444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2750
Market Overview: The Asia-Pacific Military 4D Printing Market stands at the intersection of advanced manufacturing and defense technology, heralding a new era in the production of military equipment. 4D printing, an extension of 3D printing, introduces the dimension of time, allowing objects to transform or adapt to different conditions. In the military context, this technology revolutionizes the fabrication of critical components, offering enhanced adaptability, efficiency, and customization. As nations in the Asia-Pacific region prioritize modernizing their defense capabilities, the Military 4D Printing Market emerges as a key driver of innovation and strategic advantage.
Meaning: Military 4D printing refers to the application of 4D printing technology in the defense and military sectors. Traditional 3D printing involves layer-by-layer construction of objects, while 4D printing adds the element of time, enabling the printed objects to respond to external stimuli or conditions. In the military context, this translates to the creation of adaptive and shape-changing materials that can be utilized in various applications, from equipment and gear to critical infrastructure components.
Executive Summary: The Asia-Pacific Military 4D Printing Market represents a paradigm shift in defense manufacturing, offering dynamic solutions that align with the region’s evolving security challenges. As nations strive to enhance their military capabilities, the adoption of 4D printing technology provides a competitive edge by enabling the rapid production of customized components, reducing logistical challenges, and enhancing operational flexibility. This executive summary provides a glimpse into the transformative potential of Military 4D Printing in the Asia-Pacific region.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights:
Market Drivers:
Market Restraints:
Market Opportunities:
Market Dynamics: The Asia-Pacific Military 4D Printing Market operates in a dynamic environment shaped by geopolitical shifts, technological breakthroughs, and evolving defense strategies. The dynamics of the market necessitate adaptability from defense organizations, industry players, and governments. Understanding and responding to these dynamics are crucial for maintaining a strategic advantage and addressing emerging challenges.
Regional Analysis:
Competitive Landscape:
Leading Companies in Asia-Pacific Military 4D Printing Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
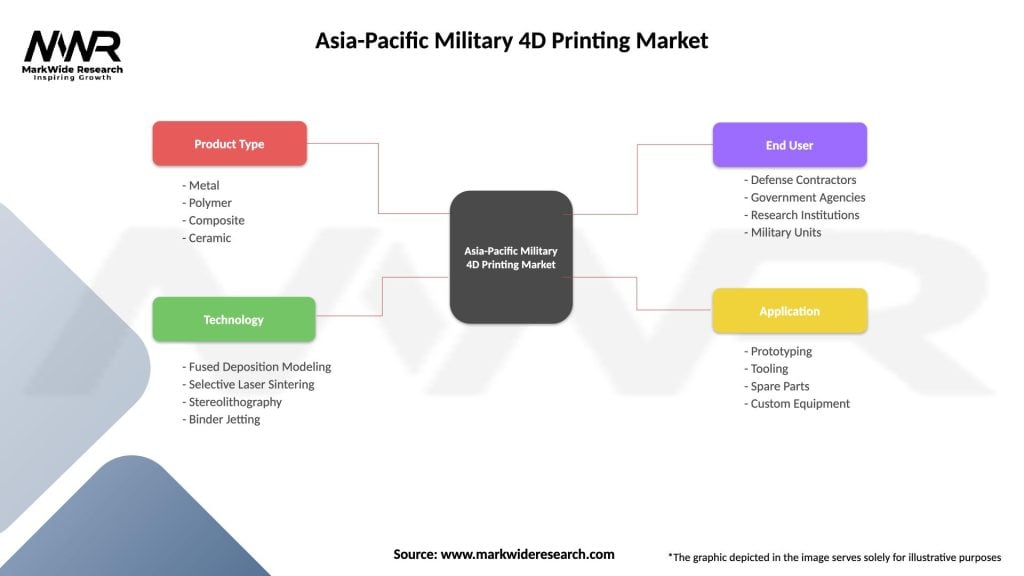
Segmentation: The Military 4D Printing Market can be segmented based on applications, materials, and end-users. Segmentation allows for a nuanced understanding of the market landscape and the identification of specific opportunities and challenges within each segment.
Category-wise Insights:
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders:
SWOT Analysis: A SWOT analysis provides insights into the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of the Asia-Pacific Military 4D Printing Market.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends:
Covid-19 Impact: The COVID-19 pandemic has underscored the importance of resilient and adaptable defense capabilities. Military 4D Printing, with its capacity for on-demand production and customization, has proven valuable during times of disruption. The pandemic has accelerated interest and investments in 4D printing technologies as nations seek to enhance their defense preparedness and reduce vulnerabilities to supply chain disruptions.
Key Industry Developments:
Analyst Suggestions:
Future Outlook: The Asia-Pacific Military 4D Printing Market is poised for significant growth, driven by a combination of strategic imperatives, technological advancements, and the need for agile defense capabilities. The future will likely see increased investments in research and development, expanded applications of 4D printing in defense, and a growing ecosystem of collaboration between governments, industry players, and research institutions.
Conclusion: The Asia-Pacific Military 4D Printing Market represents a transformative force in defense manufacturing, offering nations in the region the opportunity to reshape their defense capabilities. As technology continues to evolve, Military 4D Printing stands as a strategic enabler for nations seeking to enhance operational flexibility, reduce dependencies on external suppliers, and stay at the forefront of defense innovation. The collaboration between governments, industry stakeholders, and research institutions will play a pivotal role in realizing the full potential of 4D printing technologies and securing a resilient and technologically advanced future for the defense sector in the Asia-Pacific region.
What is Military 4D Printing?
Military 4D Printing refers to the advanced manufacturing process that allows for the creation of materials and structures that can change shape or function over time, specifically tailored for military applications such as equipment, vehicles, and weaponry.
What are the key players in the Asia-Pacific Military 4D Printing Market?
Key players in the Asia-Pacific Military 4D Printing Market include companies like Stratasys, 3D Systems, and Lockheed Martin, which are known for their innovations in additive manufacturing technologies, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the Asia-Pacific Military 4D Printing Market?
The growth of the Asia-Pacific Military 4D Printing Market is driven by the increasing demand for lightweight and customizable military equipment, advancements in materials science, and the need for rapid prototyping and production capabilities.
What challenges does the Asia-Pacific Military 4D Printing Market face?
Challenges in the Asia-Pacific Military 4D Printing Market include high initial investment costs, regulatory hurdles regarding military applications, and the need for skilled personnel to operate advanced printing technologies.
What opportunities exist in the Asia-Pacific Military 4D Printing Market?
Opportunities in the Asia-Pacific Military 4D Printing Market include the potential for developing smart materials that can adapt to battlefield conditions, collaborations between defense contractors and technology firms, and the expansion of 4D printing applications in logistics and supply chain management.
What trends are shaping the Asia-Pacific Military 4D Printing Market?
Trends in the Asia-Pacific Military 4D Printing Market include the integration of artificial intelligence in design processes, the use of biocompatible materials for medical applications, and the increasing focus on sustainability in military manufacturing practices.
Asia-Pacific Military 4D Printing Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Metal, Polymer, Composite, Ceramic |
| Technology | Fused Deposition Modeling, Selective Laser Sintering, Stereolithography, Binder Jetting |
| End User | Defense Contractors, Government Agencies, Research Institutions, Military Units |
| Application | Prototyping, Tooling, Spare Parts, Custom Equipment |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at