444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
The United States data center processor market represents a critical component of the nation’s digital infrastructure, powering the computational backbone of cloud services, enterprise applications, and emerging technologies. Data center processors serve as the fundamental processing units that enable everything from basic web hosting to complex artificial intelligence workloads across American businesses and organizations.
Market dynamics indicate robust growth driven by accelerating digital transformation initiatives, cloud migration trends, and the proliferation of data-intensive applications. The sector experiences particularly strong demand from hyperscale cloud providers, enterprise data centers, and colocation facilities seeking enhanced performance and energy efficiency. Growth projections suggest the market will expand at a compound annual growth rate of 8.2% through the forecast period, reflecting sustained investment in computational infrastructure.
Technology evolution continues reshaping processor architectures, with advanced manufacturing processes, specialized AI accelerators, and energy-efficient designs becoming increasingly prevalent. Major semiconductor companies are investing heavily in next-generation processor technologies specifically optimized for data center workloads, including enhanced parallel processing capabilities and improved power management features.
Regional concentration shows significant clustering in key technology hubs, with California accounting for approximately 35% of data center processor deployments, followed by substantial installations in Virginia, Texas, and the Pacific Northwest. This geographic distribution aligns with major cloud provider facilities and enterprise technology centers across the United States.
The United States data center processor market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem encompassing the design, manufacturing, distribution, and deployment of central processing units specifically engineered for data center environments across American facilities and organizations.
Data center processors represent specialized computing components optimized for server workloads, featuring enhanced multi-core architectures, advanced cache hierarchies, and robust reliability features essential for continuous operation in mission-critical environments. These processors differ significantly from consumer-grade chips, incorporating enterprise-specific features such as error correction capabilities, virtualization support, and enhanced security mechanisms.
Market scope encompasses various processor categories including traditional x86 processors, ARM-based alternatives, specialized AI accelerators, and emerging quantum processing units. The definition extends beyond hardware components to include associated software ecosystems, development tools, and optimization frameworks that enable efficient utilization of processing resources.
Stakeholder ecosystem involves processor manufacturers, server vendors, cloud service providers, enterprise customers, and technology integrators working collaboratively to deliver comprehensive computing solutions. This interconnected network drives innovation and ensures alignment between processor capabilities and evolving data center requirements.
Strategic positioning of the United States data center processor market reflects the nation’s leadership in global technology innovation and digital infrastructure development. The market demonstrates exceptional resilience and growth potential, supported by substantial investments from both private enterprises and government initiatives focused on maintaining technological competitiveness.
Key growth drivers include the exponential increase in data generation, widespread adoption of cloud computing services, and the emergence of artificial intelligence applications requiring specialized processing capabilities. Enterprise digital transformation initiatives contribute significantly to processor demand, with approximately 78% of organizations planning to expand their data center processing capacity within the next two years.
Competitive landscape features intense innovation cycles among leading processor manufacturers, driving continuous improvements in performance, efficiency, and specialized functionality. Market leaders are investing heavily in research and development to maintain technological advantages and address evolving customer requirements across diverse industry verticals.
Future trajectory indicates sustained growth opportunities driven by emerging technologies such as edge computing, 5G network infrastructure, and advanced analytics platforms. The market is expected to benefit from increasing demand for high-performance computing capabilities and energy-efficient processing solutions that align with sustainability objectives.
Market intelligence reveals several critical insights shaping the United States data center processor landscape and influencing strategic decision-making across the technology ecosystem:
Digital transformation acceleration serves as the primary catalyst driving unprecedented demand for data center processing capabilities across American organizations. Enterprises are rapidly modernizing their IT infrastructure to support cloud-native applications, real-time analytics, and digital customer experiences that require substantial computational resources.
Cloud computing expansion continues generating massive processor demand as hyperscale providers build new facilities and upgrade existing infrastructure to accommodate growing customer workloads. The shift toward cloud-first strategies among enterprises creates sustained demand for high-performance processors optimized for virtualized environments and multi-tenant architectures.
