444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2750
The Middle East cybersecurity market represents one of the fastest-growing technology sectors in the region, driven by increasing digital transformation initiatives and escalating cyber threats. Regional governments and private enterprises are investing heavily in advanced security solutions to protect critical infrastructure, financial systems, and sensitive data. The market encompasses a comprehensive range of security technologies including network security, endpoint protection, cloud security, and identity management solutions.
Digital transformation across various industries has accelerated the adoption of cybersecurity solutions throughout the Middle East. Countries like the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Qatar are leading the charge with ambitious smart city projects and digital government initiatives that require robust security frameworks. The market is experiencing significant growth with organizations recognizing cybersecurity as a strategic business imperative rather than merely a technical requirement.
Government initiatives and regulatory frameworks are playing a crucial role in shaping the cybersecurity landscape. The region’s commitment to becoming a global technology hub has intensified focus on cybersecurity capabilities, with substantial investments in both public and private sector security infrastructure. Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and blockchain are being integrated into cybersecurity solutions to enhance threat detection and response capabilities.
The Middle East cybersecurity market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of security technologies, services, and solutions designed to protect digital assets, infrastructure, and information systems across countries in the Middle Eastern region. This market encompasses hardware, software, and services that defend against cyber threats, ensure data privacy, and maintain the integrity of digital operations for government entities, enterprises, and critical infrastructure providers.
Cybersecurity solutions in this context include network security appliances, endpoint detection and response systems, security information and event management platforms, identity and access management tools, and cloud security services. The market also covers professional services such as security consulting, managed security services, incident response, and compliance management. Regional characteristics of this market include strong government involvement, emphasis on critical infrastructure protection, and growing awareness of cyber threats targeting oil and gas, banking, and telecommunications sectors.
Market dynamics in the Middle East cybersecurity sector are characterized by rapid technological advancement and increasing threat sophistication. The region’s strategic importance in global energy markets and its position as a bridge between East and West make it a prime target for cyber attacks, driving substantial investment in defensive capabilities. Key growth drivers include government digitization initiatives, regulatory compliance requirements, and the need to protect critical infrastructure from state-sponsored and criminal cyber activities.
Technology adoption patterns show strong preference for integrated security platforms that can address multiple threat vectors simultaneously. Organizations are moving beyond traditional perimeter-based security models toward zero-trust architectures and cloud-native security solutions. The market is witnessing increased demand for artificial intelligence-powered security tools that can provide real-time threat detection and automated response capabilities.
Regional leadership in cybersecurity investment comes primarily from the Gulf Cooperation Council countries, with the UAE and Saudi Arabia leading in both public and private sector spending. These nations are developing comprehensive national cybersecurity strategies that encompass critical infrastructure protection, cyber workforce development, and international cooperation on cyber defense initiatives.
Strategic insights reveal several critical factors shaping the Middle East cybersecurity landscape:
Digital transformation initiatives across the Middle East are creating unprecedented demand for cybersecurity solutions. Government-led smart city projects, digital banking services, and e-government platforms require comprehensive security frameworks to protect citizen data and maintain public trust. The region’s ambitious Vision 2030 programs in Saudi Arabia and similar initiatives in other countries are accelerating digital adoption while simultaneously increasing cybersecurity requirements.
Geopolitical tensions and the region’s strategic importance in global affairs have made Middle Eastern countries prime targets for sophisticated cyber attacks. State-sponsored threat actors, cybercriminal organizations, and terrorist groups are increasingly targeting critical infrastructure, government systems, and private enterprises. This threat landscape is driving organizations to invest in advanced threat detection, incident response capabilities, and cyber resilience programs.
Regulatory compliance requirements are becoming more stringent across the region, with countries implementing comprehensive data protection laws and cybersecurity regulations. The UAE’s Data Protection Law, Saudi Arabia’s Personal Data Protection Law, and similar regulations in other countries are mandating specific security controls and breach notification requirements. Financial institutions face particularly strict regulatory oversight, driving substantial investment in compliance-focused security solutions.
