444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
The ingestible sensor market is a rapidly growing sector within the healthcare and medical device industry. In recent years, there has been a significant increase in the adoption of ingestible sensor technology, driven by advancements in wireless communication, miniaturization of electronics, and the need for real-time patient monitoring. These ingestible sensors are designed to be swallowed and can transmit valuable data from inside the body to external devices, providing healthcare professionals with crucial insights into a patient’s health status.
Ingestible sensors, also known as smart pills or smart capsules, are small electronic devices that are ingested and travel through the gastrointestinal tract. These sensors are equipped with various sensors and components that can capture and transmit data, such as temperature, pH levels, pressure, and even images. The data collected by these sensors can be wirelessly transmitted to external devices for analysis and monitoring.
Executive Summary
The ingestible sensor market is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, advancements in healthcare technology, and the rising demand for personalized medicine. These sensors offer several advantages, including non-invasiveness, real-time monitoring, and improved patient compliance. As a result, healthcare providers are increasingly adopting ingestible sensors to enhance patient care and treatment outcomes.
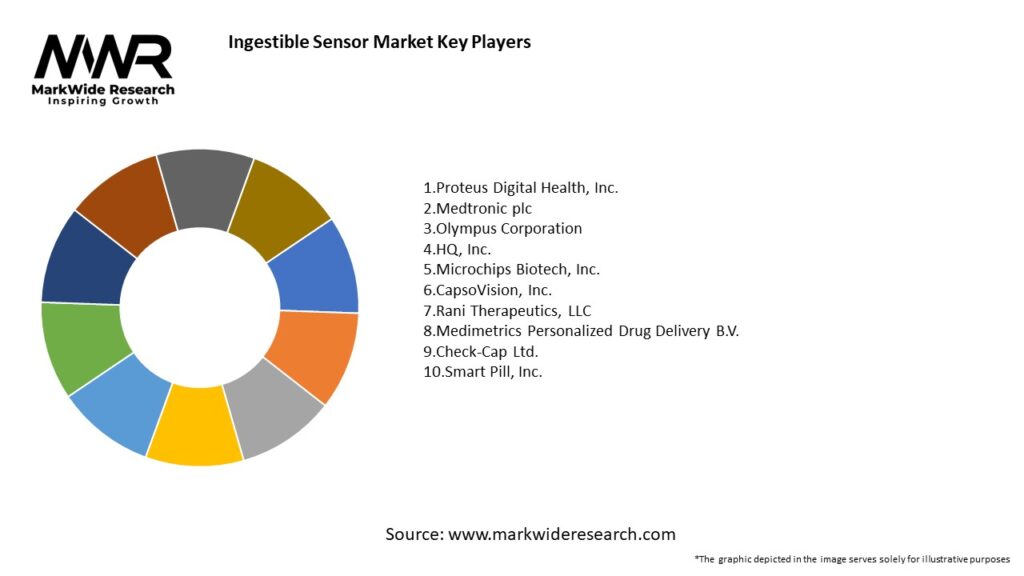
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The ingestible sensor market is highly dynamic, driven by technological advancements, changing healthcare needs, and evolving regulatory frameworks. Rapid innovation, strategic collaborations, and investments in research and development are shaping the market landscape. Additionally, the market is witnessing intense competition among established players and the entry of new startups aiming to disrupt the industry with innovative ingestible sensor solutions.
Regional Analysis
The ingestible sensor market is experiencing significant growth across various regions. North America holds a dominant position due to the presence of advanced healthcare infrastructure, favorable reimbursement policies, and early adoption of healthcare technologies. Europe is also a prominent market, driven by increased healthcare spending and a focus on personalized medicine. Meanwhile, Asia-Pacific is emerging as a lucrative market, fueled by rapid urbanization, a large patient population, and increasing healthcare expenditure.
Competitive Landscape
Leading companies in the Ingestible Sensor Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.

