444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
Market Overview
The US Integrated Delivery Network (IDN) market is a crucial component of the country’s healthcare industry. Integrated Delivery Networks refer to organizations that encompass various healthcare providers, such as hospitals, clinics, physician practices, and other ancillary service providers, collaborating to deliver comprehensive and coordinated patient care. These networks aim to improve patient outcomes, enhance operational efficiency, and reduce healthcare costs by integrating services, sharing patient information, and coordinating care across different healthcare settings.
Meaning
Integrated Delivery Networks (IDNs) play a pivotal role in the US healthcare system by facilitating seamless collaboration among healthcare providers. These networks bring together hospitals, clinics, physician groups, laboratories, pharmacies, and other healthcare entities under one umbrella. The primary objective of IDNs is to provide a unified and coordinated approach to patient care. This integration allows for better care coordination, information sharing, and resource allocation, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes and cost savings.
Executive Summary
The US Integrated Delivery Network market is witnessing significant growth and transformation due to the increasing emphasis on value-based care, population health management, and healthcare consolidation. IDNs are becoming the preferred choice for healthcare providers as they offer a comprehensive range of services, promote care coordination, and leverage economies of scale. This executive summary provides a concise overview of the key market insights, drivers, restraints, opportunities, and trends shaping the US IDN market.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The US IDN market is characterized by dynamic trends, evolving regulations, and changing consumer expectations. The market dynamics are influenced by factors such as healthcare policy reforms, technological advancements, industry consolidation, and patient-centric care models. The ongoing shift from volume-based to value-based care and the increasing focus on care coordination and patient outcomes are expected to drive the growth of the IDN market. However, challenges related to financial sustainability, interoperability, and regulatory compliance need to be addressed for the successful implementation and expansion of IDNs.
Regional Analysis
The US IDN market exhibits regional variations based on factors such as population demographics, healthcare infrastructure, reimbursement models, and regulatory environments. While IDNs are prevalent throughout the country, certain regions, such as the Northeast and the West Coast, have witnessed a higher degree of consolidation and integration among healthcare providers. Urban areas tend to have a higher concentration of IDNs compared to rural regions. Regional analysis helps identify market trends, opportunities, and challenges specific to different geographies, enabling targeted strategies for market participants.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the US Integrated Delivery Network Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.

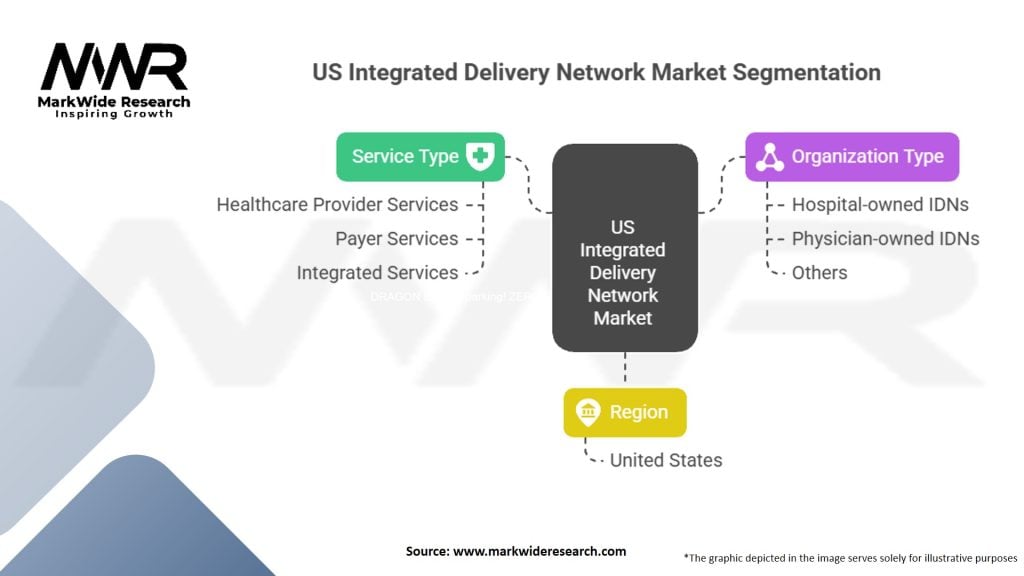
Segmentation
The US IDN market can be segmented based on several factors, including geographical location, organizational size, and service offerings. Geographically, the market can be divided into regions such as the Northeast, Midwest, South, and West. Organizational size segmentation can include small, medium, and large IDNs, based on the number of affiliated healthcare entities and patient population served. Service offerings segmentation may encompass primary care, specialty care, diagnostics, pharmacy services, and post-acute care, among others.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Strengths
Weaknesses
Opportunities
Threats