Artificial intelligence proliferation drives specialized processor requirements as organizations implement machine learning models, natural language processing systems, and computer vision applications. These AI workloads demand processors with enhanced parallel processing capabilities and dedicated acceleration units to achieve acceptable performance levels.
Edge computing emergence creates new processor deployment scenarios as organizations distribute computational resources closer to data sources and end users. This trend requires processors that balance performance with power efficiency while maintaining reliability in diverse environmental conditions.
Data explosion necessitates enhanced processing capabilities to handle exponentially growing data volumes from IoT devices, social media platforms, and business applications. Organizations require processors capable of efficiently processing, analyzing, and storing massive datasets in real-time scenarios.
Regulatory compliance requirements drive demand for processors with advanced security features and audit capabilities, particularly in financial services, healthcare, and government sectors where data protection and privacy regulations mandate specific technological safeguards.
High capital requirements present significant barriers for organizations seeking to upgrade or expand their data center processing infrastructure. The substantial investment needed for cutting-edge processors, associated cooling systems, and supporting infrastructure can strain budgets and delay implementation timelines.
Supply chain complexities create challenges in processor availability and pricing stability, particularly during periods of high demand or global semiconductor shortages. These disruptions can impact deployment schedules and force organizations to consider alternative processor options or delay infrastructure upgrades.
Technical complexity associated with modern processor architectures requires specialized expertise for optimal implementation and management. Organizations may struggle to find qualified personnel capable of effectively deploying and maintaining advanced processor technologies, limiting adoption rates.
Power consumption concerns remain significant considerations as high-performance processors generate substantial heat and require extensive cooling infrastructure. Data centers must balance processing performance with energy efficiency to manage operational costs and environmental impact.
Legacy system integration challenges complicate processor upgrades in existing data center environments where compatibility with older software and hardware components must be maintained. These integration requirements can limit processor selection options and increase implementation complexity.
Rapid technology evolution creates concerns about processor obsolescence and investment protection, as organizations worry about committing to technologies that may become outdated within short timeframes due to accelerating innovation cycles.
Emerging technology integration presents substantial opportunities for processor manufacturers and data center operators to develop specialized solutions for quantum computing, neuromorphic processing, and advanced AI applications. These cutting-edge technologies require novel processor architectures and create new market segments with significant growth potential.
Sustainability initiatives drive demand for energy-efficient processors that support corporate environmental goals and regulatory compliance requirements. Organizations increasingly prioritize green technology solutions, creating opportunities for processors that deliver superior performance per watt ratios.
5G network deployment generates new processor requirements for edge computing infrastructure and network function virtualization platforms. The rollout of 5G networks across the United States creates substantial demand for processors optimized for low-latency, high-throughput applications.
Government modernization programs offer significant opportunities as federal, state, and local agencies upgrade aging IT infrastructure and implement cloud-first policies. These initiatives require processors that meet stringent security and performance requirements while supporting legacy application compatibility.
Industry 4.0 adoption creates processor demand for manufacturing automation, predictive maintenance systems, and real-time quality control applications. Industrial organizations require processors capable of handling complex sensor data and supporting mission-critical operational systems.
Healthcare digitization drives processor requirements for electronic health records, medical imaging systems, and telemedicine platforms. The healthcare sector’s digital transformation creates opportunities for processors optimized for secure, compliant, and high-availability applications.
Competitive intensity characterizes the United States data center processor market as leading manufacturers compete aggressively on performance, efficiency, and specialized capabilities. This competition drives rapid innovation cycles and creates downward pressure on pricing while simultaneously advancing technological capabilities.
Technology convergence influences market dynamics as traditional boundaries between different processor types blur, with general-purpose processors incorporating specialized acceleration units and dedicated AI chips adding general computing capabilities. This convergence creates both opportunities and challenges for market participants.
Customer sophistication continues increasing as data center operators develop deeper technical expertise and more specific requirements for processor performance, efficiency, and features. This trend drives demand for customized solutions and closer collaboration between processor manufacturers and end users.
Ecosystem partnerships play crucial roles in market success as processor manufacturers collaborate with software vendors, cloud providers, and system integrators to optimize performance and ensure compatibility across diverse application environments. These partnerships influence product development priorities and market positioning strategies.
