444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2150
The India plastic waste management market represents a critical sector addressing one of the nation’s most pressing environmental challenges. With India generating over 3.3 million tonnes of plastic waste annually, the country faces an urgent need for comprehensive waste management solutions. The market encompasses various technologies and services including collection, segregation, recycling, and disposal of plastic waste materials across urban and rural areas.
Market dynamics indicate substantial growth potential driven by stringent government regulations, increasing environmental awareness, and technological advancements in recycling processes. The sector experiences significant momentum from the Plastic Waste Management Rules 2016 and subsequent amendments, which mandate extended producer responsibility and promote circular economy principles. Growth rates in the recycling segment demonstrate particularly strong performance, with mechanical recycling achieving 65% market penetration across organized waste management facilities.
Regional distribution shows concentrated activity in major metropolitan areas including Delhi, Mumbai, Bangalore, and Chennai, where infrastructure development and regulatory enforcement drive market expansion. The market benefits from increasing private sector participation, government initiatives promoting waste-to-energy projects, and growing consumer consciousness regarding sustainable packaging solutions.
The India plastic waste management market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of services, technologies, and infrastructure dedicated to collecting, processing, recycling, and disposing of plastic waste materials across the Indian subcontinent. This market encompasses various stakeholders including waste collection agencies, recycling facilities, technology providers, and regulatory bodies working collaboratively to address plastic pollution challenges.
Plastic waste management involves multiple stages from source segregation to final disposal or recycling, incorporating both formal and informal sector participants. The market includes mechanical recycling, chemical recycling, waste-to-energy conversion, and innovative technologies for plastic waste processing. Extended producer responsibility frameworks mandate manufacturers to take accountability for their plastic packaging throughout its lifecycle, creating structured market opportunities for waste management service providers.
Market scope extends beyond traditional waste collection to include advanced sorting technologies, plastic-to-fuel conversion systems, and circular economy initiatives that transform waste into valuable resources. The sector addresses various plastic categories including PET bottles, polyethylene bags, polystyrene packaging, and multi-layered packaging materials requiring specialized processing techniques.
India’s plastic waste management market demonstrates robust growth trajectory supported by regulatory mandates, technological innovation, and increasing environmental consciousness. The market addresses the challenge of managing substantial plastic waste generation while creating economic opportunities through recycling and resource recovery initiatives. Government policies including the Plastic Waste Management Rules and Single Use Plastic ban drive market transformation toward sustainable waste management practices.
Key market segments include collection and transportation services, mechanical recycling facilities, chemical recycling technologies, and waste-to-energy conversion systems. The organized sector experiences rapid expansion with 45% growth rate in formal waste management infrastructure development. Technology adoption accelerates across sorting facilities, with automated systems achieving 78% efficiency improvement compared to manual processes.
Market opportunities emerge from increasing urbanization, rising disposable income, and growing packaging consumption across retail and e-commerce sectors. The sector benefits from international collaboration, technology transfer agreements, and sustainable financing mechanisms supporting infrastructure development. Future prospects indicate continued expansion driven by circular economy initiatives and innovative recycling technologies.
Strategic insights reveal significant transformation occurring within India’s plastic waste management landscape, driven by regulatory compliance requirements and environmental sustainability goals. The market demonstrates increasing sophistication in waste processing technologies and growing integration between formal and informal sector participants.
Regulatory frameworks serve as primary market drivers, with the Plastic Waste Management Rules 2016 and subsequent amendments establishing mandatory compliance requirements for plastic waste generators and processors. These regulations create structured demand for waste management services while promoting extended producer responsibility principles across manufacturing sectors.
Environmental awareness among consumers and businesses drives demand for sustainable waste management solutions. Growing consciousness regarding plastic pollution impacts motivates organizations to adopt responsible waste management practices and invest in recycling infrastructure. Corporate sustainability initiatives increasingly include plastic waste reduction and recycling targets, creating market opportunities for service providers.
