444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The Real Estate Rental market serves as a cornerstone of the housing industry, providing individuals and businesses with opportunities to lease residential, commercial, and industrial properties for various purposes. This market facilitates the transfer of temporary ownership rights from property owners (landlords) to tenants in exchange for periodic rental payments. Real estate rentals offer flexibility and convenience to tenants while allowing property owners to generate income from their investments.
Meaning
The Real Estate Rental market encompasses the leasing of residential properties (apartments, houses, condos), commercial properties (office spaces, retail stores, warehouses), and industrial properties (factories, manufacturing facilities). Rentals can be short-term or long-term, and the terms of the lease agreement typically dictate the duration, rental rate, responsibilities of the landlord and tenant, and other conditions governing the rental relationship.
Executive Summary
The Real Estate Rental market is a vital component of the real estate industry, catering to the diverse needs of individuals, families, businesses, and investors seeking temporary occupancy or usage of properties without the financial commitment of ownership. This market offers opportunities for property owners to generate passive income, diversify their investment portfolios, and capitalize on property appreciation while providing tenants with housing, workspace, or operational facilities tailored to their requirements.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The Real Estate Rental market operates within a dynamic environment shaped by economic, demographic, technological, and regulatory factors. Market dynamics influence rental pricing, occupancy rates, investment decisions, and tenant preferences, requiring stakeholders to adapt and innovate to stay competitive and meet evolving market demands.
Regional Analysis
The Real Estate Rental market exhibits regional variations influenced by factors such as population density, economic activity, housing affordability, regulatory frameworks, and cultural preferences. Let’s explore some key regions and their unique rental market characteristics:
Competitive Landscape
Leading companies Real Estate Rental Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Segmentation
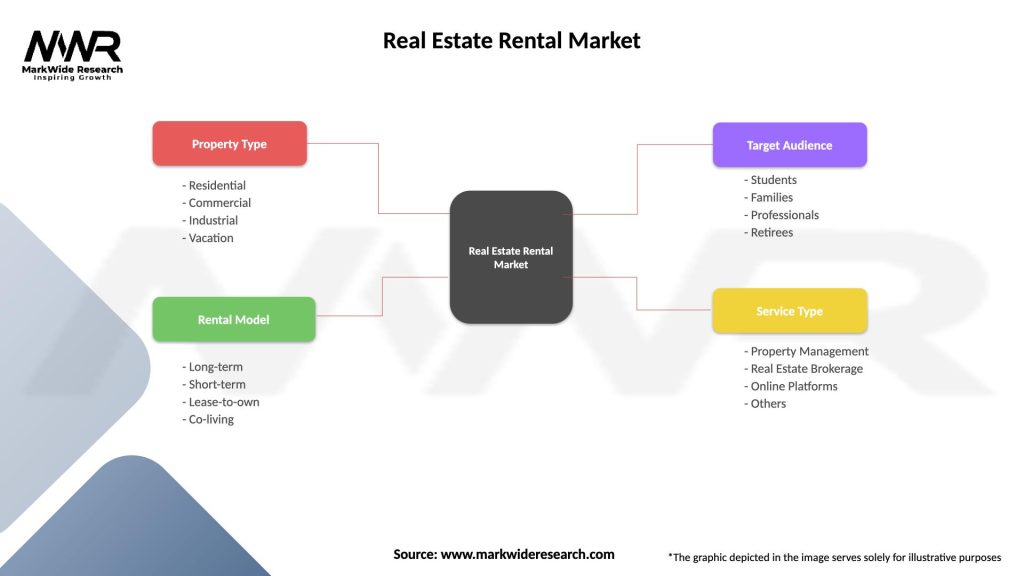
The Real Estate Rental market can be segmented based on property type, location, rental rates, and tenant demographics, providing insights into market dynamics and investment opportunities. Common segmentation categories include:
Segmentation allows landlords, investors, and property managers to target specific market segments, tailor their marketing strategies, and optimize rental property performance to maximize returns on investment.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Understanding these factors through a SWOT analysis helps stakeholders identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats in the Real Estate Rental market, informing strategic decision-making and risk management strategies.
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on the Real Estate Rental market, affecting rental demand, occupancy rates, rental prices, and property management practices:
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future outlook for Italy’s Real Estate Rental market appears promising, albeit with some challenges. As Italy recovers from the economic impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic, the rental market is expected to witness steady growth, driven by factors such as urbanization, demographic shifts, and changing lifestyle preferences. However, challenges such as housing affordability, regulatory uncertainties, and infrastructure constraints may dampen growth prospects. Innovative solutions, technological advancements, and collaborative efforts among stakeholders will be key to addressing these challenges and unlocking the full potential of Italy’s Real Estate Rental market in the coming years.
Conclusion
The Real Estate Rental market plays a vital role in providing housing, workspace, and operational facilities to individuals, families, businesses, and communities worldwide. Despite the challenges posed by economic uncertainties, regulatory complexities, and the COVID-19 pandemic, the rental market remains resilient, adaptive, and essential for meeting the diverse needs of tenants and property owners alike. By embracing innovation, sustainability, and inclusivity, stakeholders can navigate market dynamics, capitalize on emerging opportunities, and contribute to the continued growth and prosperity of the Real Estate Rental market in the years to come.
What is Real Estate Rental?
Real Estate Rental refers to the process of leasing residential or commercial properties to tenants for a specified period. This market encompasses various property types, including apartments, houses, and office spaces, catering to diverse consumer needs.
What are the key players in the Real Estate Rental Market?
Key players in the Real Estate Rental Market include companies like Zillow, Apartment List, and Redfin, which provide platforms for property listings and rental services. Additionally, property management firms and real estate agencies play significant roles in facilitating rentals, among others.
What are the main drivers of the Real Estate Rental Market?
The Real Estate Rental Market is driven by factors such as urbanization, increasing demand for flexible living arrangements, and rising housing costs. Additionally, the growth of remote work has led to a surge in demand for rental properties in suburban areas.
What challenges does the Real Estate Rental Market face?
Challenges in the Real Estate Rental Market include regulatory hurdles, fluctuating property prices, and competition from short-term rental platforms. These factors can impact rental availability and pricing strategies for landlords.
What opportunities exist in the Real Estate Rental Market?
Opportunities in the Real Estate Rental Market include the expansion of co-living spaces and the integration of technology in property management. Additionally, the increasing interest in sustainable living options presents new avenues for growth.
What trends are shaping the Real Estate Rental Market?
Trends in the Real Estate Rental Market include the rise of smart home technology, increased focus on tenant experience, and the growing popularity of flexible lease terms. These trends are influencing how properties are marketed and managed.
Real Estate Rental Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Property Type | Residential, Commercial, Industrial, Vacation |
| Rental Model | Long-term, Short-term, Lease-to-own, Co-living |
| Target Audience | Students, Families, Professionals, Retirees |
| Service Type | Property Management, Real Estate Brokerage, Online Platforms, Others |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies Real Estate Rental Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at