444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The 3D printing CAD software market encompasses a range of software solutions designed to facilitate the design, modeling, and preparation of 3D printable objects. These software tools play a crucial role in the 3D printing workflow, enabling users to create digital models, optimize designs for additive manufacturing processes, and generate printable files compatible with 3D printers.
Meaning
3D printing CAD software, also known as computer-aided design software for additive manufacturing, enables users to design, manipulate, and prepare 3D models for printing. These software solutions provide a suite of tools for creating complex geometries, optimizing designs for specific printing technologies, and simulating the printing process to identify potential issues and ensure printability.
Executive Summary
The 3D printing CAD software market is experiencing rapid growth driven by the increasing adoption of 3D printing technology across various industries, including aerospace, automotive, healthcare, and consumer goods. Key market players focus on offering user-friendly, feature-rich software solutions that address the diverse needs of designers, engineers, and manufacturers. With ongoing advancements in technology and the growing demand for customized, on-demand manufacturing solutions, the 3D printing CAD software market presents opportunities for innovation, expansion, and market differentiation.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Several factors are driving the growth of the 3D printing CAD software market:
Market Restraints
Despite the positive growth outlook, the 3D printing CAD software market faces several challenges:
Market Opportunities
Despite the challenges, the 3D printing CAD software market presents several opportunities for growth and innovation:
Market Dynamics
The 3D printing CAD software market is characterized by dynamic trends and evolving user requirements influenced by factors such as technological advancements, industry regulations, market competition, and macroeconomic conditions. Key market players must anticipate these dynamics, innovate proactively, and adapt their strategies to remain competitive and capture emerging opportunities in the market.
Regional Analysis
The 3D printing CAD software market exhibits regional variations in terms of adoption rates, industry focus, and regulatory environment:
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the 3D Printing CAD Software Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
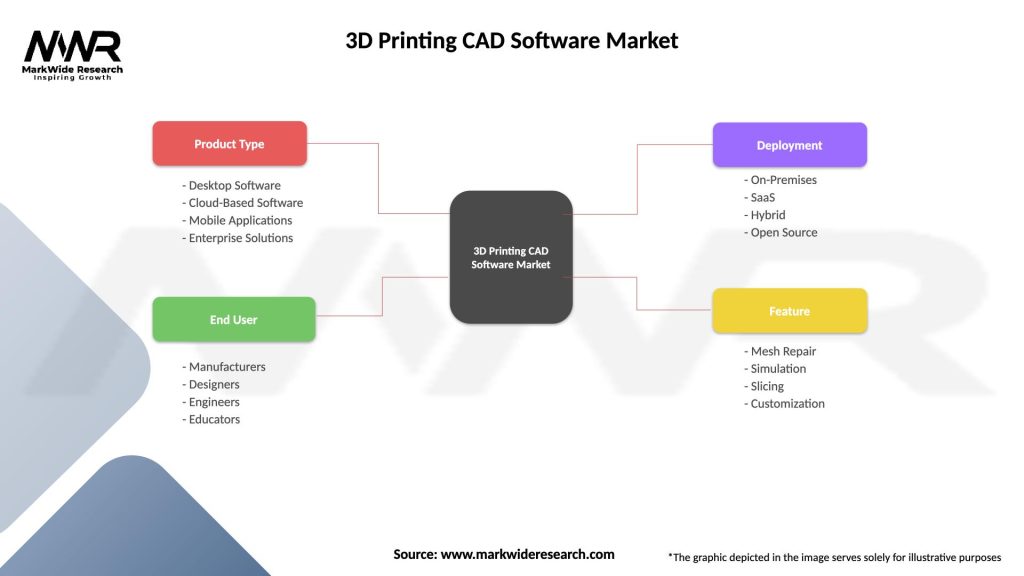
Segmentation
The 3D printing CAD software market can be segmented based on various factors, including:
Category-wise Insights
Each category of 3D printing CAD software offers unique features, capabilities, and user experiences tailored to different requirements and preferences:
Key Benefits for Users and Stakeholders
The 3D printing CAD software market offers several benefits for users, manufacturers, and industry stakeholders:
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Several key trends are shaping the 3D printing CAD software market:
Covid-19 Impact
The Covid-19 pandemic has had a mixed impact on the 3D printing CAD software market:
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Based on market trends and developments, analysts suggest the following strategies for CAD software vendors:
Future Outlook
The future outlook for the 3D printing CAD software market is optimistic, with sustained growth and innovation expected in the coming years. As additive manufacturing technologies continue to mature, and the adoption of 3D printing expands across industries and applications, the demand for CAD software solutions that enable efficient, flexible, and scalable design workflows will continue to grow. CAD software vendors that prioritize innovation, customer satisfaction, and strategic partnerships are well-positioned to capitalize on this growing market opportunity and drive the next wave of digital transformation in manufacturing and design.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the 3D printing CAD software market plays a pivotal role in driving innovation, efficiency, and creativity in the additive manufacturing industry. Despite challenges such as complexity, interoperability, and economic uncertainty, the market continues to grow rapidly, fueled by advancements in technology, increasing adoption of 3D printing technology, and the ongoing digital transformation of manufacturing workflows. By focusing on innovation, customer-centricity, and strategic partnerships, CAD software vendors can navigate market dynamics, capture emerging opportunities, and empower users to unleash their creativity and bring their design ideas to life in the world of additive manufacturing.
What is 3D Printing CAD Software?
3D Printing CAD Software refers to computer-aided design tools specifically developed for creating and modifying digital models intended for 3D printing. These software solutions enable users to design intricate geometries, optimize structures for additive manufacturing, and prepare files for printing processes.
What are the key players in the 3D Printing CAD Software Market?
Key players in the 3D Printing CAD Software Market include Autodesk, Dassault Systèmes, Siemens, and PTC, among others. These companies offer a range of software solutions that cater to various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and healthcare.
What are the growth factors driving the 3D Printing CAD Software Market?
The growth of the 3D Printing CAD Software Market is driven by the increasing adoption of additive manufacturing across industries, the demand for rapid prototyping, and advancements in software capabilities. Additionally, the rise of customized products and the need for efficient design processes contribute to market expansion.
What challenges does the 3D Printing CAD Software Market face?
The 3D Printing CAD Software Market faces challenges such as the high cost of software licenses, the complexity of software tools, and the need for skilled personnel to operate them. Furthermore, integration with existing manufacturing processes can pose difficulties for companies.
What opportunities exist in the 3D Printing CAD Software Market?
Opportunities in the 3D Printing CAD Software Market include the development of cloud-based solutions, which enhance collaboration and accessibility, and the integration of artificial intelligence for design optimization. Additionally, expanding applications in sectors like construction and consumer goods present significant growth potential.
What trends are shaping the 3D Printing CAD Software Market?
Trends shaping the 3D Printing CAD Software Market include the increasing use of generative design, which allows for innovative and efficient product designs, and the rise of open-source software solutions. Moreover, the focus on sustainability and eco-friendly materials in design processes is becoming more prominent.
3D Printing CAD Software Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Desktop Software, Cloud-Based Software, Mobile Applications, Enterprise Solutions |
| End User | Manufacturers, Designers, Engineers, Educators |
| Deployment | On-Premises, SaaS, Hybrid, Open Source |
| Feature | Mesh Repair, Simulation, Slicing, Customization |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the 3D Printing CAD Software Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at