Urbanization trends contribute significantly to market growth, with expanding urban populations generating increased plastic waste volumes requiring systematic management approaches. Economic development and rising disposable incomes lead to higher packaging consumption, particularly in retail and e-commerce sectors, necessitating robust waste management infrastructure.
Technology advancement enables improved waste processing efficiency and cost-effectiveness, making recycling operations more economically viable. Government initiatives including Swachh Bharat Mission and Smart Cities programs provide policy support and funding mechanisms for waste management infrastructure development across Indian cities.
Infrastructure limitations pose significant challenges to market expansion, particularly in smaller cities and rural areas where waste collection and processing facilities remain inadequate. Capital requirements for establishing modern recycling facilities and waste processing technologies create barriers for smaller operators seeking market entry.
Informal sector dominance in waste collection and recycling activities creates market fragmentation and limits the adoption of standardized processes and technologies. Quality concerns regarding recycled plastic materials affect market acceptance and pricing, particularly for applications requiring high-quality specifications.
Technological challenges in processing multi-layered packaging and contaminated plastic waste limit recycling efficiency and economic viability. Market awareness gaps among consumers and businesses regarding proper waste segregation practices reduce the quality of collected materials and increase processing costs.
Regulatory enforcement inconsistencies across different states and municipalities create compliance uncertainties for market participants. Economic viability concerns arise from fluctuating prices of recycled materials and competition from virgin plastic materials, affecting the sustainability of recycling operations.
Circular economy initiatives present substantial opportunities for developing innovative plastic waste management solutions that transform waste into valuable resources. Technology partnerships with international companies enable access to advanced recycling technologies and best practices for market development.
Government support through policy frameworks, financial incentives, and infrastructure development programs creates favorable conditions for market expansion. Extended producer responsibility mandates generate consistent demand for waste management services while providing revenue streams for compliant operators.
Innovation opportunities exist in developing indigenous technologies for plastic waste processing, including chemical recycling, plastic-to-fuel conversion, and biodegradable plastic alternatives. Digital transformation enables improved waste tracking, collection optimization, and stakeholder coordination through technology platforms.
Market consolidation opportunities allow organized players to acquire informal sector operations and integrate them into formal waste management systems. Export potential for recycled plastic materials and waste-derived products creates additional revenue streams for efficient operators. Public-private partnerships facilitate infrastructure development and technology deployment across urban waste management systems.
Supply-demand dynamics in India’s plastic waste management market reflect the growing gap between waste generation and processing capacity. Demand drivers include regulatory compliance requirements, corporate sustainability commitments, and increasing environmental consciousness among consumers and businesses.
Supply constraints emerge from limited processing infrastructure, technology gaps, and fragmented collection networks. Market equilibrium requires substantial investment in infrastructure development and technology adoption to match growing waste generation volumes. Price dynamics fluctuate based on virgin plastic prices, recycled material quality, and regulatory enforcement levels.
Competitive dynamics involve both organized and unorganized sector participants, with increasing consolidation toward formal operations. Technology adoption rates accelerate as operators seek efficiency improvements and regulatory compliance. MarkWide Research analysis indicates that automated sorting systems achieve 85% material recovery efficiency compared to 45% efficiency in manual operations.
Market integration between collection, processing, and end-user segments improves overall system efficiency and economic viability. Stakeholder collaboration increases across government agencies, private companies, and community organizations to address complex waste management challenges.
Research approach for analyzing India’s plastic waste management market employs comprehensive primary and secondary research methodologies to ensure accurate market assessment and trend identification. Primary research involves extensive interviews with industry stakeholders including waste management companies, recycling facility operators, government officials, and technology providers.
Secondary research encompasses analysis of government publications, industry reports, regulatory documents, and academic studies related to plastic waste management in India. Data collection methods include structured surveys, expert interviews, and field visits to waste processing facilities across major Indian cities.
