444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The In Vitro ADME-Tox market is experiencing rapid growth driven by the increasing demand for efficient and cost-effective methods to assess the absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity of pharmaceutical compounds during drug development. ADME-Tox studies play a crucial role in predicting the pharmacokinetic and safety profiles of drug candidates, reducing the risk of late-stage failures and accelerating the drug discovery process. In vitro ADME-Tox assays offer advantages such as higher throughput, reduced animal usage, and improved predictivity compared to traditional in vivo studies, making them indispensable tools for pharmaceutical companies, contract research organizations (CROs), and regulatory agencies.
Meaning
In vitro ADME-Tox refers to a set of assays conducted in laboratory settings to evaluate the absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity properties of drug candidates. These assays utilize cell-based systems, tissue cultures, and biochemical assays to simulate physiological processes and predict the behavior of drugs in the human body. In vitro ADME-Tox studies assess parameters such as drug solubility, permeability, metabolic stability, protein binding, and cytotoxicity, providing valuable data for drug optimization, candidate selection, and regulatory submissions.
Executive Summary
The In Vitro ADME-Tox market is witnessing robust growth driven by factors such as the increasing complexity of drug candidates, rising regulatory requirements, and advancements in cell culture technologies. Key market players are focusing on expanding their assay portfolios, enhancing assay performance, and improving data interpretation to meet the evolving needs of drug developers and regulatory agencies. With the growing adoption of in vitro ADME-Tox approaches in drug discovery and development, the market is poised for significant expansion in the coming years.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The In Vitro ADME-Tox market is characterized by dynamic market dynamics, including technological innovation, regulatory evolution, and shifting market trends. Market dynamics are influenced by factors such as changing drug development paradigms, emerging therapeutic modalities, and developments in predictive toxicology.
Regional Analysis
North America leads the global market for In Vitro ADME-Tox assays, driven by factors such as a strong biopharmaceutical pipeline, advanced research infrastructure, and supportive regulatory environment. Europe and Asia-Pacific are also significant markets, fueled by increasing investments in drug discovery and development, expanding CRO services, and rising adoption of in vitro ADME-Tox technologies.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the In Vitro ADME-Tox Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Segmentation
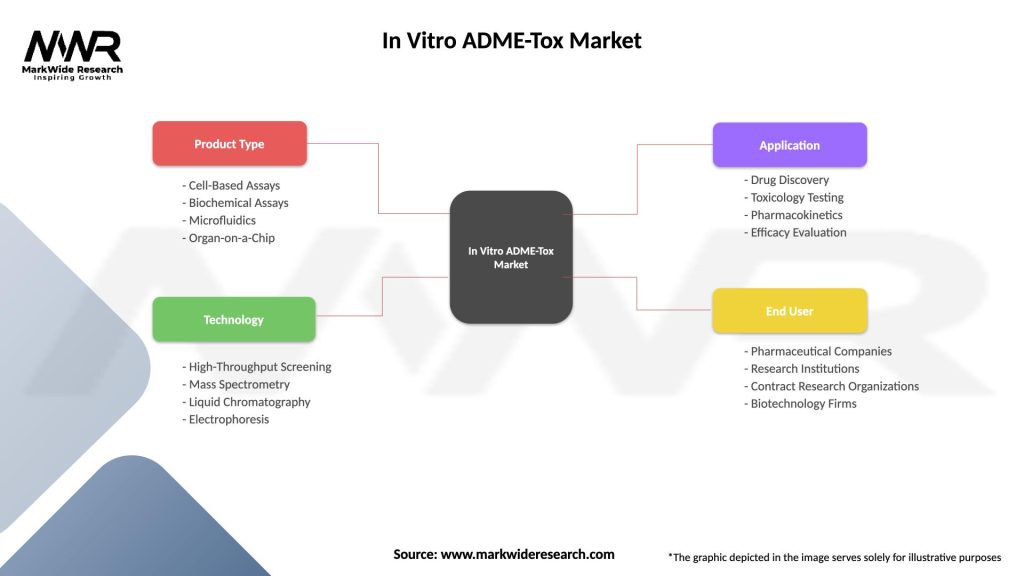
The In Vitro ADME-Tox market can be segmented based on assay type, technology platform, end-user, and geography. Assay types include drug metabolism assays, drug transport assays, drug-drug interaction assays, and cytotoxicity assays. Technology platforms include cell-based assays, biochemical assays, and computational modeling.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The Covid-19 pandemic has underscored the importance of in vitro ADME-Tox assays in drug discovery and development, particularly in vaccine development, antiviral screening, and drug repurposing efforts. In vitro ADME-Tox assays have played a critical role in assessing the pharmacokinetic and safety profiles of potential Covid-19 therapeutics, accelerating the identification of promising candidates for clinical evaluation.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The In Vitro ADME-Tox market is expected to witness significant growth in the coming years, driven by increasing demand for predictive toxicology, advancements in cell culture technologies, and expanding applications in drug discovery and development. Market players are expected to focus on innovation, assay validation, and regulatory compliance to meet the evolving needs of pharmaceutical companies, CROs, and regulatory agencies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the In Vitro ADME-Tox market presents significant growth opportunities for industry participants and stakeholders seeking to enhance the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of drug discovery and development. With advancements in technology, expanding applications in diverse therapeutic areas, and increasing regulatory acceptance, the future outlook for the market remains promising. By leveraging innovation, collaboration, and regulatory compliance, market players can contribute to advancing predictive toxicology, reducing drug development timelines, and improving patient safety globally.
What is In Vitro ADME-Tox?
In Vitro ADME-Tox refers to the assessment of Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion, and Toxicity of compounds using laboratory techniques. This approach is crucial in drug development to predict how drugs behave in the human body without the need for animal testing.
What are the key players in the In Vitro ADME-Tox Market?
Key players in the In Vitro ADME-Tox Market include companies like Charles River Laboratories, Thermo Fisher Scientific, and Eurofins Scientific. These companies provide various services and technologies to support drug development and safety assessment, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the In Vitro ADME-Tox Market?
The In Vitro ADME-Tox Market is driven by the increasing demand for drug discovery and development, the need for cost-effective testing methods, and the growing emphasis on reducing animal testing. Additionally, advancements in technology and regulatory support for in vitro methods are contributing to market growth.
What challenges does the In Vitro ADME-Tox Market face?
The In Vitro ADME-Tox Market faces challenges such as the limitations of in vitro models in fully replicating human physiology and the need for more standardized testing protocols. Additionally, regulatory hurdles and the complexity of drug interactions can complicate the assessment process.
What opportunities exist in the In Vitro ADME-Tox Market?
Opportunities in the In Vitro ADME-Tox Market include the development of more sophisticated in vitro models, such as organ-on-a-chip technologies, and the integration of artificial intelligence to enhance predictive accuracy. These innovations can lead to more efficient drug development processes.
What trends are shaping the In Vitro ADME-Tox Market?
Trends in the In Vitro ADME-Tox Market include the increasing adoption of high-throughput screening methods and the use of 3D cell cultures for more accurate toxicity assessments. There is also a growing focus on personalized medicine, which is influencing testing strategies.
In Vitro ADME-Tox Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Cell-Based Assays, Biochemical Assays, Microfluidics, Organ-on-a-Chip |
| Technology | High-Throughput Screening, Mass Spectrometry, Liquid Chromatography, Electrophoresis |
| Application | Drug Discovery, Toxicology Testing, Pharmacokinetics, Efficacy Evaluation |
| End User | Pharmaceutical Companies, Research Institutions, Contract Research Organizations, Biotechnology Firms |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the In Vitro ADME-Tox Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at