444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
Contactless smart cards have emerged as a versatile and secure solution for banking transactions, offering convenience, speed, and enhanced security to users. These cards incorporate embedded microprocessors and radio frequency identification (RFID) technology, enabling users to make payments by simply tapping or waving the card near a contactless-enabled terminal. The Contactless Smart Cards in Banking Sales Market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by factors such as increasing adoption of cashless payments, technological advancements, and growing consumer demand for seamless banking experiences.
Meaning
Contactless smart cards are payment cards embedded with an integrated circuit chip and an antenna, allowing wireless communication with contactless-enabled terminals. These cards enable users to make payments by tapping or waving the card near the terminal, eliminating the need for physical contact or swiping. Contactless smart cards are widely used in various banking applications, including credit and debit cards, transit fare cards, access control cards, and identification cards, offering fast, convenient, and secure payment solutions to consumers.
Executive Summary
The Contactless Smart Cards in Banking Sales Market is witnessing robust growth, driven by the increasing adoption of contactless payment technology, the proliferation of contactless-enabled terminals, and the growing preference for cashless transactions among consumers. This market offers lucrative opportunities for card manufacturers, financial institutions, technology providers, and retailers involved in the development, distribution, and acceptance of contactless smart cards. Understanding the key market trends, drivers, challenges, and opportunities is essential for stakeholders to capitalize on emerging market trends and gain a competitive edge.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The Contactless Smart Cards in Banking Sales Market operates in a dynamic environment shaped by technological innovations, regulatory changes, consumer preferences, and market trends. These dynamics influence market growth, competition, and strategic decision-making among industry participants. Understanding the market dynamics is essential for stakeholders to capitalize on emerging opportunities, address challenges, and stay competitive in the evolving contactless payment landscape.
Regional Analysis
The Contactless Smart Cards in Banking Sales Market exhibits regional variations in adoption, infrastructure, regulatory environment, and market dynamics. Key regions driving market growth include:
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Contactless Smart Cards in Banking Sales Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
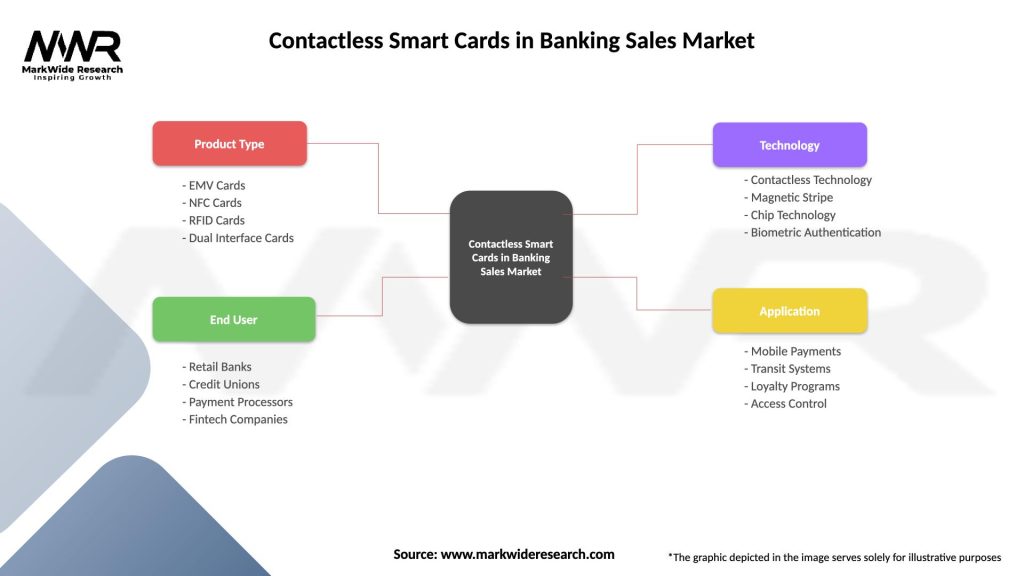
Segmentation
The Contactless Smart Cards in Banking Sales Market can be segmented based on various factors such as:
Segmentation provides insights into market trends, customer preferences, and competitive dynamics, enabling market players to customize their products and services to meet specific market requirements.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
The Contactless Smart Cards in Banking Sales Market offers several benefits for industry participants and stakeholders:
SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis of the Contactless Smart Cards in Banking Sales Market provides insights into its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats:
Understanding these factors through a SWOT analysis enables industry participants to capitalize on strengths, address weaknesses, exploit opportunities, and mitigate threats in the Contactless Smart Cards in Banking Sales Market.
