444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
The Oman EV market represents a transformative shift in the Sultanate’s transportation landscape, driven by ambitious sustainability goals and government initiatives toward carbon neutrality. Electric vehicle adoption in Oman has gained significant momentum as the country diversifies its economy beyond oil dependency and embraces clean energy solutions. The market encompasses passenger cars, commercial vehicles, two-wheelers, and public transportation systems, all contributing to a comprehensive electrification strategy.
Government support through Oman Vision 2040 has established a robust framework for EV infrastructure development, including charging networks and regulatory incentives. The market demonstrates strong growth potential with annual growth rates exceeding 25% as consumer awareness increases and charging infrastructure expands across major cities. Strategic partnerships between international automotive manufacturers and local distributors have accelerated market penetration, while falling battery costs make electric vehicles increasingly competitive with traditional internal combustion engine vehicles.
Infrastructure development remains a critical focus area, with public and private sector investments in charging stations, grid modernization, and renewable energy integration. The market benefits from Oman’s commitment to generating 30% of electricity from renewable sources by 2030, creating a sustainable ecosystem for electric vehicle adoption. Urban planning initiatives in Muscat and other major cities increasingly incorporate EV-friendly infrastructure, supporting the transition toward sustainable mobility solutions.
The Oman EV market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of electric vehicles, charging infrastructure, supporting services, and regulatory frameworks within the Sultanate of Oman. This market encompasses all battery-electric vehicles, plug-in hybrid electric vehicles, and related technologies designed to reduce transportation emissions and support sustainable mobility goals.
Market participants include automotive manufacturers, battery suppliers, charging infrastructure providers, energy companies, government agencies, and end-users ranging from individual consumers to commercial fleet operators. The market extends beyond vehicle sales to include charging services, maintenance, battery recycling, and grid integration technologies that support the broader electrification ecosystem.
Economic significance of the Oman EV market lies in its potential to reduce fuel import dependency, create new employment opportunities, and position the country as a regional leader in sustainable transportation. The market represents a strategic shift toward economic diversification while supporting environmental sustainability objectives outlined in national development plans.
Market dynamics in Oman’s electric vehicle sector reflect a rapidly evolving landscape characterized by strong government support, increasing consumer acceptance, and expanding infrastructure capabilities. The market has experienced accelerated growth driven by policy incentives, environmental awareness, and improving technology accessibility. Key growth drivers include government mandates for public sector vehicle electrification, tax incentives for EV purchases, and strategic investments in charging infrastructure development.
Competitive landscape features a mix of established international automotive brands and emerging electric vehicle manufacturers, each competing to establish market presence through local partnerships and tailored product offerings. The market benefits from reduced import duties on electric vehicles, making them more price-competitive with conventional vehicles. Infrastructure expansion has reached critical mass in urban areas, with charging station availability increasing by over 40% annually across major population centers.
Future prospects indicate sustained growth momentum supported by continued government investment, private sector participation, and evolving consumer preferences toward sustainable transportation options. The market is positioned to benefit from regional cooperation initiatives and technology transfer programs that enhance local capabilities in electric vehicle manufacturing and maintenance services.
Strategic insights reveal several critical factors shaping the Oman EV market’s development trajectory and competitive dynamics:
Environmental sustainability serves as the primary driver for Oman’s electric vehicle market development, aligning with national commitments to reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change. The government’s pledge to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050 creates strong policy momentum for transportation electrification across all sectors. Air quality improvement in urban areas provides additional motivation for EV adoption, particularly in densely populated cities where vehicle emissions contribute significantly to pollution levels.
Economic diversification objectives drive government support for electric vehicle market development as part of broader efforts to reduce oil dependency and create new economic sectors. The transition toward electric mobility supports job creation in manufacturing, maintenance, and technology services while reducing fuel import requirements. Energy security considerations favor electric vehicles powered by domestic renewable energy sources over imported petroleum products.
Technological advancement in battery technology, charging infrastructure, and vehicle performance has reached a tipping point where electric vehicles offer compelling value propositions compared to conventional alternatives. Falling battery costs and improving energy density make electric vehicles increasingly affordable and practical for Omani consumers. Digital integration features in modern electric vehicles align with growing consumer demand for connected mobility solutions and smart city initiatives.