Cloud adoption and digital infrastructure modernization are creating new security challenges that require specialized solutions. As organizations migrate workloads to cloud platforms and adopt hybrid IT architectures, traditional security models become inadequate. The growing adoption of Internet of Things devices, artificial intelligence systems, and edge computing technologies is expanding the attack surface and requiring more sophisticated security approaches.
Skills shortage represents a significant challenge for the Middle East cybersecurity market, with demand for qualified professionals far exceeding supply. The region faces a critical gap in cybersecurity expertise, particularly in specialized areas such as threat hunting, incident response, and security architecture. This shortage is driving up labor costs and creating implementation delays for security projects across both public and private sectors.
Budget constraints in some countries and organizations limit the scope and scale of cybersecurity investments. While government entities and large enterprises have substantial security budgets, small and medium-sized businesses often struggle to afford comprehensive security solutions. The high cost of advanced security technologies and professional services can be prohibitive for organizations with limited IT budgets.
Cultural and organizational resistance to cybersecurity measures can impede implementation and effectiveness of security programs. Some organizations view security controls as impediments to business operations rather than enablers of secure digital transformation. Legacy system integration challenges also create barriers, as many organizations operate aging IT infrastructure that is difficult to secure with modern cybersecurity tools.
Vendor dependency and concerns about foreign technology suppliers create procurement challenges for government and critical infrastructure organizations. Geopolitical considerations and national security concerns influence technology selection decisions, sometimes limiting access to best-in-class security solutions. Supply chain security concerns are also becoming more prominent as organizations seek to reduce risks associated with third-party technology providers.
Artificial intelligence integration presents substantial opportunities for cybersecurity vendors and service providers in the Middle East. Organizations are seeking AI-powered solutions that can provide automated threat detection, behavioral analysis, and predictive security capabilities. The growing availability of Arabic language processing capabilities and region-specific threat intelligence creates opportunities for localized AI security solutions.
Critical infrastructure protection represents a high-growth opportunity segment, particularly in energy, water, transportation, and telecommunications sectors. Government mandates for critical infrastructure cybersecurity and increasing awareness of operational technology security risks are driving demand for specialized industrial control system security solutions. Smart city initiatives across the region are creating additional opportunities for integrated security platforms that can protect interconnected urban systems.
Managed security services offer significant growth potential as organizations seek to outsource security operations to specialized providers. The shortage of internal cybersecurity expertise is driving demand for Security Operations Center services, threat monitoring, and incident response capabilities. Cloud security services represent another high-growth opportunity as organizations accelerate cloud adoption and require specialized expertise to secure cloud workloads.
Cybersecurity education and training services present opportunities for capacity building and workforce development. Government initiatives to develop local cybersecurity expertise are creating demand for training programs, certification courses, and academic partnerships. Regional threat intelligence services that provide Middle East-specific cyber threat information and analysis are also gaining traction among organizations seeking to understand their local risk environment.
Competitive dynamics in the Middle East cybersecurity market are characterized by a mix of global technology leaders and emerging regional players. International vendors such as Cisco, Palo Alto Networks, and Fortinet maintain strong market positions through established partner networks and comprehensive product portfolios. However, regional system integrators and managed service providers are gaining market share by offering localized expertise and Arabic language support.
Technology evolution is driving rapid changes in market dynamics, with traditional signature-based security solutions giving way to behavior-based and AI-powered alternatives. The shift toward cloud-native security architectures is disrupting established vendor relationships and creating opportunities for new market entrants. Zero-trust security models are gaining adoption as organizations recognize the limitations of perimeter-based security approaches.
Customer preferences are evolving toward integrated security platforms that can provide comprehensive protection across multiple threat vectors. Organizations prefer solutions that offer centralized management, automated response capabilities, and integration with existing IT infrastructure. Service delivery models are also changing, with increasing demand for subscription-based licensing and managed security services rather than traditional capital expenditure purchases.
Regulatory influence continues to shape market dynamics through evolving compliance requirements and government procurement preferences. National cybersecurity strategies are creating market opportunities while also imposing constraints on technology selection and vendor relationships. Public-private partnerships are becoming more common as governments seek to leverage private sector expertise while maintaining control over critical security capabilities.
