444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The remittance market plays a crucial role in facilitating the transfer of money across borders. It encompasses the transfer of funds from migrants or foreign workers to their home countries. These transfers are typically used to support families, invest in businesses, or meet personal financial needs. The market has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by factors such as increasing migration, advancements in technology, and the globalization of the economy.
Meaning
Remittance refers to the process of sending money by individuals living and working in a foreign country back to their home country. It serves as an essential lifeline for many households in developing nations, providing a steady stream of income and contributing to economic stability. Remittance can be sent through various channels, including banks, money transfer operators (MTOs), online platforms, and mobile payment apps
Executive Summary
The remittance market has experienced substantial growth in recent years, driven by factors such as increasing migration, technological advancements, and the need for cross-border financial transactions. This report provides an in-depth analysis of the market, focusing on key market insights, drivers, restraints, opportunities, regional analysis, competitive landscape, segmentation, and industry developments.
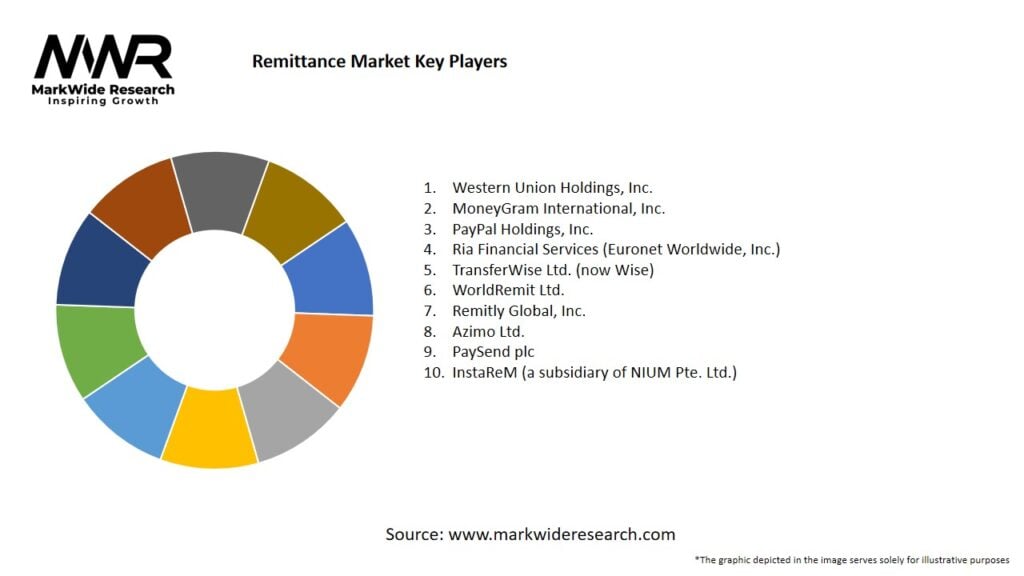
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The remittance market is dynamic and influenced by various factors. Changing migration patterns, advancements in technology, regulatory developments, and economic conditions play a significant role in shaping the market landscape. The industry is highly competitive, with both traditional financial institutions and fintech startups vying for market share. Market participants need to stay abreast of these dynamics and adapt their strategies accordingly to thrive in the evolving landscape.