Infrastructure limitations continue to present challenges for widespread electric vehicle adoption, particularly in rural and remote areas where charging station density remains insufficient. The current charging network, while expanding rapidly, requires further development to support long-distance travel and provide convenient charging options for all user segments. Grid capacity constraints in some regions may limit the ability to support large-scale electric vehicle charging without significant electrical infrastructure upgrades.
Initial purchase costs for electric vehicles remain higher than comparable conventional vehicles, despite government incentives and falling battery prices. This cost differential particularly affects price-sensitive consumer segments and may slow adoption rates among middle-income households. Financing challenges for electric vehicle purchases persist due to limited specialized lending products and uncertainty about residual values in the secondary market.
Consumer awareness and education gaps continue to influence purchase decisions, with concerns about battery life, maintenance costs, and charging convenience affecting market acceptance. Limited local service capabilities for electric vehicle maintenance and repair create additional barriers to adoption. Range anxiety remains a psychological barrier despite improving battery technology and expanding charging infrastructure coverage.
Tourism sector electrification presents significant opportunities for electric vehicle market expansion, with eco-tourism initiatives and sustainable travel programs driving demand for clean transportation options. The development of electric vehicle rental services and tour operators using electric fleets can showcase technology benefits while serving growing environmental tourism segments. Hotel and resort partnerships for charging infrastructure installation create additional market development opportunities.
Commercial fleet conversion offers substantial market potential as businesses seek to reduce operational costs and enhance sustainability credentials. Delivery services, taxi operators, and corporate fleets represent high-volume adoption opportunities that can drive economies of scale and infrastructure development. Last-mile delivery electrification particularly benefits from electric vehicle cost advantages in urban environments with frequent stop-and-go driving patterns.
Manufacturing and assembly opportunities emerge as market volumes reach levels that justify local production capabilities. Strategic partnerships with international manufacturers can establish assembly operations, creating employment and reducing import dependency. Battery recycling and second-life applications for electric vehicle batteries present emerging business opportunities as the installed base grows and batteries reach end-of-life stages.
Supply chain evolution in the Oman EV market reflects global trends toward localization and resilience, with increasing emphasis on regional sourcing and assembly capabilities. International automotive manufacturers are establishing partnerships with local distributors and service providers to create comprehensive support networks for electric vehicle customers. Technology transfer initiatives enable local companies to develop capabilities in electric vehicle maintenance, charging infrastructure installation, and battery management systems.
Regulatory framework development continues to shape market dynamics through evolving standards for vehicle safety, charging infrastructure, and grid integration. The government’s proactive approach to establishing clear regulations and incentive structures provides market certainty that encourages private sector investment. Standards harmonization with regional and international frameworks facilitates technology adoption and cross-border compatibility.
Market competition intensifies as more manufacturers enter the Omani market with diverse product offerings targeting different consumer segments and use cases. Price competition and feature differentiation drive innovation while improving value propositions for consumers. Service competition extends beyond vehicle sales to include charging services, maintenance programs, and integrated mobility solutions that enhance customer experience and loyalty.
Primary research methodologies employed in analyzing the Oman EV market include comprehensive surveys of consumers, automotive dealers, fleet operators, and government officials to understand adoption patterns, preferences, and barriers. In-depth interviews with industry stakeholders provide qualitative insights into market dynamics, competitive strategies, and future development plans. Focus group discussions with potential electric vehicle buyers reveal consumer attitudes, concerns, and decision-making factors that influence purchase behavior.
Secondary research encompasses analysis of government publications, industry reports, automotive registration data, and charging infrastructure deployment statistics to establish market baselines and trend analysis. International benchmarking studies compare Oman’s electric vehicle market development with similar economies and regional markets. Data triangulation methods ensure accuracy and reliability by cross-referencing multiple information sources and validation techniques.
Market modeling approaches utilize statistical analysis, scenario planning, and forecasting methodologies to project market development trajectories under different policy and economic conditions. Quantitative analysis of adoption curves, infrastructure deployment rates, and cost trends provides foundation for market projections. Stakeholder validation processes ensure research findings accurately reflect market realities and stakeholder perspectives through expert review and feedback incorporation.