Regulatory influences shape market dynamics through data protection requirements, export controls, and government procurement policies that favor domestic technology suppliers. These regulatory factors create both constraints and opportunities for market participants depending on their strategic positioning.
Investment patterns reflect strong venture capital and private equity interest in processor innovation, particularly for specialized applications such as AI acceleration and edge computing. This financial support enables rapid technology development and market entry for innovative processor solutions.
Comprehensive analysis of the United States data center processor market employs multiple research methodologies to ensure accuracy, reliability, and depth of insights. The research approach combines quantitative data collection with qualitative analysis to provide a complete market perspective.
Primary research involves extensive interviews with industry executives, technology leaders, and key decision-makers across processor manufacturers, data center operators, and enterprise customers. These interviews provide firsthand insights into market trends, challenges, and opportunities that shape strategic decision-making.
Secondary research encompasses analysis of industry reports, financial statements, patent filings, and technical documentation from leading market participants. This research provides historical context and validates primary research findings through multiple independent sources.
Market modeling utilizes advanced analytical techniques to project market growth, segment performance, and competitive dynamics based on historical trends and identified market drivers. These models incorporate multiple scenarios to account for potential market variations and uncertainties.
Technology assessment involves detailed evaluation of processor architectures, performance benchmarks, and emerging technologies to understand their potential market impact. This technical analysis ensures research findings reflect actual technological capabilities and limitations.
Data validation processes ensure research accuracy through cross-referencing multiple sources, statistical analysis of data consistency, and expert review of findings and conclusions. This validation approach maintains research quality and reliability standards throughout the analysis process.
Geographic distribution of the United States data center processor market reveals significant regional variations driven by technology industry concentration, infrastructure development, and regulatory factors. MarkWide Research analysis indicates distinct regional characteristics that influence market dynamics and growth patterns.
West Coast dominance continues with California maintaining the largest market share at approximately 35% of total processor deployments, driven by major technology companies, cloud service providers, and innovative startups concentrated in Silicon Valley and surrounding areas. This region benefits from proximity to processor manufacturers and advanced technology ecosystems.
East Coast growth shows Virginia emerging as a significant market with roughly 18% market share, primarily due to government data centers, financial services infrastructure, and the “Data Center Alley” corridor that hosts numerous hyperscale facilities. The region benefits from favorable regulatory environments and robust fiber connectivity.
Texas expansion demonstrates rapid growth with approximately 15% market share, driven by favorable business climates, abundant land availability, and competitive energy costs that attract major data center investments. The state’s central location provides strategic advantages for nationwide service delivery.
Pacific Northwest presence maintains around 12% market share, supported by abundant renewable energy resources, favorable climate conditions for cooling, and proximity to major technology companies. This region particularly attracts environmentally conscious organizations seeking sustainable data center solutions.
Emerging markets in the Midwest and Southeast show increasing activity as organizations seek cost-effective alternatives to traditional technology hubs while maintaining connectivity and infrastructure quality. These regions offer growing opportunities representing approximately 20% of the total market.
Market leadership in the United States data center processor sector features intense competition among established semiconductor giants and emerging specialized companies, each pursuing distinct strategies to capture market share and drive innovation.
Innovation strategies vary significantly among competitors, with some focusing on architectural improvements, others emphasizing specialized acceleration capabilities, and several pursuing custom silicon approaches tailored to specific customer requirements and use cases.
Partnership ecosystems play crucial roles in competitive positioning as processor manufacturers collaborate with software vendors, cloud providers, and system integrators to optimize performance and ensure broad compatibility across diverse application environments.
Technology segmentation reveals distinct processor categories serving different data center requirements and application scenarios across the United States market:
By Processor Type:
By Application:
By End User:
x86 processor dominance continues across enterprise and cloud environments due to extensive software ecosystem support, mature development tools, and proven reliability in mission-critical applications. However, this category faces increasing pressure from alternative architectures offering superior energy efficiency and specialized capabilities.