Primary research methodologies employed in analyzing the Middle East cybersecurity market include comprehensive surveys of IT decision-makers, security professionals, and government officials across key countries in the region. In-depth interviews with cybersecurity vendors, system integrators, and managed service providers provide insights into market trends, competitive dynamics, and customer requirements. Expert consultations with regional cybersecurity leaders and academic researchers contribute specialized knowledge about emerging threats and technology developments.
Secondary research encompasses analysis of government cybersecurity strategies, regulatory frameworks, and public sector procurement data. Industry reports, vendor financial disclosures, and technology market analyses provide quantitative data on market sizing and growth trends. Threat intelligence sources and cybersecurity incident databases offer insights into the regional threat landscape and its impact on security investment priorities.
Market segmentation analysis utilizes multiple data sources to categorize the market by technology type, deployment model, organization size, and industry vertical. Cross-referencing of vendor revenue data, customer case studies, and industry surveys ensures accuracy in market share estimations and competitive positioning analysis. Regional analysis incorporates country-specific economic indicators, technology adoption rates, and regulatory environments to provide granular market insights.
Validation processes include triangulation of data sources, expert review panels, and statistical analysis to ensure research accuracy and reliability. MarkWide Research employs rigorous quality control measures to verify market data and projections, including peer review by cybersecurity industry experts and validation against publicly available market indicators.
United Arab Emirates leads the Middle East cybersecurity market with the most mature technology infrastructure and highest per-capita security spending. The country’s position as a regional business hub and its ambitious smart city initiatives drive substantial investment in cybersecurity solutions. Dubai and Abu Dhabi serve as regional headquarters for many international cybersecurity vendors, creating a competitive marketplace with access to cutting-edge technologies.
Saudi Arabia represents the largest cybersecurity market by absolute spending, driven by Vision 2030 digital transformation initiatives and substantial government investment in critical infrastructure protection. The kingdom’s focus on developing a domestic technology sector includes significant cybersecurity capabilities, with NEOM and other mega-projects requiring comprehensive security frameworks. Government entities and oil and gas companies constitute the primary customer segments.
Qatar demonstrates strong cybersecurity investment driven by preparations for major international events and the development of smart city infrastructure. The country’s small size enables rapid deployment of advanced security technologies and serves as a testing ground for innovative solutions. Financial services and government sectors lead cybersecurity adoption, with growing interest from healthcare and education organizations.
Kuwait, Oman, and Bahrain represent emerging cybersecurity markets with increasing government focus on digital security. These countries are developing national cybersecurity strategies and investing in critical infrastructure protection, though at smaller scales than their larger neighbors. Regional cooperation initiatives are facilitating knowledge sharing and joint cybersecurity capabilities development across the Gulf Cooperation Council countries.
Market leadership in the Middle East cybersecurity sector is dominated by established international vendors with strong regional presence and local partnership networks:
Regional players and system integrators are gaining market share through specialized expertise and localized service delivery. Companies such as Help AG, Injazat, and Bespin Global provide managed security services and consulting capabilities tailored to Middle Eastern market requirements. These organizations often serve as implementation partners for international vendors while developing their own security service offerings.
Emerging vendors specializing in artificial intelligence, cloud security, and industrial control system protection are establishing regional presence through partnerships and direct sales efforts. The competitive landscape continues to evolve as new technologies and changing customer requirements create opportunities for innovative security solutions.
By Technology Type:
By Deployment Model:
By Organization Size:
By Industry Vertical:
Network Security remains the largest category within the Middle East cybersecurity market, driven by the need to protect perimeter defenses and internal network infrastructure. Next-generation firewalls with advanced threat prevention capabilities are experiencing strong demand as organizations seek to block sophisticated attacks. Software-defined perimeter solutions are gaining traction as organizations adopt zero-trust network architectures.