Regional Analysis
The remittance market exhibits variations across different regions. Asia Pacific, particularly countries like India, China, and the Philippines, has traditionally been the largest recipient of remittances due to large diaspora populations. The Middle East is a significant source of remittance outflows, driven by the presence of expatriate workers. Africa and Latin America also witness substantial remittance flows. Regional differences in regulatory frameworks, infrastructure, and economic conditions influence market dynamics and the choice of remittance channels.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Remittance Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
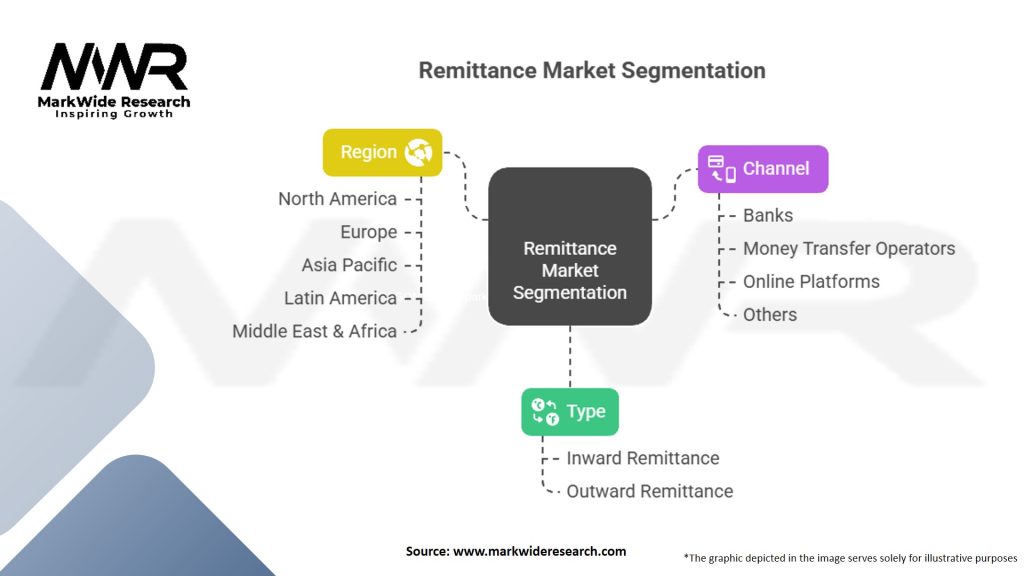
Segmentation
The remittance market can be segmented based on the type of remittance channel, including banks, money transfer operators, online platforms, and mobile payment apps. It can also be segmented by the mode of transfer, such as cash-to-cash, bank-to-bank, cash-to-account, and account-to-cash. Additionally, the market can be segmented by the purpose of remittance, including family support, education, investments, and savings.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic had a significant impact on the remittance market. The global travel restrictions, economic slowdown, and job losses among migrant populations disrupted remittance flows. However, the pandemic also accelerated the adoption of digital remittance channels as traditional physical channels faced challenges. The pandemic highlighted the importance of resilient and efficient remittance systems, driving market players to invest in digital infrastructure and customer-centric solutions.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The remittance market is expected to continue its growth trajectory in the coming years. Factors such as increasing global migration, technological advancements, and the focus on financial inclusion will drive market expansion. Digital channels will dominate the market, with the adoption of blockchain technology and AI-powered solutions offering enhanced security and convenience. Regulatory reforms and collaborative efforts will shape the industry landscape, fostering a competitive and customer-centric market.
Conclusion
The remittance market plays a vital role in facilitating cross-border money transfers, supporting families, and driving economic development. The market is evolving rapidly, driven by increasing migration, technological advancements, and changing customer preferences. Industry players need to embrace digital transformation, collaborate with fintech startups, and ensure regulatory compliance to thrive in the competitive landscape. The future of the remittance market looks promising, with a focus on digital channels, innovation, and financial inclusion, offering new opportunities for industry participants and stakeholders.
What is the remittance?
Remittance refers to the transfer of money by a foreign worker to an individual in their home country. This financial flow is crucial for many economies, providing essential support for families and contributing to local development.
Who are the major players in the remittance market?
Major players in the remittance market include Western Union, MoneyGram, PayPal, and TransferWise, among others. These companies offer various services to facilitate cross-border money transfers, catering to different consumer needs.
What are the key drivers of growth in the remittance market?
Key drivers of growth in the remittance market include increasing migration rates, the rise of digital payment platforms, and the growing need for financial inclusion in developing countries. These factors enhance the accessibility and efficiency of remittance services.
What challenges does the remittance market face?
The remittance market faces challenges such as high transaction fees, regulatory compliance issues, and competition from informal money transfer methods. These factors can hinder the growth and efficiency of formal remittance services.
What opportunities exist in the remittance market for future growth?
Opportunities in the remittance market include the expansion of blockchain technology for faster transactions, partnerships with fintech companies, and the increasing demand for mobile money services. These trends can enhance service delivery and customer experience.
What trends are shaping the remittance market today?
Current trends in the remittance market include the shift towards digital and mobile platforms, the integration of artificial intelligence for fraud detection, and the growing popularity of cryptocurrency for cross-border transactions. These innovations are transforming how remittances are sent and received.
Remittance Market
| Segmentation | Details |
|---|---|
| Type | Inward Remittance, Outward Remittance |
| Channel | Banks, Money Transfer Operators, Online Platforms, Others |
| Region | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Remittance Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at