ARM processor adoption accelerates as cloud providers develop custom silicon solutions and software ecosystems mature to support ARM-based server deployments. This category particularly appeals to organizations prioritizing energy efficiency and cost optimization over maximum raw performance.
GPU acceleration growth reflects increasing demand for AI and machine learning capabilities across diverse industries. These processors excel in parallel processing scenarios but require specialized software optimization and expertise for effective deployment and management.
FPGA flexibility attracts organizations requiring customizable acceleration for specific workloads such as financial trading, network processing, and scientific computing. While offering superior customization capabilities, FPGAs require significant development expertise and longer implementation timelines.
Hybrid approaches emerge as organizations deploy multiple processor types within single data centers to optimize performance and cost-effectiveness for diverse workload requirements. This trend drives demand for management tools and expertise capable of handling heterogeneous processing environments.
Specialized processors gain traction for specific applications such as quantum computing, neuromorphic processing, and advanced cryptography, creating niche markets with significant growth potential despite current limited deployment volumes.
Performance advantages delivered by modern data center processors enable organizations to achieve superior application responsiveness, enhanced user experiences, and improved operational efficiency. These performance gains translate directly into competitive advantages and customer satisfaction improvements.
Cost optimization opportunities arise through improved processor efficiency, reduced power consumption, and enhanced consolidation ratios that lower total cost of ownership. Organizations can achieve significant operational savings while simultaneously improving performance and capability.
Scalability benefits enable organizations to efficiently accommodate growth and changing requirements through flexible processor architectures that support seamless capacity expansion and workload adaptation. This scalability reduces the need for major infrastructure overhauls and associated disruptions.
Innovation enablement allows organizations to implement cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence, real-time analytics, and advanced automation that require substantial processing capabilities. Modern processors provide the foundation for digital transformation initiatives and competitive differentiation.
Energy efficiency improvements support sustainability objectives while reducing operational costs through lower power consumption and cooling requirements. These efficiency gains become increasingly important as organizations face environmental regulations and stakeholder pressure for sustainable operations.
Security enhancements built into modern processors provide hardware-level protection against cyber threats and support compliance with data protection regulations. These security features reduce risk exposure and enable organizations to safely implement cloud and digital technologies.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Artificial intelligence integration represents the most significant trend reshaping the data center processor landscape, with AI-optimized processors experiencing adoption rates exceeding 45% among new deployments. Organizations increasingly require processors capable of efficiently handling machine learning inference and training workloads alongside traditional computing tasks.
Energy efficiency focus drives processor design priorities as data centers seek to reduce operational costs and meet sustainability commitments. Advanced manufacturing processes and architectural improvements enable power efficiency improvements of 40-60% compared to previous generations while maintaining or improving performance levels.
Custom silicon adoption accelerates as major cloud providers and technology companies develop processors specifically optimized for their unique workload requirements. This trend challenges traditional processor manufacturers while creating opportunities for specialized design services and manufacturing partnerships.
Edge computing expansion creates demand for processors that balance performance with power efficiency and environmental resilience for deployment in distributed locations. These processors must operate reliably in challenging conditions while maintaining connectivity to central data centers.
Heterogeneous computing becomes standard practice as organizations deploy multiple processor types within single data centers to optimize performance and cost-effectiveness for diverse workload requirements. This approach requires sophisticated management tools and expertise to coordinate different processor architectures effectively.
Security enhancement receives increased priority as processors incorporate hardware-level security features including encryption acceleration, secure boot capabilities, and isolated execution environments to protect against evolving cyber threats and support regulatory compliance requirements.
Manufacturing investments across the United States reflect government and private sector commitments to strengthening domestic semiconductor production capabilities. Major processor manufacturers are establishing new fabrication facilities and expanding existing operations to reduce dependence on overseas manufacturing.
Research partnerships between processor manufacturers, academic institutions, and government agencies drive innovation in advanced processor architectures, quantum computing, and neuromorphic processing technologies. These collaborations accelerate technology development and ensure alignment with national strategic objectives.