Cloud Security represents the fastest-growing category as organizations accelerate cloud adoption and require specialized protection for cloud workloads. Cloud access security brokers and cloud security posture management tools are experiencing rapid adoption as organizations seek visibility and control over cloud environments. Multi-cloud security management platforms are becoming essential as organizations adopt hybrid and multi-cloud strategies.
Identity and Access Management solutions are critical for organizations implementing zero-trust security models and managing remote workforce access. Privileged access management tools are particularly important for protecting administrative accounts and critical systems. Biometric authentication and behavioral analytics are emerging as key technologies for enhancing identity verification and fraud prevention.
Security Analytics and threat intelligence platforms are becoming essential for organizations seeking to detect and respond to advanced threats. Security information and event management systems with artificial intelligence capabilities provide automated threat detection and response capabilities. Threat hunting services and platforms are gaining adoption among organizations with mature security operations.
Government entities benefit from enhanced national security capabilities, improved citizen service delivery, and strengthened critical infrastructure protection. Cybersecurity investments enable governments to pursue digital transformation initiatives while maintaining public trust and protecting sensitive information. Regulatory compliance capabilities help government organizations meet international standards and demonstrate cybersecurity maturity.
Private enterprises gain competitive advantages through improved operational resilience, enhanced customer trust, and reduced business risk. Cybersecurity investments protect intellectual property, customer data, and business operations from cyber threats. Digital transformation initiatives become more viable with robust security foundations that enable safe adoption of new technologies and business models.
Critical infrastructure operators achieve improved operational reliability, reduced downtime, and enhanced safety through industrial cybersecurity solutions. Protection of operational technology systems ensures continuity of essential services and prevents cyber attacks from disrupting critical infrastructure. Compliance capabilities help operators meet regulatory requirements and industry standards for cybersecurity.
Financial institutions benefit from enhanced fraud prevention, improved regulatory compliance, and strengthened customer trust. Cybersecurity investments protect customer financial data, prevent unauthorized transactions, and maintain the integrity of financial systems. Digital banking initiatives require robust security frameworks to ensure safe and secure customer experiences.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Zero-trust architecture adoption is accelerating across the Middle East as organizations recognize the limitations of traditional perimeter-based security models. This approach requires verification of every user and device attempting to access network resources, regardless of their location. Implementation strategies focus on identity verification, device compliance, and continuous monitoring of user behavior and access patterns.
Artificial intelligence integration is transforming cybersecurity capabilities through automated threat detection, behavioral analysis, and predictive security measures. Machine learning algorithms are being deployed to identify anomalous network traffic, detect advanced persistent threats, and automate incident response procedures. AI-powered solutions are particularly valuable for organizations with limited cybersecurity expertise, providing automated protection capabilities.
Cloud-first security strategies are emerging as organizations migrate workloads to cloud platforms and adopt cloud-native applications. Security architectures are being redesigned to protect cloud workloads, container environments, and serverless applications. Cloud security posture management tools are becoming essential for maintaining visibility and control over cloud infrastructure configurations and security policies.
Operational technology security is gaining prominence as industrial organizations recognize the cybersecurity risks associated with connected manufacturing systems, power grids, and oil and gas facilities. Convergence of IT and OT security is driving demand for specialized solutions that can protect industrial control systems without disrupting operational processes. According to MarkWide Research analysis, OT security investments are growing at 12% annually across the region.
National cybersecurity strategies are being implemented across the Middle East, with countries establishing dedicated cybersecurity agencies and comprehensive policy frameworks. The UAE’s National Cybersecurity Strategy 2031 and Saudi Arabia’s National Cybersecurity Authority represent significant developments in regional cybersecurity governance. Regulatory frameworks are being strengthened to mandate cybersecurity controls for critical infrastructure and financial services organizations.
Public-private partnerships are expanding to leverage private sector expertise in government cybersecurity initiatives. Collaborative programs between government agencies and cybersecurity vendors are developing specialized solutions for critical infrastructure protection and national security applications. Information sharing mechanisms are being established to facilitate threat intelligence exchange between public and private sector organizations.
