444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The Biomarker Testing Market plays a critical role in modern healthcare, offering diagnostic, prognostic, and predictive insights for various diseases and conditions. Biomarkers, including proteins, genes, metabolites, and other molecular entities, serve as indicators of biological processes, disease progression, and treatment response. Biomarker testing encompasses a wide range of laboratory techniques and assays used to detect, measure, and analyze biomarkers in biological samples, such as blood, urine, tissue, and saliva.
Meaning
Biomarker testing involves the identification, measurement, and analysis of specific biomolecules or molecular signatures in biological samples to assess physiological or pathological conditions, guide clinical decision-making, and monitor disease progression or treatment response. Biomarkers can be used for diagnostic purposes, prognostic assessments, therapeutic monitoring, and patient stratification in various medical specialties, including oncology, cardiology, neurology, and infectious diseases.
Executive Summary
The Biomarker Testing Market is experiencing rapid growth and innovation, driven by advancements in molecular biology, genomics, proteomics, and diagnostic technologies. The market offers significant opportunities for healthcare providers, diagnostic companies, pharmaceutical firms, and research institutions to improve disease detection, personalize treatment approaches, and enhance patient outcomes. However, challenges such as biomarker validation, regulatory compliance, and reimbursement complexities require strategic planning and collaboration to navigate successfully.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The Biomarker Testing Market operates in a dynamic landscape influenced by technological innovations, regulatory developments, market trends, and healthcare system challenges. Market dynamics shape industry strategies, investment priorities, and product development efforts to address unmet clinical needs, drive innovation, and deliver value to patients and healthcare stakeholders.
Regional Analysis
The Biomarker Testing Market exhibits regional variations in market dynamics, healthcare infrastructure, regulatory frameworks, and reimbursement policies. North America leads the market due to robust research and development ecosystem, favorable regulatory environment, and high demand for advanced diagnostic technologies. Europe follows closely, driven by initiatives in precision medicine, collaborative research networks, and strong clinical validation infrastructure. Asia-Pacific presents growth opportunities fueled by rising healthcare expenditure, increasing disease burden, and government initiatives to promote precision medicine and biomarker-based diagnostics.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Biomarker Testing Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
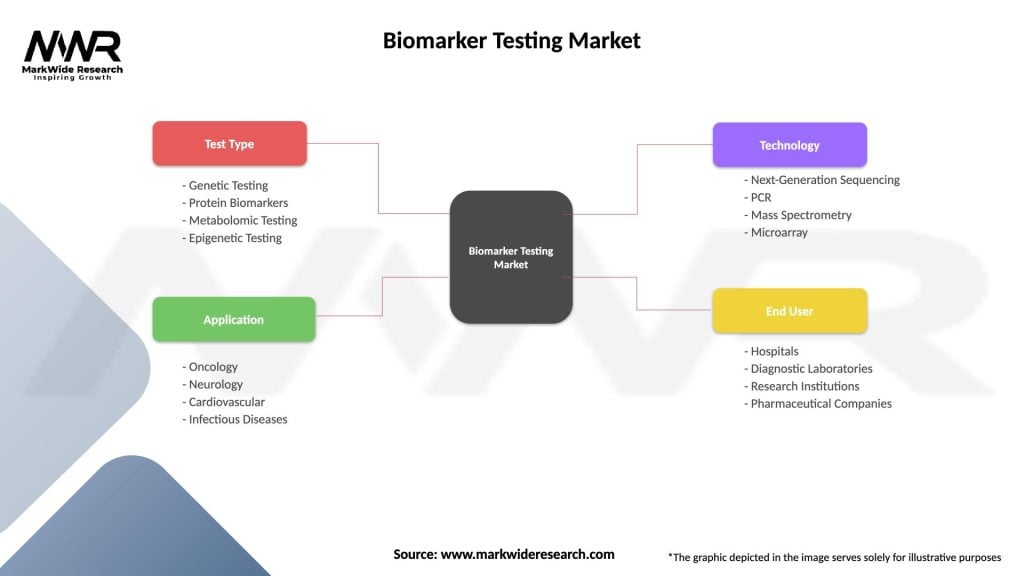
Segmentation
The Biomarker Testing Market can be segmented based on various factors, including:
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has both accelerated and reshaped the biomarker testing market:
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The Biomarker Testing Market is poised for significant growth and innovation, driven by advances in molecular diagnostics, precision medicine, and digital health technologies. Key trends shaping the future of biomarker testing include the expansion of companion diagnostics, integration of digital biomarkers, and adoption of point-of-care testing solutions. Continued investment in biomarker discovery, validation, and clinical translation efforts, coupled with regulatory support and reimbursement reforms, will drive market expansion and facilitate the widespread adoption of biomarker-based diagnostics in personalized healthcare delivery.
Conclusion
As the healthcare industry evolves towards value-based care models, biomarker testing will play an increasingly pivotal role in improving diagnostic accuracy, treatment efficacy, and patient outcomes across diverse disease areas and patient populations. Collaborative partnerships, interdisciplinary research consortia, and data-driven approaches will drive biomarker innovation, accelerate therapeutic development, and transform clinical practice towards more precise, predictive, and personalized healthcare interventions. With continued investment, innovation, and collaboration, the Biomarker Testing Market is poised to shape the future of healthcare delivery and redefine the paradigm of precision medicine for years to come.
What is Biomarker Testing?
Biomarker testing refers to the analysis of biological markers in the body to identify disease states, predict disease progression, and guide treatment decisions. It is widely used in oncology, cardiology, and personalized medicine.
What are the key players in the Biomarker Testing Market?
Key players in the Biomarker Testing Market include Roche, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Illumina, and QIAGEN, among others. These companies are known for their innovative technologies and extensive product portfolios in biomarker testing.
What are the main drivers of growth in the Biomarker Testing Market?
The growth of the Biomarker Testing Market is driven by the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, advancements in genomics and proteomics, and the rising demand for personalized medicine. Additionally, the integration of biomarker testing in clinical trials is enhancing its adoption.
What challenges does the Biomarker Testing Market face?
The Biomarker Testing Market faces challenges such as high costs of testing, regulatory hurdles, and the need for standardized testing protocols. These factors can limit accessibility and slow down the adoption of biomarker testing in clinical settings.
What opportunities exist in the Biomarker Testing Market?
Opportunities in the Biomarker Testing Market include the development of novel biomarkers for early disease detection, expansion into emerging markets, and the increasing use of liquid biopsies. These trends are expected to enhance the market’s growth potential.
What are the current trends in the Biomarker Testing Market?
Current trends in the Biomarker Testing Market include the rise of companion diagnostics, the use of artificial intelligence in data analysis, and the growing focus on non-invasive testing methods. These innovations are shaping the future of biomarker testing.
Biomarker Testing Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Test Type | Genetic Testing, Protein Biomarkers, Metabolomic Testing, Epigenetic Testing |
| Application | Oncology, Neurology, Cardiovascular, Infectious Diseases |
| Technology | Next-Generation Sequencing, PCR, Mass Spectrometry, Microarray |
| End User | Hospitals, Diagnostic Laboratories, Research Institutions, Pharmaceutical Companies |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Biomarker Testing Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at