444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The Global Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) Market is a crucial component of modern urban transportation systems, revolutionizing the way people commute in densely populated areas. MRT systems, often referred to as subways or metros, provide efficient, fast, and sustainable modes of public transportation. They have become an essential part of urban infrastructure, contributing to reduced traffic congestion, improved air quality, and enhanced mobility in metropolitan regions worldwide. The market’s significance lies in its role in shaping the future of urban transportation, promoting sustainable living, and addressing the challenges of rapid urbanization.
Meaning
The Global Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) Market embodies the transformation of urban mobility. It represents the culmination of technological advancements, engineering excellence, and the collective effort to create efficient and sustainable transportation solutions for densely populated cities. MRT systems are more than just trains; they are lifelines, connecting communities, reducing pollution, and promoting economic growth. The market signifies progress toward smarter, greener, and more accessible urban living. It symbolizes the commitment to addressing the challenges of urbanization while improving the quality of life for millions of people worldwide.
Executive Summary
The executive summary of the Global Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) Market provides a concise overview of the market’s significance in the context of urban transportation. It emphasizes the pivotal role of MRT systems in alleviating traffic congestion, reducing environmental impact, and enhancing the overall quality of life in densely populated cities. The summary highlights key market insights, challenges, and opportunities, setting the stage for a comprehensive analysis of the MRT industry.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
The Global Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) Market is characterized by several key insights that underscore its significance and potential:
Market Drivers
The Global Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) Market is driven by several key factors:
Market Restraints
Despite its significance, the Global Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) Market faces certain challenges and restraints:
Market Opportunities
The Global Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) Market offers several opportunities for growth and development:
Market Dynamics
The Global Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) Market is characterized by dynamic factors that shape its growth and evolution:
Regional Analysis
The Global Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) Market exhibits regional variations influenced by factors such as urbanization levels, government investments, and transportation priorities:
Asia-Pacific: The Asia-Pacific region leads in MRT development and expansion, with countries like China and India investing heavily in urban transportation infrastructure to address rapid urbanization.
Europe: European cities boast well-established and efficient MRT systems, emphasizing sustainability and integrated transportation networks.
North America: North American cities are expanding MRT systems to reduce traffic congestion and provide alternatives to private car usage.
Middle East and Africa: Some Middle Eastern cities are investing in MRT systems to address urban transportation challenges and promote economic growth.
Latin America: Latin American countries are exploring MRT expansion to improve mobility and reduce environmental impact in major cities.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Global Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.

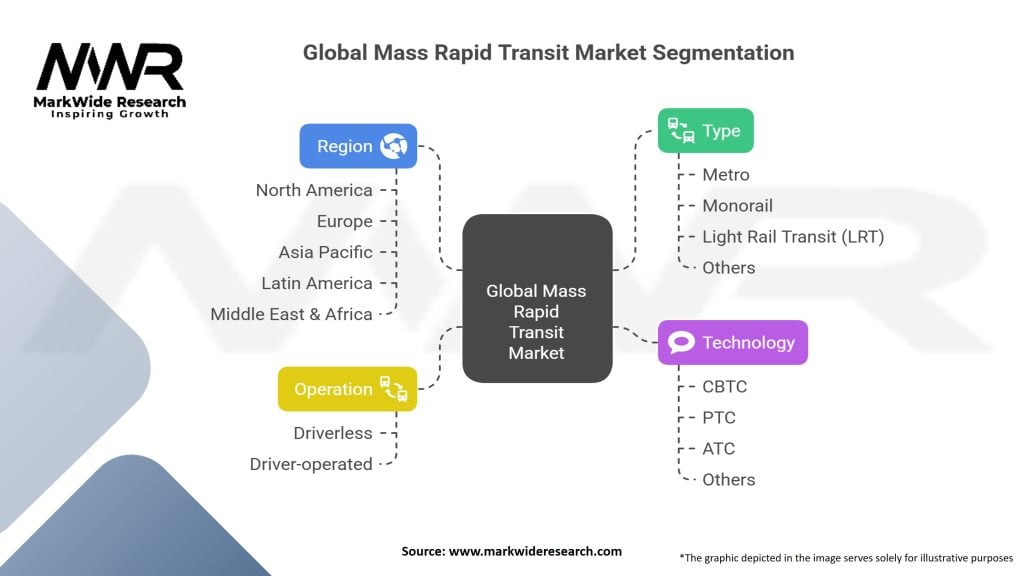
Segmentation
The Global Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) Market can be segmented based on several factors to gain a comprehensive understanding of its diverse offerings and applications:
By Type:
By Technology:
By Region:
Segmentation provides insights into the specific types of MRT systems, their technologies, and regional preferences within the market.
