444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The Role-based Access Control (RBAC) market is a pivotal segment within the broader realm of cybersecurity and access management solutions. RBAC represents a sophisticated approach to defining and managing user permissions within an organization’s digital infrastructure. This market plays a crucial role in enhancing data security, regulatory compliance, and overall governance by ensuring that individuals are granted access based on their roles and responsibilities.
Meaning
Role-based Access Control (RBAC) is a security model that regulates system access by assigning specific roles to users. These roles, defined by an organization’s administrators, determine the level of access and permissions individuals have within digital systems. RBAC provides a structured and efficient method for managing user privileges, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
Executive Summary
The RBAC market has witnessed substantial growth as organizations increasingly recognize the significance of granular access control. The need for robust cybersecurity measures, compliance with data protection regulations, and the rising complexity of digital environments contribute to the market’s expansion. RBAC solutions offer a strategic approach to access management, aligning user permissions with organizational hierarchies and operational requirements.
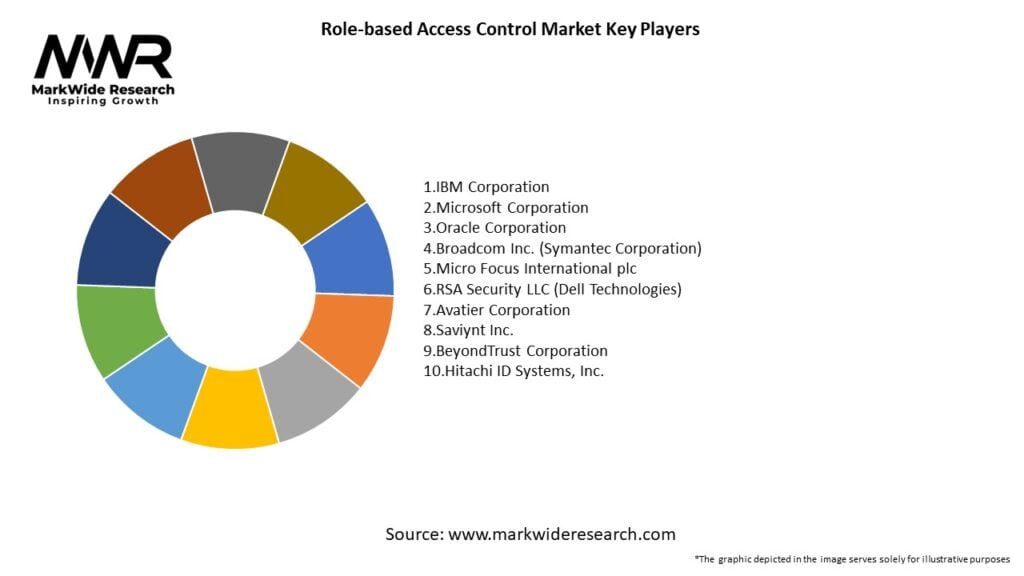

Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The RBAC market operates within a dynamic cybersecurity landscape influenced by factors such as evolving threat vectors, technological advancements, regulatory changes, and the continuous expansion of digital ecosystems. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for organizations seeking to enhance their access management capabilities and strengthen their overall cybersecurity posture.
