444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
The global earthquake early warning system market is witnessing significant growth due to the rising awareness about the importance of early detection and warning of seismic activities. An earthquake early warning system is designed to detect and provide alerts for seismic events, enabling individuals and organizations to take necessary precautions and mitigate potential damages.
An earthquake early warning system is a sophisticated technology that uses seismic sensors to detect the initial waves of an earthquake and quickly relay the information to a network of receivers. These receivers then issue alerts to various end-users, such as government agencies, emergency services, infrastructure operators, and the general public, allowing them to take immediate actions to minimize the impact of earthquakes.
Executive Summary
The earthquake early warning system market is experiencing rapid growth due to the increasing adoption of these systems across various sectors. The market is driven by the growing need to protect lives and infrastructure from the devastating effects of earthquakes. This report provides comprehensive insights into the market, including key trends, drivers, restraints, opportunities, and regional analysis.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
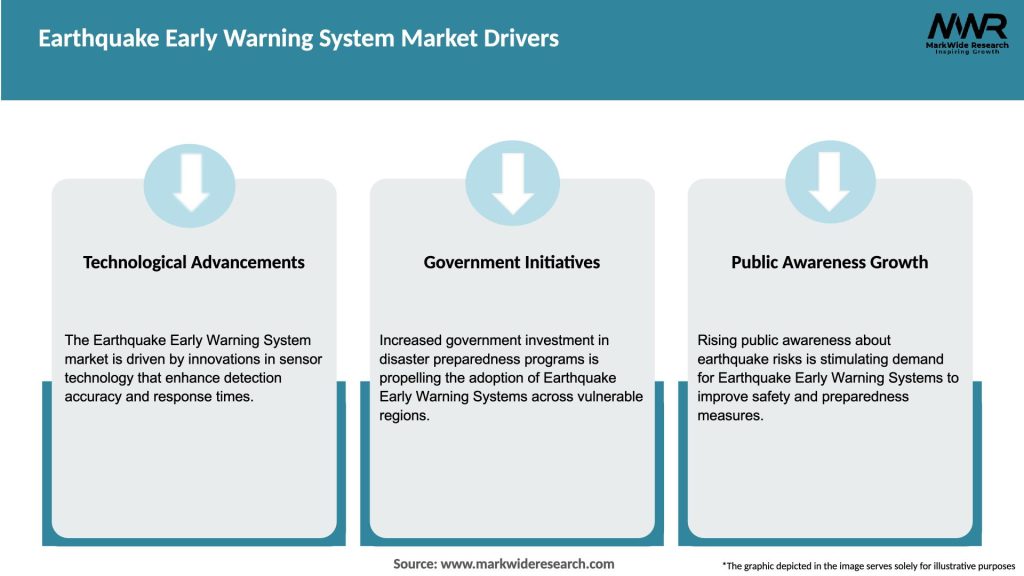
Market Dynamics
The earthquake early warning system market is driven by a combination of factors, including technological advancements, government initiatives, and increasing public awareness. The market is highly competitive, with key players investing in research and development to gain a competitive edge. Additionally, collaborations and partnerships between industry participants are becoming increasingly common to leverage expertise and expand market reach.
