444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The Banking Smart Cards market represents a pivotal intersection between banking services and cutting-edge technology. Smart cards, embedded with microprocessors, provide secure and convenient access to various banking services, including payments, withdrawals, transfers, and authentication. These cards offer enhanced security features, such as encryption and biometric authentication, to safeguard users’ financial information and transactions. With the increasing digitization of banking services and the growing demand for secure and seamless payment solutions, the Banking Smart Cards market is poised for significant growth and innovation.
Meaning
Banking Smart Cards are advanced payment cards equipped with embedded microprocessors, enabling secure transactions and access to banking services. These cards utilize encryption technology and authentication mechanisms, such as PINs, fingerprints, or facial recognition, to protect users’ sensitive financial data and ensure the integrity of transactions. Banking Smart Cards encompass various types, including debit cards, credit cards, prepaid cards, and multi-application cards, each offering distinct features and functionalities tailored to users’ needs and preferences.
Executive Summary
The Banking Smart Cards market is experiencing rapid expansion, driven by factors such as the proliferation of digital banking services, the rise of contactless payments, and the increasing emphasis on security and fraud prevention. Smart cards offer numerous benefits for both consumers and financial institutions, including enhanced security, convenience, and interoperability. However, challenges such as technological obsolescence, regulatory compliance, and competition from alternative payment methods need to be addressed to maximize the potential of Banking Smart Cards in the evolving landscape of digital finance.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The Banking Smart Cards market operates in a dynamic environment shaped by technological advancements, regulatory changes, competitive pressures, and evolving consumer behaviors. Financial institutions and card issuers must navigate these dynamics by prioritizing innovation, security, interoperability, and customer experience to maintain their competitive edge and drive growth in the increasingly digital and interconnected world of finance.
Regional Analysis
The Banking Smart Cards market exhibits regional variations in adoption rates, market maturity, regulatory frameworks, and consumer preferences. Developed markets in North America, Europe, and Asia Pacific lead in Smart Card penetration and innovation, driven by robust banking infrastructure, high digital literacy, and strong regulatory support. Emerging markets in Latin America, Africa, and the Middle East offer growth opportunities due to expanding financial services, rising smartphone penetration, and government initiatives to promote financial inclusion and digitization.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Banking Smart Cards Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
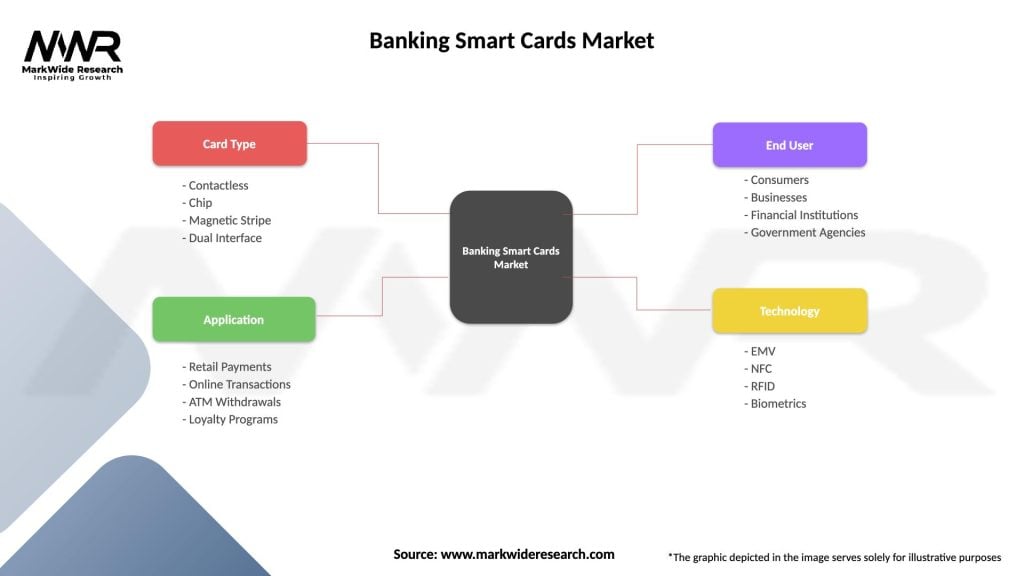
Segmentation
The Banking Smart Cards market can be segmented based on various factors, including card type, application, functionality, and geography. Common types of Smart Cards include:
Segmentation enables card issuers and financial institutions to target specific market segments effectively and tailor their offerings to meet diverse user needs, preferences, and use cases.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerates the adoption of contactless payment solutions, including Banking Smart Cards, as consumers seek safer and more hygienic ways to make transactions and avoid physical contact with cash and payment terminals. Smart Cards equipped with contactless technology enable users to make fast and secure payments by tapping their cards or mobile devices, reducing the risk of virus transmission and enhancing user confidence in the safety of electronic payments.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The Banking Smart Cards market is poised for continued growth and innovation, driven by factors such as technological advancements, changing consumer behaviors, regulatory initiatives, and market dynamics. Smart Card issuers and financial institutions must prioritize security, convenience, interoperability, and user experience to capitalize on emerging opportunities, address evolving challenges, and unlock the full potential of Banking Smart Cards in the digital economy.
Conclusion
The Banking Smart Cards market represents a dynamic and transformative segment of the digital payments ecosystem, offering secure, convenient, and versatile solutions for users to access banking services, make transactions, and manage their finances seamlessly. As the market continues to evolve, Smart Card issuers and financial institutions must prioritize innovation, security, interoperability, and customer experience to stay competitive and meet the evolving needs and expectations of users in the rapidly changing landscape of digital finance. By leveraging technological advancements, partnerships, and user-centric design principles, industry players can unlock new opportunities, drive growth, and deliver value-added solutions that enhance financial inclusion, security, and convenience for users worldwide.
What is Banking Smart Cards?
Banking smart cards are secure payment cards that utilize embedded microchips to store and process data, enabling secure transactions and identity verification. They are widely used in financial services for both consumer and business transactions.
What are the key players in the Banking Smart Cards Market?
Key players in the Banking Smart Cards Market include Visa, Mastercard, and American Express, which are known for their extensive payment networks and innovative card technologies. Other notable companies include Gemalto and NXP Semiconductors, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the Banking Smart Cards Market?
The growth of the Banking Smart Cards Market is driven by the increasing demand for secure payment solutions, the rise in contactless payment adoption, and the expansion of e-commerce. Additionally, advancements in card technology and consumer preference for digital transactions contribute to market growth.
What challenges does the Banking Smart Cards Market face?
The Banking Smart Cards Market faces challenges such as the risk of data breaches and fraud, high costs associated with card production and technology upgrades, and regulatory compliance issues. These factors can hinder market expansion and consumer trust.
What opportunities exist in the Banking Smart Cards Market?
Opportunities in the Banking Smart Cards Market include the development of advanced security features, integration with mobile payment systems, and the potential for growth in emerging markets. The increasing focus on digital banking also presents new avenues for innovation.
What trends are shaping the Banking Smart Cards Market?
Trends in the Banking Smart Cards Market include the rise of contactless payments, the integration of biometric authentication, and the shift towards mobile wallet solutions. These innovations are enhancing user experience and security in financial transactions.
Banking Smart Cards Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Card Type | Contactless, Chip, Magnetic Stripe, Dual Interface |
| Application | Retail Payments, Online Transactions, ATM Withdrawals, Loyalty Programs |
| End User | Consumers, Businesses, Financial Institutions, Government Agencies |
| Technology | EMV, NFC, RFID, Biometrics |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Banking Smart Cards Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at