Market sizing methodology incorporates waste generation data, processing capacity analysis, and regulatory compliance requirements to assess market scope and growth potential. Trend analysis examines historical data patterns, current market developments, and future projections based on regulatory changes and technology adoption rates.
Validation processes include cross-referencing multiple data sources, expert opinion verification, and statistical analysis to ensure research accuracy and reliability. Regional analysis covers major metropolitan areas, tier-2 cities, and rural regions to provide comprehensive market coverage and insights.
Northern India demonstrates significant market activity concentrated in Delhi NCR, with 25% market share in organized waste management operations. The region benefits from strong regulatory enforcement, government initiatives, and proximity to major manufacturing centers. Infrastructure development includes multiple waste-to-energy plants and advanced recycling facilities serving the Delhi metropolitan area.
Western India leads market development with Maharashtra and Gujarat accounting for 35% regional market share. Mumbai and Pune serve as major hubs for plastic waste processing, supported by industrial infrastructure and port connectivity for material exports. Technology adoption rates remain highest in this region, with several international technology partnerships established.
Southern India shows robust growth in Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, and Telangana, representing 30% market concentration. Bangalore and Chennai emerge as innovation centers for waste management technologies and startup ecosystem development. Government support through state-level policies and incentives drives market expansion across the region.
Eastern India experiences gradual market development with West Bengal leading regional initiatives. Infrastructure challenges limit growth potential, though government programs increasingly focus on waste management system improvements. Market opportunities exist for organized players to establish operations in underserved areas with growing urban populations.
Market competition involves diverse participants ranging from large integrated waste management companies to specialized recycling technology providers. Organized sector players increasingly dominate market share through superior infrastructure, technology capabilities, and regulatory compliance.
Competitive strategies include technology innovation, capacity expansion, strategic partnerships, and geographic diversification. Market consolidation trends favor companies with strong financial capabilities and regulatory compliance expertise.
By Technology:
By Application:
By End-User:
PET Bottle Recycling represents the most developed segment with established collection networks and processing infrastructure. Market maturity in this category enables consistent material supply and quality standards meeting industry requirements. Value chain integration from collection to end-product manufacturing creates economic viability for operators.
Flexible Packaging Waste presents significant challenges due to multi-layered construction and contamination issues. Technology development focuses on advanced sorting and cleaning processes to improve material recovery rates. Innovation opportunities exist for developing specialized processing equipment and chemical recycling solutions.
Single-Use Plastics management gains priority following government bans and restrictions on specific items. Alternative material development and biodegradable substitutes create market opportunities for sustainable packaging solutions. Compliance requirements drive businesses to adopt responsible waste management practices and circular economy principles.
Industrial Plastic Waste offers consistent material supply and quality characteristics suitable for recycling operations. Partnership opportunities with manufacturing companies enable direct waste collection and processing arrangements. Quality standards for recycled materials meet industrial application requirements, supporting market growth.
Waste Management Companies benefit from growing market demand, regulatory support, and technology advancement opportunities. Revenue diversification through multiple service offerings including collection, processing, and consulting services enhances business sustainability. Government contracts and extended producer responsibility mandates provide stable income streams.
Manufacturing Companies achieve regulatory compliance, sustainability goals, and cost optimization through efficient waste management partnerships. Brand reputation enhancement results from demonstrated environmental responsibility and circular economy participation. Resource efficiency improvements reduce raw material costs through recycled content utilization.
Government Agencies accomplish environmental protection objectives, regulatory enforcement, and public health improvements through effective waste management systems. Economic development benefits include job creation, technology transfer, and infrastructure development across urban and rural areas.
Technology Providers access growing market opportunities for innovative waste processing solutions and equipment supply. Partnership potential with local companies enables technology transfer and market penetration strategies. Research collaboration with academic institutions and government agencies supports technology development and validation.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Circular Economy Integration emerges as a dominant trend with companies adopting closed-loop systems for plastic waste management. Extended producer responsibility implementation drives systematic waste collection and processing infrastructure development across manufacturing sectors.
