanding workloads.
GPU Accelerator Segment demonstrates rapid growth driven by AI and machine learning applications, with data center GPUs optimized for training and inference workloads showing particularly strong adoption. French organizations are increasingly deploying GPU clusters for research computing, financial modeling, and industrial AI applications.
AI Processor Category represents the fastest-growing segment, with specialized chips designed for neural network processing, deep learning, and real-time AI inference applications. Edge AI processors are gaining traction for distributed intelligence applications requiring local processing capabilities.
Network Processing Units show steady growth driven by 5G deployment, network security requirements, and software-defined networking implementations. Programmable network processors offer flexibility for evolving network protocols and security standards.
FPGA Solutions provide adaptability for specialized applications requiring custom processing logic, with growing adoption in financial trading, telecommunications, and research computing applications where flexibility and performance optimization are critical requirements.
Technology Vendors benefit from expanding market opportunities driven by digital transformation initiatives, AI adoption, and edge computing deployment across French organizations. Revenue growth potential exists through specialized processor development addressing specific industry requirements and emerging application areas.
System Integrators gain opportunities to provide comprehensive solutions combining advanced processors with supporting infrastructure, software, and services. Value-added services including system optimization, performance tuning, and ongoing support create recurring revenue streams and strengthen customer relationships.
Cloud Service Providers achieve competitive advantages through deployment of advanced processors enabling superior performance, energy efficiency, and specialized capabilities for customer workloads. Service differentiation through processor-optimized offerings creates opportunities for premium pricing and market expansion.
Enterprise Organizations realize benefits including improved application performance, reduced operational costs through energy efficiency, and enhanced capabilities for AI and analytics applications. Digital transformation acceleration enables competitive advantages and new business model development.
Research Institutions gain access to advanced computing capabilities supporting scientific research, academic collaboration, and innovation development. High-performance processors enable breakthrough research in areas including climate modeling, medical research, and materials science.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Artificial Intelligence Integration represents the most significant trend shaping processor requirements, with French organizations increasingly implementing AI-driven applications requiring specialized computational capabilities. Machine learning workloads are driving demand for processors optimized for neural network processing and real-time inference applications.
Edge Computing Proliferation is creating new deployment patterns for processors optimized for distributed environments, supporting applications requiring low-latency processing and local decision-making capabilities. IoT expansion and Industry 4.0 initiatives are driving edge processor adoption across manufacturing, logistics, and smart city applications.
Sustainability Emphasis is influencing processor selection criteria, with organizations prioritizing energy-efficient solutions that reduce operational costs and environmental impact. Green data center initiatives are driving adoption of processors with superior performance-per-watt characteristics and reduced cooling requirements.
Hybrid Cloud Strategies are creating demand for processors capable of seamlessly supporting workloads across on-premises and cloud environments. Multi-cloud deployments require processors with flexibility to optimize performance across diverse platform architectures and service models.
Security Enhancement Focus is driving adoption of processors with built-in security features, hardware-based encryption capabilities, and trusted execution environments. Cybersecurity concerns are influencing processor selection to include advanced security features addressing evolving threat landscapes.
Major processor manufacturers are establishing stronger presence in the French market through partnerships with local system integrators and cloud service providers. Intel Corporation has expanded its data center processor portfolio with specialized AI accelerators and energy-efficient designs targeting French enterprise requirements.
NVIDIA Corporation has strengthened its position in the AI processor segment through partnerships with French research institutions and cloud providers, supporting machine learning and high-performance computing applications. GPU cluster deployments are increasing across academic and commercial organizations implementing AI-driven solutions.
Advanced Micro Devices has gained market share through competitive processor offerings optimized for cloud computing and enterprise applications. EPYC processor family adoption is growing among French organizations seeking alternatives to traditional x86 solutions with enhanced performance characteristics.
Emerging processor technologies including quantum processing units and neuromorphic processors are gaining attention from French research institutions and technology companies exploring next-generation computing capabilities. Government research programs are supporting development of advanced processor technologies for strategic applications.
Cloud service providers are investing in custom processor development and deployment to optimize performance for specific workload types while reducing operational costs. Hyperscale operators are increasingly utilizing specialized processors designed for their unique application requirements and performance objectives.
Strategic recommendations for market participants include focusing on energy-efficient processor solutions that address sustainability objectives while delivering required performance levels. MarkWide Research analysis indicates that organizations prioritizing total cost of ownership optimization will drive demand for processors with superior performance-per-watt characteristics.
Technology vendors should develop specialized processor solutions addressing specific French market requirements, including data sovereignty compliance, regulatory adherence, and sector-specific performance optimization. Partnership strategies with local system integrators and service providers can accelerate market penetration and customer adoption.