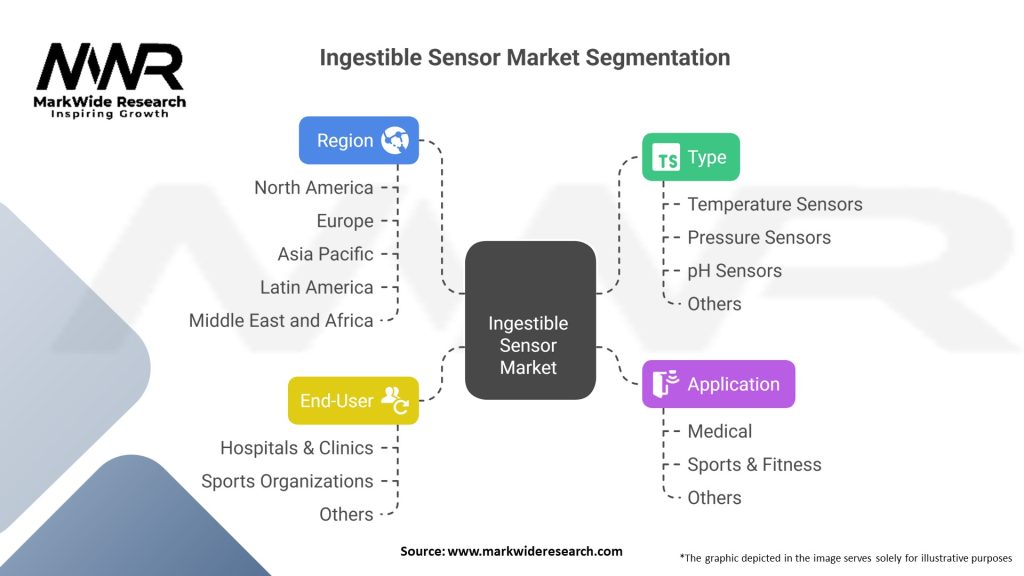
Segmentation
The ingestible sensor market can be segmented based on technology, application, end-user, and geography. By technology, the market can be divided into wireless communication, sensing, and imaging technologies. Application-wise, the market includes gastrointestinal disorders, metabolic disorders, and patient monitoring. End-users of ingestible sensors are hospitals, clinics, and research institutes.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a mixed impact on the ingestible sensor market. On one hand, the pandemic has accelerated the adoption of remote patient monitoring and telehealth solutions, creating opportunities for ingestible sensors. On the other hand, disruptions in the healthcare system and delays in elective procedures have affected the implementation of these sensors. However, the long-term outlook for the market remains positive as the need for remote patient monitoring and personalized healthcare continues to grow.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future of the ingestible sensor market looks promising, with continued advancements in technology, increasing adoption of telehealth, and the growing focus on personalized medicine. The market is expected to witness significant growth, driven by the expanding application areas, integration with IoT, and the rising demand for remote patient monitoring solutions.
Conclusion
The ingestible sensor market is poised for substantial growth, driven by technological advancements, increasing healthcare needs, and the demand for personalized medicine. These sensors offer non-invasiveness, real-time monitoring, and improved patient compliance, leading to enhanced patient care and treatment outcomes. While there are challenges such as regulatory compliance and privacy concerns, opportunities in telehealth, IoT integration, and emerging markets present immense growth potential.
Industry participants need to navigate these dynamics,embrace innovation, and address the evolving needs of the healthcare industry to thrive in the competitive ingestible sensor market. By staying at the forefront of technological advancements, collaborating with stakeholders, and prioritizing patient privacy and security, the market players can capitalize on the growing demand for ingestible sensors and contribute to the advancement of healthcare delivery and patient outcomes.
What is an ingestible sensor?
An ingestible sensor is a device designed to be swallowed, which can monitor various health metrics within the gastrointestinal tract. These sensors are often used for applications such as medication adherence, digestive health monitoring, and chronic disease management.
What are the key companies in the ingestible sensor market?
Key companies in the ingestible sensor market include Proteus Digital Health, Medtronic, and Philips, among others.
What are the main drivers of growth in the ingestible sensor market?
The growth of the ingestible sensor market is driven by increasing demand for remote patient monitoring, advancements in sensor technology, and the rising prevalence of chronic diseases requiring continuous health tracking.
What challenges does the ingestible sensor market face?
Challenges in the ingestible sensor market include regulatory hurdles, concerns over data privacy, and the need for patient acceptance and adherence to using these devices.
What future opportunities exist in the ingestible sensor market?
Future opportunities in the ingestible sensor market include the integration of artificial intelligence for data analysis, expansion into new therapeutic areas, and partnerships with healthcare providers to enhance patient engagement.
What trends are shaping the ingestible sensor market?
Trends in the ingestible sensor market include the development of multi-functional sensors that can track various health parameters simultaneously, increased focus on personalized medicine, and the growing use of telehealth solutions.
Ingestible Sensor Market
| Segmentation | Details |
|---|---|
| Type | Temperature Sensors, Pressure Sensors, pH Sensors, Others |
| Application | Medical, Sports & Fitness, Others |
| End-User | Hospitals & Clinics, Sports Organizations, Others |
| Region | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Middle East and Africa |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the Ingestible Sensor Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at