Category-wise Insights
Each category within the Global Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) Market offers unique insights and considerations:
Type: Distinct MRT types cater to various urban settings, from densely populated city centers to medium-density suburbs, allowing for customized solutions to meet diverse transportation needs.
Technology: The choice between automated and conventional MRT systems impacts safety, operational efficiency, and capital costs, requiring careful evaluation based on local requirements and budget constraints.
Each category presents opportunities for customization and specialization, ensuring that MRT solutions align with urban planning goals and passenger expectations.
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
Industry participants and stakeholders in the Global Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) Market can expect several key benefits:
SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis provides a comprehensive view of the Global Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) Market’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats:
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
The Global Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) Market is characterized by several key trends that shape its trajectory:
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic had significant impacts on the Global Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) Market:
Key Industry Developments
Several key industry developments have shaped the Global Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) Market:
Analyst suggestions offer practical recommendations for industry participants, including a focus on technological innovation, sustainability, smart city integration, and financial resilience.
Future Outlook
The future of the Global Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) Market is characterized by several key trends and factors that will shape its trajectory:
The market is poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of urban transportation, promoting sustainability, and improving the quality of life for urban residents.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Global Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) Market stands at the forefront of urban transportation innovation, offering efficient, sustainable, and interconnected mobility solutions for the world’s growing urban populations. MRT systems symbolize progress toward smarter, greener, and more accessible cities, addressing the challenges of rapid urbanization while enhancing the overall quality of life for millions.
Analyst suggestions offer practical recommendations for industry participants, including a focus on automation, sustainability, smart city integration, and financial resilience. The future outlook anticipates continued automation, sustainability commitment, integrated mobility, technological advancements, transit-oriented development, flexible scheduling, digitalization, and resilience in navigating uncertainties. The market is positioned to shape the future of urban transportation, promoting sustainability, and improving the quality of life for urban residents while adapting to evolving trends and challenges.
What is Global Mass Rapid Transit (MRT)?
Global Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) refers to a public transportation system designed to move large numbers of people efficiently within urban areas. It includes various modes such as subways, light rail, and bus rapid transit, aimed at reducing traffic congestion and promoting sustainable urban mobility.
Who are the key players in the Global Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) Market?
Key players in the Global Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) Market include Siemens AG, Bombardier Inc., Alstom SA, and Hitachi Ltd., among others. These companies are involved in the development and implementation of MRT systems worldwide.
What are the main drivers of growth in the Global Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) Market?
The main drivers of growth in the Global Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) Market include increasing urbanization, rising environmental concerns, and government investments in public transportation infrastructure. These factors contribute to the demand for efficient and sustainable transit solutions.
What challenges does the Global Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) Market face?
The Global Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) Market faces challenges such as high initial capital costs, regulatory hurdles, and the need for ongoing maintenance and upgrades. Additionally, public resistance to changes in transportation infrastructure can hinder project implementation.
What opportunities exist in the Global Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) Market?
Opportunities in the Global Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) Market include the integration of smart technologies, expansion into underserved regions, and the development of eco-friendly transit solutions. These trends can enhance operational efficiency and improve user experience.
What trends are shaping the Global Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) Market?
Trends shaping the Global Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) Market include the adoption of electric and autonomous vehicles, the implementation of contactless payment systems, and the focus on enhancing passenger experience through digital solutions. These innovations aim to make transit systems more efficient and user-friendly.
Global Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) Market:
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | Metro, Monorail, Light Rail Transit (LRT), Others |
| Technology | CBTC, PTC, ATC, Others |
| Operation | Driverless, Driver-operated |
| Region | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Global Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at