Technology Digitization transforms waste management operations through IoT sensors, GPS tracking, and data analytics platforms. Smart waste management systems optimize collection routes, monitor bin levels, and improve operational efficiency. Blockchain technology enables transparent waste tracking and compliance verification for regulatory requirements.
Chemical Recycling Advancement gains momentum as a solution for processing complex plastic waste streams unsuitable for mechanical recycling. Pyrolysis and depolymerization technologies convert mixed plastic waste into valuable chemicals and fuels, expanding recycling possibilities.
Public-Private Partnerships increase across urban waste management systems, combining government policy support with private sector efficiency and innovation. Startup ecosystem development focuses on innovative waste management solutions, alternative materials, and technology platforms. MWR analysis indicates that startup investments in waste management technologies grew by 120% over the past two years.
Regulatory Milestones include the implementation of Plastic Waste Management Rules amendments and Single Use Plastic bans affecting market dynamics. Extended producer responsibility guidelines establish clear compliance frameworks for plastic packaging manufacturers and importers.
Infrastructure Investments accelerate with multiple waste-to-energy plants and advanced recycling facilities commissioned across major cities. Technology partnerships between Indian companies and international technology providers enable knowledge transfer and capacity building.
Corporate Initiatives expand as major brands commit to plastic waste reduction and recycling targets. Sustainability programs include packaging redesign, alternative material adoption, and waste collection infrastructure support. Industry collaborations promote best practices sharing and technology development across waste management sectors.
Innovation Developments include indigenous technology solutions for plastic waste processing and value-added product manufacturing. Research partnerships between industry and academic institutions focus on developing cost-effective recycling technologies suitable for Indian conditions.
Strategic Recommendations for market participants include investing in technology upgrades, expanding geographic coverage, and developing integrated service offerings. Operational excellence through process optimization, quality improvement, and cost reduction enhances competitive positioning in the growing market.
Partnership Development with government agencies, manufacturing companies, and technology providers creates synergistic opportunities for market expansion. Compliance focus ensures regulatory adherence while building credibility with customers and stakeholders.
Innovation Investment in research and development enables differentiation through advanced technologies and specialized solutions. Market diversification across different plastic waste categories and end-user segments reduces business risks and enhances growth potential.
Capacity Building through workforce training, technology adoption, and infrastructure development supports sustainable business growth. Financial planning for capital investments and working capital requirements ensures adequate resources for market expansion initiatives.
Market trajectory indicates continued expansion driven by regulatory enforcement, technology advancement, and increasing environmental consciousness. Growth projections suggest sustained momentum with 12-15% annual growth in organized sector operations over the next five years.
Technology evolution will focus on chemical recycling, artificial intelligence integration, and automated processing systems improving efficiency and material recovery rates. Market consolidation trends favor organized players with superior infrastructure and compliance capabilities.
Policy developments will likely include stricter enforcement mechanisms, expanded producer responsibility mandates, and incentives for circular economy initiatives. International cooperation in technology transfer and best practices sharing will accelerate market development.
Investment flows into waste management infrastructure and technology development will support market expansion across tier-2 and tier-3 cities. MarkWide Research projections indicate that organized sector participation will reach 70% market share by 2028, compared to current levels of approximately 40%.
India’s plastic waste management market represents a critical sector addressing environmental challenges while creating substantial economic opportunities. The market demonstrates strong growth potential driven by regulatory mandates, technology advancement, and increasing stakeholder awareness regarding sustainable waste management practices.
Key success factors include regulatory compliance, technology adoption, infrastructure development, and stakeholder collaboration across the waste management value chain. Market transformation from informal to organized operations creates opportunities for efficient service providers and technology companies.