Regional Analysis
The earthquake early warning system market is analyzed across major regions, including North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East and Africa. Asia Pacific dominates the market due to the high seismic activity in countries such as Japan, China, and India. North America and Europe also witness significant market growth due to increased investments in early warning systems and infrastructure resilience.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Earthquake Early Warning System Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
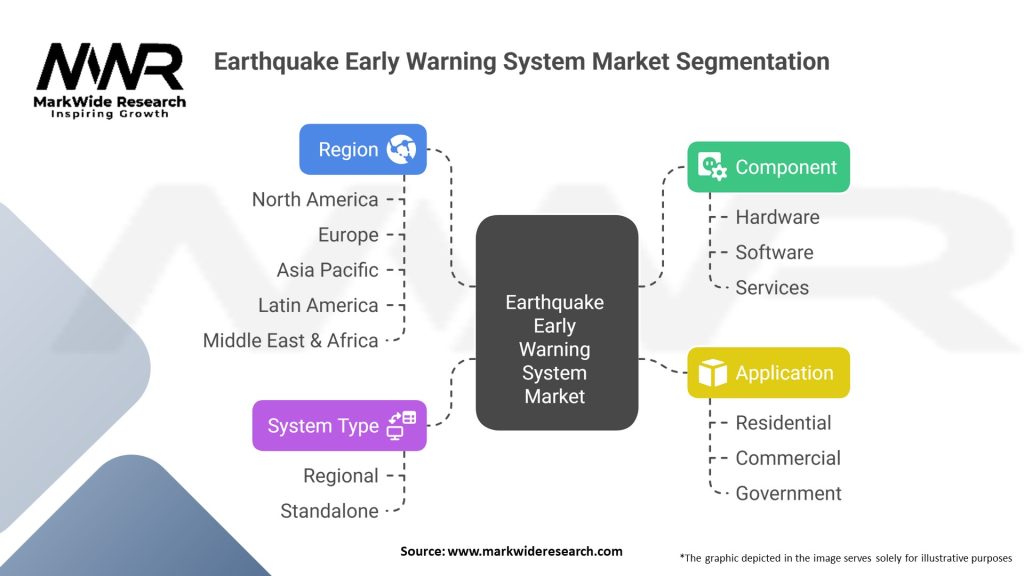
Segmentation
The earthquake early warning system market is segmented based on system type, end-user, and region. By system type, the market is categorized into sensor networks, communication systems, and user interfaces. The end-user segment includes government agencies, emergency services, educational institutions, transportation and infrastructure operators, and others.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The Covid-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on the earthquake early warning system market. While the pandemic itself did not directly affect the need for early warning systems, it influenced the implementation and operations of these systems in several ways:
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future of the earthquake early warning system market appears promising, driven by increasing investments, technological advancements, and growing awareness of the importance of early detection and warning capabilities. Key trends such as AI integration, mobile applications, and IoT connectivity will continue to shape the market.
As seismic activities continue to pose significant risks to lives and infrastructure, governments, organizations, and communities will prioritize the implementation of robust early warning systems. The market is expected to witness substantial growth, particularly in emerging economies where the need for effective disaster management strategies is high.
Conclusion
The earthquake early warning system market is experiencing rapid growth, driven by the rising global awareness of the importance of timely detection and response to seismic activities. Governments, organizations, and individuals are increasingly recognizing the value of these systems in saving lives and minimizing damages.
Technological advancements, such as AI, ML, and IoT integration, are enhancing the capabilities of early warning systems, improving accuracy, speed, and reliability. Public-private partnerships and international collaborations are fostering innovation, knowledge exchange, and resource sharing.
While challenges such as cost, prediction accuracy, and infrastructure limitations exist, concerted efforts in research, public awareness, and infrastructure resilience can address these concerns. The future outlook for the market is promising, with continued growth, innovation, and widespread adoption of earthquake early warning systems expected to make a significant impact in mitigating the effects of seismic events worldwide.
What is an Earthquake Early Warning System?
An Earthquake Early Warning System is a technology designed to detect seismic activity and provide alerts to individuals and organizations before the shaking from an earthquake reaches them. This system can help mitigate damage and save lives by allowing people to take protective actions.
What are the key companies in the Earthquake Early Warning System Market?
Key companies in the Earthquake Early Warning System Market include Early Warning Labs, ShakeAlert, and GeoSIG, among others.
What are the main drivers of growth in the Earthquake Early Warning System Market?
The main drivers of growth in the Earthquake Early Warning System Market include increasing urbanization in seismic zones, advancements in sensor technology, and heightened awareness of earthquake risks among populations.
What challenges does the Earthquake Early Warning System Market face?
Challenges in the Earthquake Early Warning System Market include the high costs of implementation, the need for widespread infrastructure, and the variability in public response to alerts.
What future opportunities exist in the Earthquake Early Warning System Market?
Future opportunities in the Earthquake Early Warning System Market include the integration of AI for improved prediction accuracy, expansion into developing regions, and partnerships with mobile technology providers for broader alert systems.
What trends are shaping the Earthquake Early Warning System Market?
Trends shaping the Earthquake Early Warning System Market include the increasing use of IoT devices for real-time data collection, the development of mobile applications for public alerts, and enhanced collaboration between government agencies and private companies.
Earthquake Early Warning System Market:
| Segmentation | Details |
|---|---|
| Component | Hardware, Software, Services |
| System Type | Regional, Standalone |
| Application | Residential, Commercial, Government |
| Region | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Earthquake Early Warning System Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at