444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The Waste to Energy (WTE) market is a pivotal segment within the renewable energy sector, focused on converting various types of waste into energy sources such as electricity, heat, and biofuels. This process not only addresses waste management challenges but also contributes to sustainable energy production, reducing reliance on fossil fuels. With increasing global emphasis on environmental sustainability and circular economy practices, the WTE market plays a crucial role in waste diversion from landfills and greenhouse gas emissions reduction.
Meaning
Waste to Energy (WTE) refers to the process of generating energy in the form of electricity or heat from the combustion of waste materials. It involves converting non-recyclable waste into renewable energy sources, thereby addressing waste management issues while contributing to sustainable energy production. The WTE process typically involves incineration, gasification, or pyrolysis technologies to extract energy from waste, emphasizing resource recovery and environmental stewardship.
Executive Summary
The Waste to Energy (WTE) market is witnessing significant growth driven by rising waste volumes, stringent environmental regulations, and increasing energy demand. Key market players are investing in advanced technologies, improving efficiency, and expanding their operational capacities to capitalize on the expanding market opportunities. With a focus on waste reduction, energy recovery, and sustainable development goals, the WTE market is poised for continued expansion across global markets.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Several factors are propelling the growth of the Waste to Energy (WTE) market:
Market Restraints
Despite its growth prospects, the Waste to Energy (WTE) market faces several challenges:
Market Opportunities
The Waste to Energy (WTE) market offers promising opportunities for growth and innovation:
Market Dynamics
The Waste to Energy (WTE) market dynamics are shaped by evolving waste management practices, regulatory landscapes, technological innovations, and market competition. Continuous advancements in waste conversion technologies, strategic partnerships, and policy frameworks are critical for addressing global waste challenges and accelerating the transition towards a low-carbon economy.
Regional Analysis
The Waste to Energy (WTE) market exhibits varying trends and regulatory frameworks across regions:
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in Waste to Energy (WTE) Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
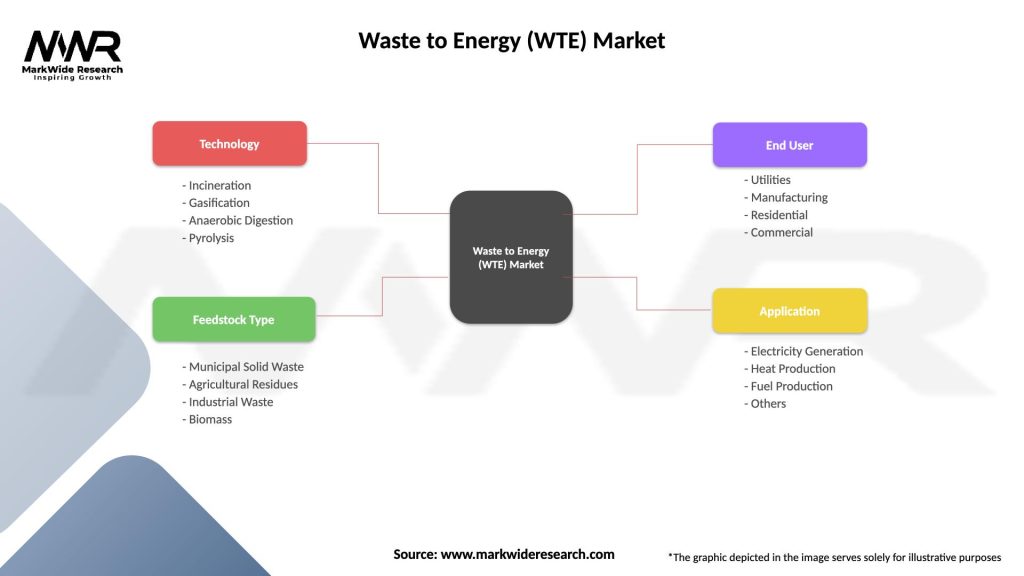
Segmentation
The Waste to Energy (WTE) market can be segmented based on:
Category-wise Insights
Different categories within the Waste to Energy (WTE) market cater to diverse waste streams and energy applications:
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
Industry participants benefit from leveraging Waste to Energy (WTE) solutions:
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Key trends shaping the Waste to Energy (WTE) market include:
Covid-19 Impact
The Covid-19 pandemic has influenced the Waste to Energy (WTE) market in several ways:
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Based on market trends and developments, analysts recommend the following strategies for industry participants:
Future Outlook
The future outlook for the Waste to Energy (WTE) market is optimistic, driven by increasing waste volumes, regulatory support for renewable energy, and advancements in technology and innovation. As global economies recover from the Covid-19 pandemic, the WTE sector is expected to play a critical role in sustainable development, circular economy practices, and climate change mitigation efforts. Strategic investments in technology, market expansion initiatives, and stakeholder engagement will be essential to capitalize on emerging opportunities and navigate challenges in the evolving energy landscape.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Waste to Energy (WTE) market represents a dynamic sector within the renewable energy industry, offering solutions to waste management challenges while contributing to sustainable development goals. Despite challenges such as high capital costs, regulatory complexities, and public perception issues, the market is poised for growth driven by technological advancements, policy support, and increasing global awareness of environmental sustainability. By embracing innovation, collaboration, and adaptive strategies, industry stakeholders can unlock the full potential of Waste to Energy solutions, driving economic growth, environmental stewardship, and energy security in a rapidly evolving global landscape.
What is Waste to Energy (WTE)?
Waste to Energy (WTE) refers to the process of generating energy in the form of electricity or heat from the treatment of waste. This process can involve various technologies, including incineration, anaerobic digestion, and gasification, which convert waste materials into usable energy.
What are the key companies in the Waste to Energy (WTE) Market?
Key companies in the Waste to Energy (WTE) Market include Veolia, Covanta, and SUEZ, which are involved in various aspects of waste management and energy recovery. These companies focus on developing innovative technologies and solutions to enhance energy production from waste, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the Waste to Energy (WTE) Market?
The Waste to Energy (WTE) Market is driven by increasing waste generation, the need for sustainable waste management solutions, and rising energy demands. Additionally, government initiatives promoting renewable energy sources and reducing landfill use further support market growth.
What challenges does the Waste to Energy (WTE) Market face?
The Waste to Energy (WTE) Market faces challenges such as high initial investment costs, public opposition to waste treatment facilities, and regulatory hurdles. These factors can hinder the development and expansion of WTE projects in various regions.
What opportunities exist in the Waste to Energy (WTE) Market?
Opportunities in the Waste to Energy (WTE) Market include advancements in technology that improve efficiency and reduce emissions, as well as increasing collaboration between public and private sectors. The growing emphasis on circular economy practices also presents new avenues for investment and innovation.
What trends are shaping the Waste to Energy (WTE) Market?
Trends shaping the Waste to Energy (WTE) Market include the integration of smart technologies for better waste management, the rise of decentralized energy systems, and a focus on sustainability and carbon neutrality. These trends are influencing how waste is processed and energy is generated.
Waste to Energy (WTE) Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Technology | Incineration, Gasification, Anaerobic Digestion, Pyrolysis |
| Feedstock Type | Municipal Solid Waste, Agricultural Residues, Industrial Waste, Biomass |
| End User | Utilities, Manufacturing, Residential, Commercial |
| Application | Electricity Generation, Heat Production, Fuel Production, Others |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in Waste to Energy (WTE) Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at