Muscat Governorate leads the Oman EV market with approximately 60% of total electric vehicle registrations, driven by higher income levels, better charging infrastructure, and greater environmental awareness among urban consumers. The capital region benefits from concentrated government initiatives, including public sector fleet electrification and demonstration projects that showcase electric vehicle capabilities. Infrastructure density in Muscat significantly exceeds other regions, with charging stations available in major shopping centers, government buildings, and residential complexes.
Dhofar Governorate represents the second-largest regional market, accounting for approximately 15% of electric vehicle adoption, supported by tourism sector initiatives and government facility electrification in Salalah. The region’s focus on sustainable tourism creates opportunities for electric vehicle rental services and eco-friendly transportation options. Renewable energy projects in Dhofar provide clean electricity sources that enhance the environmental benefits of electric vehicle adoption.
Northern governorates including Al Batinah North and South show growing electric vehicle interest, particularly in industrial and commercial applications where operational cost savings provide compelling business cases. These regions benefit from proximity to Muscat’s infrastructure and service networks while developing local charging capabilities. Industrial zone electrification initiatives in these areas support commercial vehicle adoption and fleet conversion programs.
Market leadership in Oman’s electric vehicle sector features a diverse mix of established automotive brands and emerging electric vehicle specialists, each pursuing distinct strategies to capture market share and establish customer loyalty:
By Vehicle Type: The Oman EV market segmentation reveals distinct patterns across different vehicle categories, with passenger cars dominating current adoption while commercial vehicles show strong growth potential.
By Technology: Battery electric vehicles dominate the market while plug-in hybrids serve as transitional technology for consumers concerned about range limitations.
Luxury segment electric vehicles demonstrate strong performance in Oman’s market, with premium brands capturing significant market share among high-income consumers who value advanced technology and environmental responsibility. These vehicles typically feature cutting-edge battery technology, autonomous driving capabilities, and premium interior appointments that justify higher price points. Brand prestige plays a crucial role in luxury electric vehicle adoption, with consumers viewing these purchases as statements of environmental consciousness and technological sophistication.
Mid-market segment represents the largest growth opportunity, with mainstream automotive brands introducing competitively priced electric vehicles that offer practical range, reasonable charging times, and comprehensive warranty coverage. These vehicles target middle-income families and professionals seeking reliable, efficient transportation with lower operating costs than conventional vehicles. Value proposition emphasis on total cost of ownership helps overcome initial price premiums through fuel savings and maintenance benefits.
Commercial segment adoption accelerates as businesses recognize operational advantages of electric vehicles in urban delivery, taxi services, and corporate fleet applications. Electric commercial vehicles offer significant fuel cost savings, reduced maintenance requirements, and enhanced corporate sustainability credentials. Fleet operators particularly benefit from centralized charging infrastructure and predictable route patterns that maximize electric vehicle advantages while minimizing range limitations.
Automotive manufacturers benefit from entering the Oman EV market through access to a growing customer base with strong government support and favorable regulatory environment. Early market entry provides competitive advantages through brand establishment and dealer network development before market saturation occurs. Technology differentiation opportunities allow manufacturers to showcase advanced electric vehicle capabilities and build customer loyalty through superior performance and service.
Energy companies gain new revenue streams through charging infrastructure development, electricity sales, and grid services that support electric vehicle integration. The transition to electric mobility creates opportunities for renewable energy project development and smart grid technologies that optimize energy distribution. Strategic partnerships with automotive manufacturers and charging network operators enable energy companies to participate in the complete electric mobility ecosystem.
Government stakeholders achieve multiple policy objectives through electric vehicle market development, including emission reduction, energy security improvement, and economic diversification. Electric vehicle adoption supports job creation in new technology sectors while reducing fuel import dependency and improving air quality. International cooperation opportunities emerge through electric vehicle initiatives that demonstrate environmental leadership and attract sustainable investment.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Charging infrastructure evolution represents a critical trend shaping the Oman EV market, with rapid deployment of fast-charging stations along major highways and strategic locations. Ultra-fast charging technology adoption reduces charging times significantly, addressing consumer concerns about convenience and travel flexibility. Smart charging systems integrate with renewable energy sources and grid management systems to optimize electricity usage and reduce operational costs for both operators and users.