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of contactless payments, driven by hygiene concerns, social distancing measures, and the shift towards cashless transactions. The pandemic has highlighted the importance of contactless smart cards in reducing physical contact with surfaces, minimizing the risk of virus transmission, and enhancing user safety. As consumers prioritize health and safety, contactless payments have become the preferred payment method in retail, transit, hospitality, and other sectors, driving market growth and adoption.
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The Contactless Smart Cards in Banking Sales Market is poised for continued growth and innovation, driven by factors such as technological advancements, changing consumer preferences, regulatory initiatives, and market dynamics. The future of contactless smart cards lies in enhancing security, expanding acceptance infrastructure, fostering innovation, and delivering seamless and personalized payment experiences to users worldwide.
Conclusion
Contactless smart cards have emerged as a versatile and secure payment solution, offering convenience, speed, and enhanced security to users in various banking applications. The Contactless Smart Cards in Banking Sales Market is witnessing robust growth, driven by increasing adoption of contactless payments, technological advancements, and changing consumer behavior. Industry participants and stakeholders can capitalize on emerging market trends by investing in security, expanding acceptance infrastructure, educating consumers, innovating, and delivering personalized payment experiences. By embracing digital transformation and enhancing user engagement, the Contactless Smart Cards in Banking Sales Market can unlock new opportunities, drive market growth, and reshape the future of banking and payments.
What is Contactless Smart Cards in Banking?
Contactless smart cards in banking refer to secure payment cards that utilize RFID or NFC technology to enable transactions without physical contact. These cards enhance convenience and speed for consumers during point-of-sale transactions.
What are the key players in the Contactless Smart Cards in Banking Sales Market?
Key players in the Contactless Smart Cards in Banking Sales Market include Visa, Mastercard, and Gemalto, which are known for their innovative payment solutions and secure transaction technologies, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the Contactless Smart Cards in Banking Sales Market?
The growth of the Contactless Smart Cards in Banking Sales Market is driven by increasing consumer demand for convenience, the rise of e-commerce, and the need for enhanced security in financial transactions.
What challenges does the Contactless Smart Cards in Banking Sales Market face?
Challenges in the Contactless Smart Cards in Banking Sales Market include concerns over security vulnerabilities, the need for widespread infrastructure to support contactless payments, and consumer resistance to adopting new technologies.
What future opportunities exist in the Contactless Smart Cards in Banking Sales Market?
Future opportunities in the Contactless Smart Cards in Banking Sales Market include the integration of biometric authentication, the expansion of mobile payment solutions, and the potential for partnerships with fintech companies to enhance user experience.
What trends are shaping the Contactless Smart Cards in Banking Sales Market?
Trends shaping the Contactless Smart Cards in Banking Sales Market include the increasing adoption of mobile wallets, advancements in card technology such as dual-interface cards, and a growing focus on sustainability in card production.
Contactless Smart Cards in Banking Sales Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | EMV Cards, NFC Cards, RFID Cards, Dual Interface Cards |
| End User | Retail Banks, Credit Unions, Payment Processors, Fintech Companies |
| Technology | Contactless Technology, Magnetic Stripe, Chip Technology, Biometric Authentication |
| Application | Mobile Payments, Transit Systems, Loyalty Programs, Access Control |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Contactless Smart Cards in Banking Sales Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at