Cybersecurity education initiatives are addressing the regional skills shortage through university programs, professional certification courses, and government-sponsored training programs. The establishment of cybersecurity research centers and academic partnerships with international institutions is building local expertise and research capabilities. Workforce development programs are targeting both technical cybersecurity skills and cybersecurity management competencies.
Regional cybersecurity cooperation is strengthening through initiatives such as the Gulf Cooperation Council Cybersecurity Framework and joint cyber defense exercises. Cross-border threat intelligence sharing and coordinated incident response capabilities are being developed to address regional cyber threats. International partnerships with cybersecurity organizations in Europe, North America, and Asia are facilitating knowledge transfer and technology cooperation.
Investment priorities should focus on developing comprehensive cybersecurity capabilities that address both current threats and emerging risks. Organizations should prioritize zero-trust architecture implementation, cloud security capabilities, and artificial intelligence-powered threat detection systems. Skills development investments are critical for building sustainable cybersecurity capabilities and reducing dependence on external expertise.
Technology selection should emphasize integrated security platforms that can provide comprehensive protection across multiple threat vectors while simplifying management and reducing operational complexity. Organizations should evaluate solutions based on their ability to integrate with existing IT infrastructure and support future technology adoption. Vendor partnerships should include local support capabilities and Arabic language interfaces to ensure effective implementation and ongoing support.
Regulatory compliance strategies should anticipate evolving requirements and implement security controls that exceed minimum compliance standards. Organizations should establish governance frameworks that can adapt to changing regulatory environments while maintaining operational efficiency. Risk management approaches should incorporate cybersecurity considerations into business planning and decision-making processes.
Regional cooperation initiatives should be leveraged to share threat intelligence, develop joint defense capabilities, and coordinate incident response efforts. Organizations should participate in industry information sharing programs and collaborate with government cybersecurity agencies. MWR recommends establishing formal partnerships with regional cybersecurity organizations to enhance collective defense capabilities.
Market growth is expected to continue at a robust pace, driven by ongoing digital transformation initiatives and increasing cyber threat sophistication. The integration of emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, quantum computing, and 5G networks will create new cybersecurity requirements and market opportunities. Government investment in cybersecurity capabilities is projected to remain strong as national security considerations drive policy priorities.
Technology evolution will focus on autonomous security systems that can detect, analyze, and respond to threats with minimal human intervention. Cloud-native security architectures will become the standard approach for protecting modern IT environments and supporting digital business initiatives. Quantum-resistant cryptography will emerge as a critical requirement as quantum computing capabilities advance and threaten current encryption methods.
Industry consolidation is expected to continue as cybersecurity vendors seek to provide comprehensive security platforms through acquisitions and partnerships. Regional system integrators and managed service providers will play increasingly important roles in delivering localized cybersecurity capabilities. Specialization trends will create opportunities for vendors focusing on specific industry verticals or emerging technology areas.
Workforce development initiatives will gradually address the regional skills shortage, though demand for cybersecurity expertise will continue to exceed supply in the near term. Educational institutions and professional training organizations will expand cybersecurity programs to meet growing demand. MarkWide Research projects that cybersecurity employment in the region will grow by 15% annually over the next five years, creating substantial opportunities for cybersecurity professionals and service providers.
The Middle East cybersecurity market represents a dynamic and rapidly evolving sector driven by digital transformation initiatives, increasing cyber threats, and strong government support for cybersecurity capabilities. Regional organizations are investing substantially in comprehensive security solutions that can protect critical infrastructure, enable digital business initiatives, and maintain competitive advantages in an increasingly connected world.
Market opportunities are abundant across all technology categories and industry verticals, with particular growth potential in artificial intelligence-powered security solutions, cloud security services, and operational technology protection. The region’s strategic importance and substantial financial resources create favorable conditions for cybersecurity market expansion, though challenges such as skills shortages and regulatory complexity must be addressed.
Future success in the Middle East cybersecurity market will depend on organizations’ ability to adapt to evolving threat landscapes, integrate emerging technologies, and develop sustainable cybersecurity capabilities. The continued evolution toward zero-trust architectures, cloud-first security strategies, and AI-powered threat detection will shape market dynamics and create new opportunities for innovative cybersecurity solutions and services.