Investment priorities should focus on AI processor capabilities, edge computing optimization, and security feature enhancement to address evolving customer requirements. Research and development investments in next-generation processor architectures will be critical for maintaining competitive positioning in rapidly evolving market conditions.
Market entry strategies for new participants should emphasize differentiated value propositions through specialized capabilities, superior energy efficiency, or unique features addressing specific application requirements. Ecosystem development including software tools, development platforms, and technical support will be essential for successful market penetration.
Customer engagement approaches should focus on demonstrating clear return on investment through performance improvements, operational cost reductions, and enhanced capabilities for emerging applications. Proof-of-concept deployments and pilot programs can help organizations evaluate processor technologies before full-scale implementation.
Long-term growth prospects for the France data center processor market remain highly positive, with compound annual growth rates expected to maintain strong momentum driven by continued digital transformation, AI adoption, and edge computing expansion. Market evolution will be characterized by increasing specialization of processor architectures for specific application requirements and workload optimization.
Technology advancement will focus on delivering processors with enhanced AI capabilities, improved energy efficiency, and specialized features supporting emerging applications including quantum computing, autonomous systems, and advanced analytics. Performance improvements of approximately 20-25% annually are anticipated across key processor categories through architectural innovations and manufacturing process advances.
Market expansion will be driven by growing adoption of edge computing, 5G network deployment, and increasing implementation of AI-driven applications across various sectors. French organizations will continue investing in advanced processor technologies to support competitive positioning and operational efficiency objectives.
Competitive dynamics will intensify as established manufacturers compete with emerging specialized processor developers, creating opportunities for innovative solutions addressing specific market requirements. Consolidation activities may occur as companies seek to strengthen their technology portfolios and market positioning.
Regulatory developments including European digital sovereignty initiatives and sustainability requirements will influence processor selection criteria and deployment strategies. MWR projections indicate that compliance-focused processor solutions will gain importance as organizations navigate evolving regulatory landscapes while maintaining performance objectives.
The France data center processor market represents a dynamic and rapidly evolving ecosystem characterized by strong growth potential, technological innovation, and diverse application requirements across multiple sectors. Market fundamentals remain robust, supported by continued digital transformation initiatives, artificial intelligence adoption, and edge computing expansion driving sustained demand for advanced processor technologies.
Strategic opportunities exist for technology vendors, system integrators, and service providers capable of delivering specialized solutions addressing specific French market requirements including data sovereignty compliance, energy efficiency optimization, and sector-specific performance needs. Competitive positioning will depend on the ability to provide comprehensive solutions combining advanced processors with supporting ecosystem components.
Future success in the market will require continued investment in research and development, strategic partnerships with local organizations, and deep understanding of evolving customer requirements across diverse application areas. Organizations that can effectively balance performance, efficiency, and cost considerations while addressing regulatory compliance requirements will achieve sustainable competitive advantages in this expanding market opportunity.
What is Data Center Processor?
Data Center Processors are specialized computing units designed to handle the demands of data centers, focusing on performance, efficiency, and scalability. They are essential for managing large volumes of data and supporting various applications such as cloud computing, big data analytics, and enterprise resource planning.
What are the key players in the France Data Center Processor Market?
Key players in the France Data Center Processor Market include Intel Corporation, Advanced Micro Devices (AMD), NVIDIA Corporation, and ARM Holdings, among others. These companies are known for their innovative technologies and contributions to the development of high-performance processors for data centers.
What are the growth factors driving the France Data Center Processor Market?
The France Data Center Processor Market is driven by the increasing demand for cloud services, the rise of big data analytics, and the need for enhanced processing power in enterprise applications. Additionally, the growing trend of digital transformation across various industries is further fueling market growth.
What challenges does the France Data Center Processor Market face?
The France Data Center Processor Market faces challenges such as high energy consumption, the need for advanced cooling solutions, and the rapid pace of technological change. Additionally, competition among manufacturers can lead to pricing pressures and the need for continuous innovation.
What opportunities exist in the France Data Center Processor Market?
Opportunities in the France Data Center Processor Market include the expansion of edge computing, the increasing adoption of artificial intelligence, and the development of energy-efficient processors. These trends present avenues for growth and innovation in the sector.
What trends are shaping the France Data Center Processor Market?
Trends shaping the France Data Center Processor Market include the shift towards multi-core processors, advancements in AI and machine learning capabilities, and the integration of security features within processors. These trends are influencing how data centers operate and manage workloads.
France Data Center Processor Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Server Processors, Edge Processors, High-Performance Processors, Microprocessors |
| Technology | ARM, x86, RISC-V, SPARC |
| End User | Telecommunications, Cloud Service Providers, Enterprises, Government Agencies |
| Deployment | On-Premises, Hybrid Cloud, Public Cloud, Private Cloud |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the France Data Center Processor Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at