Acquisition activities reshape the competitive landscape as established companies acquire specialized processor developers and emerging technology companies to expand their capabilities and market reach. These acquisitions often focus on AI acceleration, edge computing, and specialized processing technologies.
Standards development initiatives work to establish common interfaces and compatibility frameworks for diverse processor architectures and acceleration technologies. These standards efforts aim to simplify deployment and management while promoting innovation and competition.
Sustainability programs launched by major processor manufacturers focus on reducing environmental impact through improved energy efficiency, sustainable manufacturing processes, and circular economy principles. These initiatives respond to customer demands and regulatory requirements for environmentally responsible technology.
Government policies supporting domestic semiconductor manufacturing and technology leadership include funding programs, tax incentives, and regulatory frameworks designed to strengthen the United States position in global processor markets and reduce strategic dependencies.
Strategic positioning recommendations emphasize the importance of developing comprehensive processor strategies that balance performance, efficiency, and cost considerations while preparing for emerging technology trends. Organizations should evaluate their current and future processing requirements to make informed investment decisions.
Technology diversification appears prudent as organizations consider deploying multiple processor architectures to optimize performance and reduce vendor dependence. This approach requires careful planning and expertise development but offers significant benefits in flexibility and cost optimization.
Partnership development with processor manufacturers, software vendors, and system integrators can provide access to expertise, optimization tools, and preferential pricing that improve deployment success and ongoing performance. These relationships become increasingly valuable as processor technologies become more complex.
Skill development investments in processor expertise and management capabilities will become critical success factors as organizations deploy increasingly sophisticated processing technologies. Training programs and talent acquisition strategies should prioritize these technical competencies.
Sustainability planning should incorporate energy efficiency considerations into processor selection criteria as environmental regulations and stakeholder expectations continue evolving. Organizations that proactively address sustainability will gain competitive advantages and regulatory compliance benefits.
Security integration requires comprehensive approaches that leverage hardware-level security features while implementing appropriate software and operational security measures. Processor security capabilities should be evaluated as part of overall cybersecurity strategies and compliance frameworks.
Growth trajectory for the United States data center processor market remains strongly positive, supported by continued digital transformation, artificial intelligence adoption, and infrastructure modernization initiatives. MWR projections indicate sustained expansion driven by both replacement cycles and new capacity requirements across diverse industry sectors.
Technology evolution will accelerate with advanced manufacturing processes, novel architectures, and specialized acceleration capabilities becoming standard features. The next generation of processors will likely incorporate quantum processing elements, neuromorphic capabilities, and advanced AI acceleration that fundamentally change computational possibilities.
Market consolidation may occur as smaller specialized processor companies are acquired by larger manufacturers seeking to expand their capabilities and market reach. However, innovation opportunities will continue attracting new entrants with breakthrough technologies and novel approaches to processing challenges.
Regulatory influences will likely increase as governments implement policies supporting domestic semiconductor manufacturing and technology leadership. These policies may create both opportunities and constraints for market participants depending on their strategic positioning and manufacturing locations.
Customer sophistication will continue growing as organizations develop deeper technical expertise and more specific requirements for processor performance, efficiency, and features. This trend will drive demand for customized solutions and closer collaboration between manufacturers and customers.
Sustainability requirements will become increasingly important as environmental regulations and stakeholder expectations drive demand for energy-efficient processors and sustainable manufacturing practices. Organizations that prioritize sustainability will gain competitive advantages in both cost and market positioning.
The United States data center processor market stands at a pivotal juncture characterized by unprecedented technological innovation, evolving customer requirements, and significant growth opportunities. The convergence of artificial intelligence, edge computing, and sustainability initiatives creates a dynamic environment that rewards innovation while challenging traditional approaches to processor design and deployment.
Market fundamentals remain exceptionally strong, supported by continued digital transformation across industries, government modernization initiatives, and the emergence of new technologies requiring substantial processing capabilities. The combination of established market leaders and innovative newcomers ensures continued technological advancement and competitive pricing that benefits customers and drives market growth.