Fleet electrification acceleration drives market volume growth as government agencies and private companies commit to electric vehicle adoption for operational and sustainability benefits. Large-scale fleet conversions create economies of scale that reduce costs and improve service infrastructure availability. Corporate sustainability initiatives increasingly include transportation electrification as companies seek to reduce carbon footprints and enhance environmental credentials.
Technology integration trends include advanced driver assistance systems, over-the-air software updates, and connected vehicle services that enhance electric vehicle value propositions beyond basic transportation. MarkWide Research analysis indicates growing consumer demand for integrated mobility solutions that combine vehicle ownership with charging services, maintenance programs, and digital connectivity features.
Strategic partnerships between international automotive manufacturers and local distributors have accelerated market entry and service network development across Oman. These collaborations enable technology transfer, local assembly capabilities, and comprehensive customer support systems that enhance electric vehicle adoption rates. Joint ventures for charging infrastructure development create integrated solutions that address range anxiety and improve customer experience.
Government initiatives include the launch of comprehensive electric vehicle adoption programs for public sector fleets, demonstration projects in major cities, and incentive programs that reduce total cost of ownership for consumers. New regulations establish safety standards, charging infrastructure requirements, and grid integration protocols that support market development. Public-private partnerships facilitate infrastructure investment and technology deployment across the country.
Technology advancements in battery chemistry, charging systems, and vehicle efficiency continue to improve electric vehicle performance while reducing costs. Local service capabilities expand through training programs and certification initiatives that ensure adequate maintenance and repair support for growing electric vehicle populations. Innovation centers and research partnerships with international institutions support local capability development in electric mobility technologies.
Infrastructure acceleration should remain the top priority for sustained market growth, with coordinated investment in charging networks that serve both urban and rural areas effectively. Standardization of charging protocols and payment systems will improve user experience and reduce barriers to adoption. Grid integration planning must anticipate future electric vehicle loads and incorporate smart charging capabilities that optimize electricity distribution and renewable energy utilization.
Consumer education programs should address persistent concerns about electric vehicle ownership, including battery life, maintenance costs, and charging convenience. Demonstration programs and test drive opportunities can effectively showcase electric vehicle benefits and address misconceptions. Financing innovation through specialized lending products and leasing options can improve affordability and accelerate adoption among price-sensitive consumer segments.
Local capability development through training programs, certification initiatives, and technology transfer partnerships will ensure sustainable market growth and reduce dependency on imported expertise. MWR recommends establishing centers of excellence for electric vehicle technology that can serve regional markets and attract international investment in research and development activities.
Market trajectory for Oman’s electric vehicle sector indicates sustained growth momentum supported by continued government commitment, improving technology economics, and expanding infrastructure capabilities. The market is positioned to achieve significant penetration rates exceeding 15% of new vehicle sales within the next five years as charging infrastructure reaches critical mass and consumer acceptance increases. Technology maturation will continue reducing costs while improving performance, making electric vehicles increasingly competitive with conventional alternatives.
Infrastructure development will accelerate through public-private partnerships and regional cooperation initiatives that create comprehensive charging networks supporting both domestic and cross-border travel. Smart grid integration and renewable energy expansion will enhance the environmental benefits of electric vehicle adoption while reducing operational costs. Manufacturing opportunities may emerge as market volumes justify local assembly operations and component production capabilities.
Regional integration trends suggest Oman’s electric vehicle market will benefit from GCC coordination on standards, infrastructure, and policy frameworks that facilitate seamless electric mobility across borders. MarkWide Research projects that successful market development in Oman will position the country as a regional leader in sustainable transportation and attract additional investment in clean technology sectors. The market’s evolution will contribute significantly to national economic diversification objectives while supporting environmental sustainability goals.
Oman’s electric vehicle market represents a strategic opportunity for sustainable transportation development supported by strong government commitment, favorable policy frameworks, and growing consumer acceptance. The market has demonstrated resilience and growth potential despite initial challenges related to infrastructure limitations and cost considerations. Government leadership through Vision 2040 initiatives and public sector adoption creates a solid foundation for continued market expansion and private sector investment.