What is Cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity refers to the practices and technologies designed to protect networks, devices, and data from unauthorized access, attacks, or damage. It encompasses various measures including firewalls, encryption, and intrusion detection systems.
What are the key players in the Middle East Cybersecurity Market?
Key players in the Middle East Cybersecurity Market include companies like DarkMatter, Paladion, and Help AG, which provide a range of cybersecurity solutions and services. These companies focus on protecting critical infrastructure, financial services, and government sectors, among others.
What are the main drivers of growth in the Middle East Cybersecurity Market?
The main drivers of growth in the Middle East Cybersecurity Market include the increasing frequency of cyberattacks, the rising adoption of cloud services, and the growing regulatory requirements for data protection. Organizations are investing in advanced security solutions to safeguard sensitive information.
What challenges does the Middle East Cybersecurity Market face?
The Middle East Cybersecurity Market faces challenges such as a shortage of skilled cybersecurity professionals, the complexity of managing diverse security solutions, and the evolving nature of cyber threats. These factors can hinder effective security implementation.
What opportunities exist in the Middle East Cybersecurity Market?
Opportunities in the Middle East Cybersecurity Market include the growing demand for managed security services, the rise of IoT devices requiring protection, and the increasing focus on cybersecurity awareness and training programs. These trends present avenues for growth and innovation.
What trends are shaping the Middle East Cybersecurity Market?
Trends shaping the Middle East Cybersecurity Market include the integration of artificial intelligence in threat detection, the shift towards zero-trust security models, and the emphasis on compliance with international cybersecurity standards. These trends are influencing how organizations approach their security strategies.
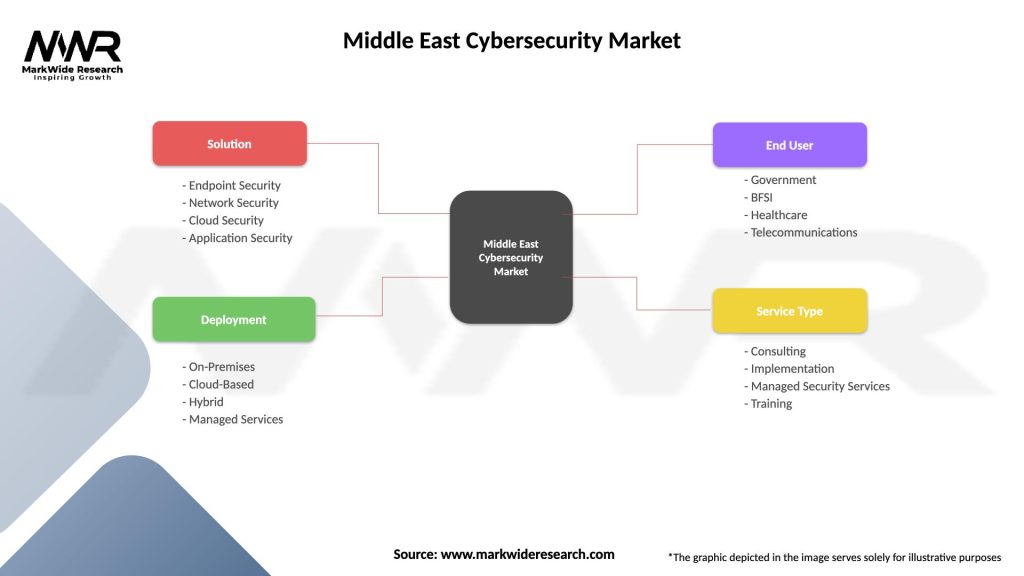
Middle East Cybersecurity Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Solution | Endpoint Security, Network Security, Cloud Security, Application Security |
| Deployment | On-Premises, Cloud-Based, Hybrid, Managed Services |
| End User | Government, BFSI, Healthcare, Telecommunications |
| Service Type | Consulting, Implementation, Managed Security Services, Training |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the Middle East Cybersecurity Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at