Regional Analysis
The adoption of RBAC solutions varies across regions due to factors such as cybersecurity awareness, regulatory environments, and industry practices. A regional analysis provides insights into the deployment and growth of RBAC solutions in key geographical areas:
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Role-based Access Control Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
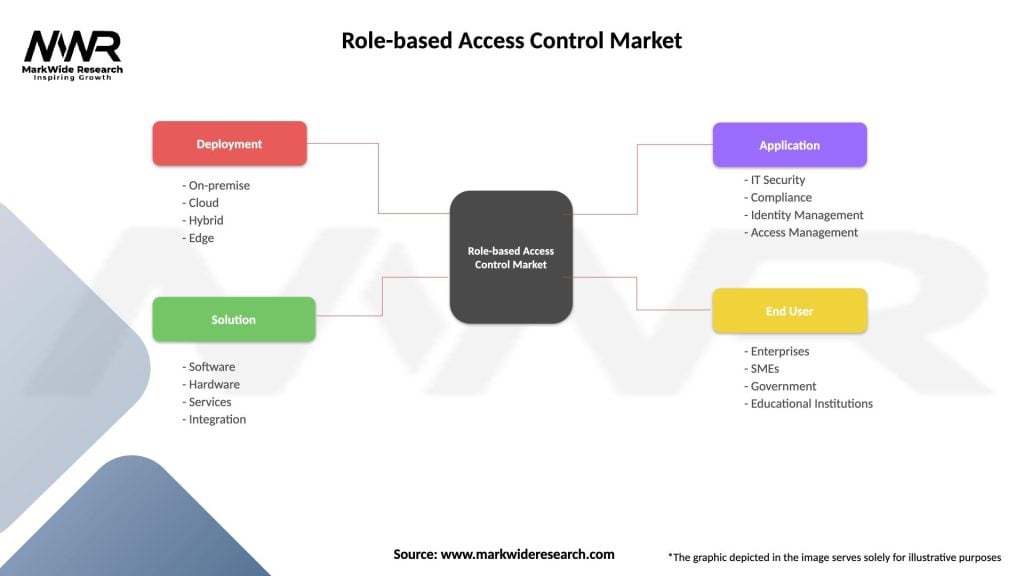
Segmentation
The RBAC market can be segmented based on various factors, including:
Segmentation provides a nuanced understanding of the RBAC market landscape, allowing organizations to select solutions that align with their specific needs and operational requirements.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
The RBAC market offers several benefits for industry participants and stakeholders:
SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis provides a comprehensive view of the RBAC market’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats:
Understanding these factors through a SWOT analysis assists organizations, solution providers, and stakeholders in making informed decisions, leveraging strengths, addressing weaknesses, capitalizing on opportunities, and mitigating potential threats.
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has influenced the RBAC market in several ways:
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future outlook for the RBAC market remains positive, driven by the increasing importance of access controls in the face of evolving cybersecurity threats. The market is expected to witness continued innovation, with a focus on enhancing user authentication methods, integrating with emerging technologies, and adapting to the changing landscape of remote and distributed work.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Role-based Access Control (RBAC) market stands at the forefront of cybersecurity solutions, providing organizations with a strategic and structured approach to access management. As organizations navigate complex digital environments, RBAC emerges as a fundamental tool for ensuring that user permissions align with organizational hierarchies, operational requirements, and regulatory standards. The market’s evolution, marked by technological advancements, regulatory shifts, and a heightened awareness of cybersecurity, positions RBAC as a critical element in safeguarding sensitive data and mitigating access-related risks. By embracing continuous innovation, adapting to remote work trends, and integrating seamlessly with broader cybersecurity strategies, RBAC solutions contribute significantly to creating resilient and secure digital ecosystems for organizations across diverse industries.
What is Role-based Access Control?
Role-based Access Control (RBAC) is a method of regulating access to computer or network resources based on the roles of individual users within an organization. It helps in managing permissions and ensuring that users have access only to the information necessary for their job functions.
What are the key players in the Role-based Access Control Market?
Key players in the Role-based Access Control Market include Microsoft, IBM, Okta, and SailPoint, among others. These companies provide various solutions that help organizations implement and manage RBAC effectively.
What are the main drivers of growth in the Role-based Access Control Market?
The main drivers of growth in the Role-based Access Control Market include the increasing need for data security, the rise in cyber threats, and the growing adoption of cloud-based services. Organizations are prioritizing RBAC to enhance their security frameworks and comply with regulations.
What challenges does the Role-based Access Control Market face?
The Role-based Access Control Market faces challenges such as the complexity of implementation, resistance to change from employees, and the need for continuous updates to access policies. These factors can hinder the effective deployment of RBAC systems.
What opportunities exist in the Role-based Access Control Market?
Opportunities in the Role-based Access Control Market include the integration of artificial intelligence for smarter access management and the expansion of RBAC solutions in small and medium-sized enterprises. Additionally, the increasing focus on regulatory compliance presents further growth potential.
What trends are shaping the Role-based Access Control Market?
Trends shaping the Role-based Access Control Market include the shift towards zero trust security models, the rise of identity and access management solutions, and the growing importance of user behavior analytics. These trends are influencing how organizations approach access control strategies.
Role-based Access Control Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Deployment | On-premise, Cloud, Hybrid, Edge |
| Solution | Software, Hardware, Services, Integration |
| Application | IT Security, Compliance, Identity Management, Access Management |
| End User | Enterprises, SMEs, Government, Educational Institutions |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Role-based Access Control Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at