Future prospects remain positive with continued government support, corporate sustainability commitments, and innovation in recycling technologies. Strategic positioning through operational excellence, technology integration, and partnership development will determine market leadership in this evolving sector. The market’s evolution toward circular economy principles and sustainable waste management practices positions it as a vital component of India’s environmental protection and economic development strategies.
What is Plastic Waste Management?
Plastic Waste Management refers to the processes involved in the collection, recycling, and disposal of plastic waste to minimize its impact on the environment. This includes various strategies such as waste segregation, recycling technologies, and public awareness initiatives.
What are the key players in the India Plastic Waste Management Market?
Key players in the India Plastic Waste Management Market include companies like Ramky Enviro Engineers, EcoWise, and Suez, which are involved in waste collection, recycling, and environmental services, among others.
What are the main drivers of the India Plastic Waste Management Market?
The main drivers of the India Plastic Waste Management Market include increasing environmental awareness, government regulations promoting recycling, and the growing demand for sustainable packaging solutions across various industries.
What challenges does the India Plastic Waste Management Market face?
Challenges in the India Plastic Waste Management Market include inadequate infrastructure for waste collection and processing, public resistance to recycling initiatives, and the high costs associated with advanced recycling technologies.
What opportunities exist in the India Plastic Waste Management Market?
Opportunities in the India Plastic Waste Management Market include the development of innovative recycling technologies, partnerships between public and private sectors, and the increasing investment in sustainable waste management practices.
What trends are shaping the India Plastic Waste Management Market?
Trends shaping the India Plastic Waste Management Market include the rise of circular economy practices, increased use of biodegradable plastics, and the implementation of stricter regulations on plastic waste disposal.
India Plastic Waste Management Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
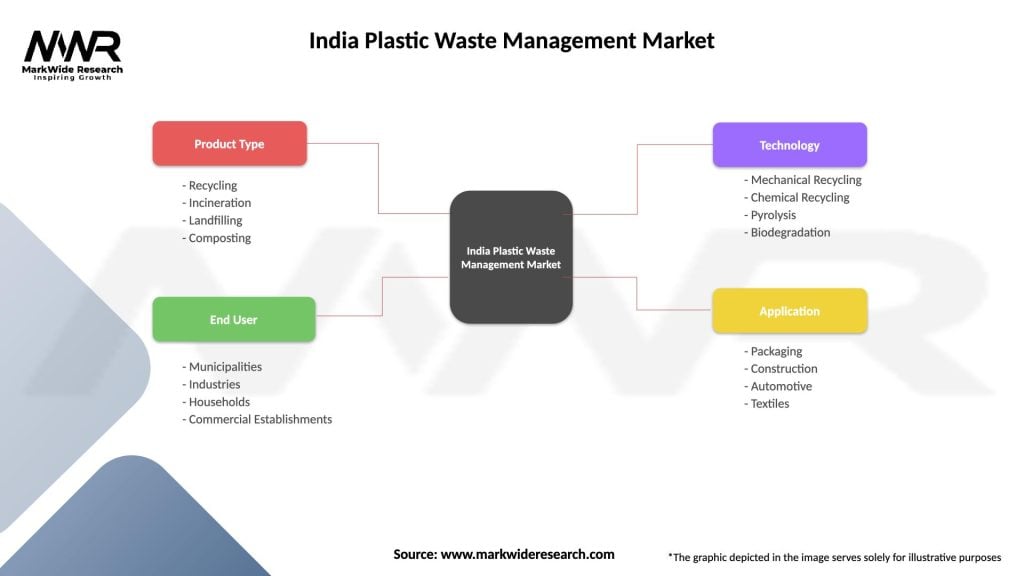
| Product Type | Recycling, Incineration, Landfilling, Composting |
| End User | Municipalities, Industries, Households, Commercial Establishments |
| Technology | Mechanical Recycling, Chemical Recycling, Pyrolysis, Biodegradation |
| Application | Packaging, Construction, Automotive, Textiles |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the India Plastic Waste Management Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at