Future success will depend on continued infrastructure development, consumer education, and technology advancement that addresses remaining barriers to widespread adoption. The market benefits from global trends toward electric mobility while leveraging Oman’s strategic advantages in renewable energy and regional connectivity. Stakeholder collaboration between government, industry, and consumers will be essential for realizing the full potential of electric vehicle adoption in supporting economic diversification and environmental sustainability objectives.
What is EV?
EV stands for electric vehicle, which is a type of vehicle that is powered by one or more electric motors, using energy typically stored in rechargeable batteries. In the context of the Oman EV Market, these vehicles are gaining traction due to environmental concerns and government initiatives promoting sustainable transportation.
What are the key players in the Oman EV Market?
Key players in the Oman EV Market include companies like Tesla, Nissan, and BMW, which are known for their electric vehicle offerings. Additionally, local companies are also emerging to support the growing demand for EVs in the region, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the Oman EV Market?
The Oman EV Market is driven by factors such as increasing environmental awareness, government incentives for electric vehicle adoption, and advancements in battery technology. Additionally, the rising cost of fossil fuels is encouraging consumers to consider electric alternatives.
What challenges does the Oman EV Market face?
The Oman EV Market faces challenges such as limited charging infrastructure, high initial costs of electric vehicles, and consumer skepticism regarding battery life and performance. These factors can hinder the widespread adoption of EVs in the region.
What opportunities exist in the Oman EV Market?
The Oman EV Market presents opportunities for growth in areas such as renewable energy integration for charging stations, development of local manufacturing capabilities, and partnerships with technology firms for smart mobility solutions. These opportunities can enhance the overall EV ecosystem in Oman.
What trends are shaping the Oman EV Market?
Trends in the Oman EV Market include the increasing popularity of hybrid vehicles, advancements in autonomous driving technology, and a shift towards sustainable urban mobility solutions. These trends are influencing consumer preferences and shaping the future of transportation in Oman.
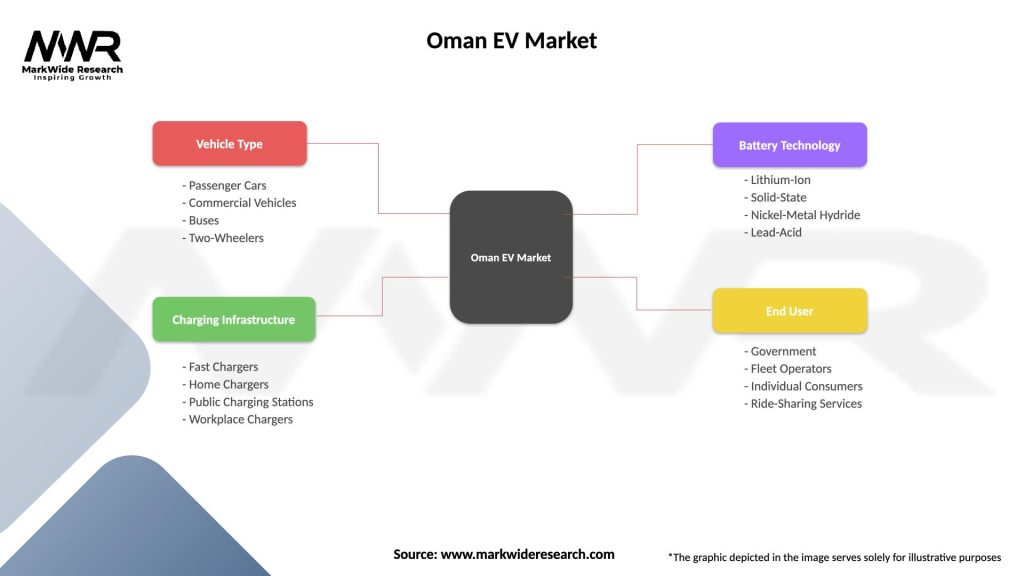
Oman EV Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Vehicle Type | Passenger Cars, Commercial Vehicles, Buses, Two-Wheelers |
| Charging Infrastructure | Fast Chargers, Home Chargers, Public Charging Stations, Workplace Chargers |
| Battery Technology | Lithium-Ion, Solid-State, Nickel-Metal Hydride, Lead-Acid |
| End User | Government, Fleet Operators, Individual Consumers, Ride-Sharing Services |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the Oman EV Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at