444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
Market Overview
The Germany waste-to-energy market refers to the sector within Germany that focuses on converting waste materials into usable forms of energy. It involves the process of generating electricity and heat through the combustion of waste materials, such as municipal solid waste, biomass, and industrial waste. Waste-to-energy technologies play a crucial role in waste management, environmental sustainability, and renewable energy production.
Meaning
Waste-to-energy is a process that converts waste materials into energy, typically in the form of electricity or heat. It utilizes various technologies, including incineration, anaerobic digestion, gasification, and pyrolysis, to extract energy from waste. The process not only reduces the volume of waste but also produces renewable energy, contributing to resource conservation and mitigating environmental impact.
Executive Summary
The Germany waste-to-energy market has experienced significant growth in recent years due to the country’s commitment to sustainable waste management practices and renewable energy production. The market offers opportunities for waste management companies, technology providers, and energy producers to contribute to the circular economy and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The Germany waste-to-energy market is influenced by a combination of waste management practices, renewable energy policies, and environmental considerations. The market dynamics are shaped by factors such as waste generation patterns, regulatory frameworks, technological advancements, and public perception of waste-to-energy technologies.
Regional Analysis
The Germany waste-to-energy market can be analyzed on a regional basis, considering factors such as waste generation rates, population density, and industrial activities. Regional analysis provides insights into variations in waste management practices, energy demands, and the potential for waste-to-energy projects across different regions of Germany.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Germany Waste-to-Energy Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
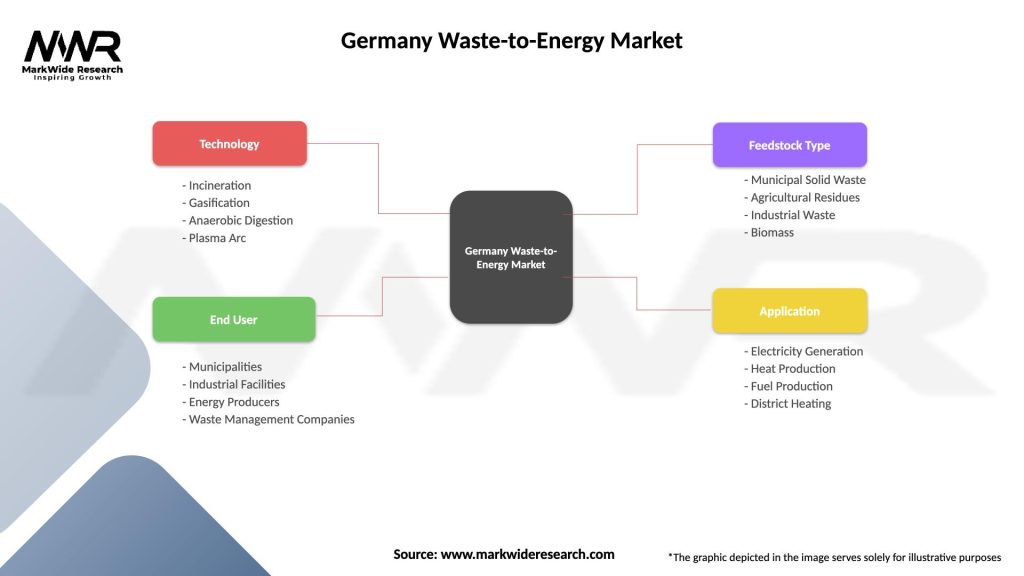
Segmentation
The Germany waste-to-energy market can be segmented based on the following factors:
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
The Germany waste-to-energy market offers several benefits for industry participants and stakeholders, including:
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic had varying impacts on the Germany waste-to-energy market. While waste generation from commercial and industrial sectors may have been affected by temporary closures and reduced activities, the residential waste stream experienced an increase due to changes in consumer behavior. The pandemic also highlighted the importance of resilient waste management systems and sustainable energy sources.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future of the Germany waste-to-energy market holds significant potential, driven by the country’s commitment to sustainable waste management practices, renewable energy targets, and circular economy principles. Technological advancements, including improved waste-to-energy processes and enhanced resource utilization, will contribute to market growth. The integration of waste-to-energy with other renewable energy sources and the development of decentralized waste management solutions will shape the future landscape of the market.
Conclusion
The Germany waste-to-energy market presents opportunities for waste management companies, technology providers, and energy producers to contribute to sustainable waste management practices, renewable energy production, and the circular economy. Waste-to-energy technologies offer a viable solution to address waste generation challenges while producing clean energy. With advancements in technology, public engagement, and collaboration, the Germany waste-to-energy market is poised for continued growth, contributing to a more sustainable and resource-efficient future.
What is Waste-to-Energy?
Waste-to-Energy refers to the process of generating energy in the form of electricity or heat from the treatment of waste. This process involves various technologies that convert waste materials into usable energy, contributing to waste management and energy production.
What are the key players in the Germany Waste-to-Energy Market?
Key players in the Germany Waste-to-Energy Market include companies such as Veolia, Remondis, and EEW Energy from Waste, which are involved in waste management and energy recovery solutions, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the Germany Waste-to-Energy Market?
The growth of the Germany Waste-to-Energy Market is driven by increasing waste generation, rising energy demands, and a strong focus on sustainable waste management practices. Additionally, government policies promoting renewable energy sources play a significant role.
What challenges does the Germany Waste-to-Energy Market face?
The Germany Waste-to-Energy Market faces challenges such as public opposition to waste incineration, regulatory hurdles, and competition from alternative energy sources. These factors can hinder the expansion and acceptance of waste-to-energy facilities.
What opportunities exist in the Germany Waste-to-Energy Market?
Opportunities in the Germany Waste-to-Energy Market include advancements in technology that improve energy efficiency and reduce emissions. Additionally, increasing investments in infrastructure and public-private partnerships can enhance market growth.
What trends are shaping the Germany Waste-to-Energy Market?
Trends in the Germany Waste-to-Energy Market include the integration of circular economy principles, the development of advanced waste sorting technologies, and the growing emphasis on reducing landfill usage. These trends are influencing how waste is managed and energy is produced.
Germany Waste-to-Energy Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Technology | Incineration, Gasification, Anaerobic Digestion, Plasma Arc |
| End User | Municipalities, Industrial Facilities, Energy Producers, Waste Management Companies |
| Feedstock Type | Municipal Solid Waste, Agricultural Residues, Industrial Waste, Biomass |
| Application | Electricity Generation, Heat Production, Fuel Production, District Heating |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Germany Waste-to-Energy Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at