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic had a profound impact on the US healthcare system and accelerated the adoption of integrated care delivery models. IDNs played a critical role in responding to the crisis by coordinating testing, treatment, and vaccination efforts. The pandemic highlighted the importance of care coordination, data sharing, and virtual care capabilities within IDNs. The increased use of telehealth services and remote monitoring technologies during the pandemic further emphasized the need for integrated healthcare systems. As the healthcare system continues to recover and adapt to the post-pandemic landscape, IDNs are expected to play a vital role in ensuring the resilience and effectiveness of healthcare delivery.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The US Integrated Delivery Network market is poised for continued growth and transformation. The ongoing shift towards value-based care, advancements in healthcare technology, and the increasing focus on care coordination and patient outcomes will drive the expansion of IDNs. The integration of digital health solutions, telehealth, and data analytics will further enhance the capabilities of IDNs in delivering high-quality, cost-effective care. However, challenges related to interoperability, financial sustainability, and regulatory compliance need to be effectively addressed for the successful development and scalability of IDNs.
Conclusion
The US Integrated Delivery Network market is a vital component of the healthcare industry, aimed at improving patient outcomes, enhancing care coordination, and reducing healthcare costs. IDNs bring together various healthcare providers under one umbrella, promoting collaboration, information sharing, and comprehensive care delivery. The market is driven by factors such as the shift towards value-based care, rising healthcare costs, technological advancements, and the need for population health management. Despite challenges, IDNs present significant opportunities for industry participants and stakeholders, including enhanced care coordination, improved patient outcomes, cost savings, and data-driven decision-making. Looking ahead, IDNs are expected to play a crucial role in shaping the future of healthcare delivery in the United States.
What is the US Integrated Delivery Network?
The US Integrated Delivery Network refers to a coordinated system of healthcare providers and organizations that deliver a continuum of care to patients. This model aims to improve healthcare quality, reduce costs, and enhance patient satisfaction through integrated services across various settings.
Who are the key players in the US Integrated Delivery Network Market?
Key players in the US Integrated Delivery Network Market include major healthcare organizations such as Kaiser Permanente, HCA Healthcare, and Ascension Health, among others. These companies are known for their extensive networks that provide a range of healthcare services.
What are the main drivers of growth in the US Integrated Delivery Network Market?
The main drivers of growth in the US Integrated Delivery Network Market include the increasing demand for coordinated care, the rise in chronic diseases, and the push for cost-effective healthcare solutions. Additionally, advancements in technology and patient engagement strategies are contributing to this growth.
What challenges does the US Integrated Delivery Network Market face?
The US Integrated Delivery Network Market faces challenges such as regulatory compliance, the complexity of integrating diverse healthcare services, and the need for significant investment in technology. These factors can hinder the effective implementation of integrated care models.
What opportunities exist in the US Integrated Delivery Network Market?
Opportunities in the US Integrated Delivery Network Market include the potential for expanding telehealth services, enhancing patient data analytics, and developing partnerships with technology firms. These opportunities can lead to improved patient outcomes and operational efficiencies.
What trends are shaping the US Integrated Delivery Network Market?
Trends shaping the US Integrated Delivery Network Market include the increasing focus on value-based care, the integration of artificial intelligence in patient management, and the growing emphasis on preventive care. These trends are transforming how healthcare is delivered and managed.
US Integrated Delivery Network Market
| Segmentation | Details |
|---|---|
| Service Type | Healthcare Provider Services, Payer Services, Integrated Services |
| Organization Type | Hospital-owned IDNs, Physician-owned IDNs, Others |
| Region | United States |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the US Integrated Delivery Network Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at