Strategic success in this evolving market requires careful attention to technology trends, customer requirements, and competitive dynamics while maintaining focus on performance, efficiency, and cost optimization. Organizations that develop comprehensive processor strategies and invest in appropriate expertise will be best positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities and navigate potential challenges in this critical technology sector.
What is Data Center Processor?
Data Center Processors are specialized computing units designed to handle the demands of data centers, focusing on high performance, energy efficiency, and reliability. They are essential for managing large volumes of data and supporting various applications such as cloud computing and big data analytics.
What are the key players in the United States Data Center Processor Market?
Key players in the United States Data Center Processor Market include Intel Corporation, Advanced Micro Devices (AMD), and NVIDIA Corporation, among others. These companies are known for their innovative technologies and competitive offerings in the processor segment.
What are the growth factors driving the United States Data Center Processor Market?
The growth of the United States Data Center Processor Market is driven by the increasing demand for cloud services, the rise of artificial intelligence applications, and the need for enhanced data processing capabilities. Additionally, the expansion of data centers to support digital transformation initiatives contributes to market growth.
What challenges does the United States Data Center Processor Market face?
The United States Data Center Processor Market faces challenges such as the high cost of advanced processors, the rapid pace of technological change, and increasing competition among manufacturers. These factors can impact profitability and market share for companies operating in this space.
What opportunities exist in the United States Data Center Processor Market?
Opportunities in the United States Data Center Processor Market include the growing adoption of edge computing, advancements in processor technology, and the increasing focus on energy-efficient solutions. These trends present avenues for innovation and market expansion.
What trends are shaping the United States Data Center Processor Market?
Trends shaping the United States Data Center Processor Market include the shift towards multi-core processors, the integration of AI capabilities, and the emphasis on sustainability in data center operations. These trends are influencing product development and consumer preferences.
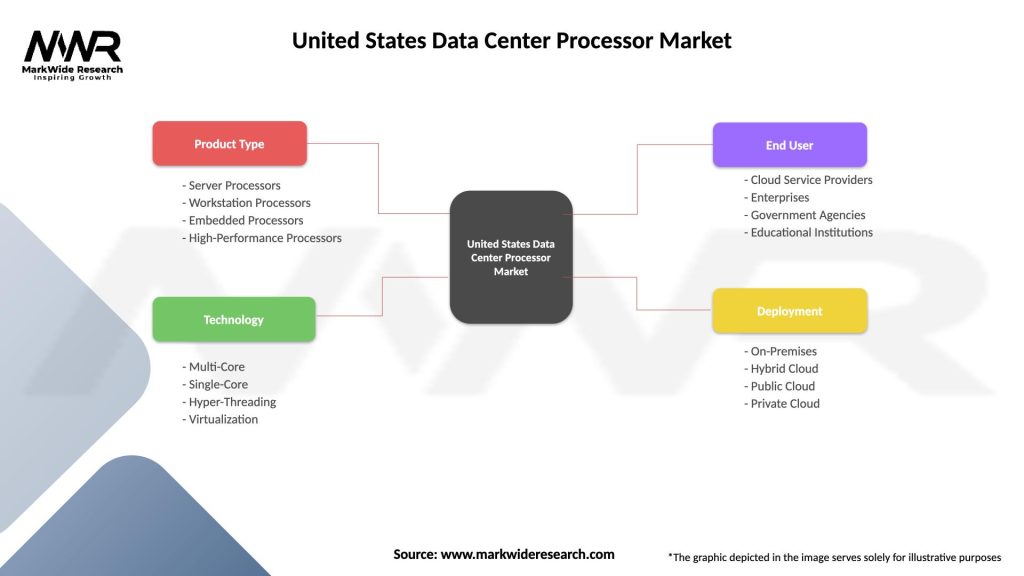
United States Data Center Processor Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Server Processors, Workstation Processors, Embedded Processors, High-Performance Processors |
| Technology | Multi-Core, Single-Core, Hyper-Threading, Virtualization |
| End User | Cloud Service Providers, Enterprises, Government Agencies, Educational Institutions |
| Deployment | On-Premises, Hybrid Cloud, Public Cloud, Private Cloud |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the United States Data Center Processor Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at