444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The Building-to-Grid Technology market is experiencing significant growth and is poised to revolutionize the way we manage energy consumption in buildings. This innovative technology allows for a seamless integration between buildings and the power grid, enabling efficient energy management, cost savings, and a more sustainable future. Building-to-Grid technology involves the bi-directional flow of electricity and information between buildings and the power grid, allowing for optimized energy usage, demand response, and grid stability. This market overview provides an in-depth analysis of the Building-to-Grid Technology market, including its meaning, key market insights, drivers, restraints, opportunities, dynamics, regional analysis, competitive landscape, segmentation, category-wise insights, benefits for industry participants and stakeholders, SWOT analysis, key trends, the impact of Covid-19, key industry developments, analyst suggestions, future outlook, and a concluding summary.
Meaning
Building-to-Grid Technology refers to the integration of buildings and the power grid through advanced energy management systems and communication technologies. It enables the bi-directional exchange of electricity and information between buildings and the grid, facilitating optimized energy consumption, demand response, and grid stability. This technology allows buildings to actively participate in the electricity market by adjusting their energy consumption based on real-time pricing, grid conditions, and environmental factors. Building-to-Grid Technology also enables the efficient utilization of renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and wind turbines, by integrating them into the grid and balancing the supply-demand dynamics. In essence, it transforms buildings into active participants in the energy ecosystem, promoting sustainability and cost-effectiveness.
Executive Summary
The Building-to-Grid Technology market is witnessing remarkable growth due to the increasing focus on energy efficiency, sustainability, and the integration of renewable energy sources. This technology offers numerous benefits, including optimized energy consumption, cost savings, grid stability, and reduced environmental impact. The market is driven by factors such as government initiatives promoting energy conservation, the rising adoption of smart buildings, and the growing demand for reliable and clean energy. However, certain challenges, such as high implementation costs and interoperability issues, hinder the market’s growth potential. Nevertheless, the market presents significant opportunities for industry participants, including technology providers, building owners, utilities, and policymakers. The market dynamics are characterized by technological advancements, strategic collaborations, and regulatory frameworks aimed at promoting Building-to-Grid Technology adoption. The market is segmented based on technology type, end-use sector, and geography, allowing for targeted strategies and customization. The competitive landscape is highly fragmented, with key players focusing on product development, partnerships, and acquisitions to gain a competitive edge. The market is expected to witness substantial growth in the coming years, driven by ongoing advancements, supportive policies, and increased awareness of the benefits offered by Building-to-Grid Technology.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
The Building-to-Grid Technology market is experiencing robust growth, driven by several key market insights. Firstly, the increasing demand for energy-efficient solutions and sustainable buildings is propelling the adoption of Building-to-Grid Technology. Buildings account for a significant portion of energy consumption, and integrating them into the grid allows for optimized energy usage and reduced carbon emissions. Secondly, government initiatives promoting energy conservation and clean energy sources are creating a favorable regulatory environment for Building-to-Grid Technology. Policies such as tax incentives, grants, and mandatory energy efficiency standards encourage building owners to invest in advanced energy management systems. Thirdly, the growing adoption of smart buildings, equipped with IoT sensors, automation systems, and energy management platforms, provides a solid foundation for Building-to-Grid Technology integration. Smart buildings enable real-time monitoring, data analytics, and automated energy demand response, enhancing grid stability and efficiency. Lastly, the increasing focus on renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, necessitates effective integration into the power grid. Building-to-Grid Technology enables the seamless incorporation of renewable energy generation into the grid, ensuring a balanced supply-demand relationship and promoting a greener energy ecosystem.
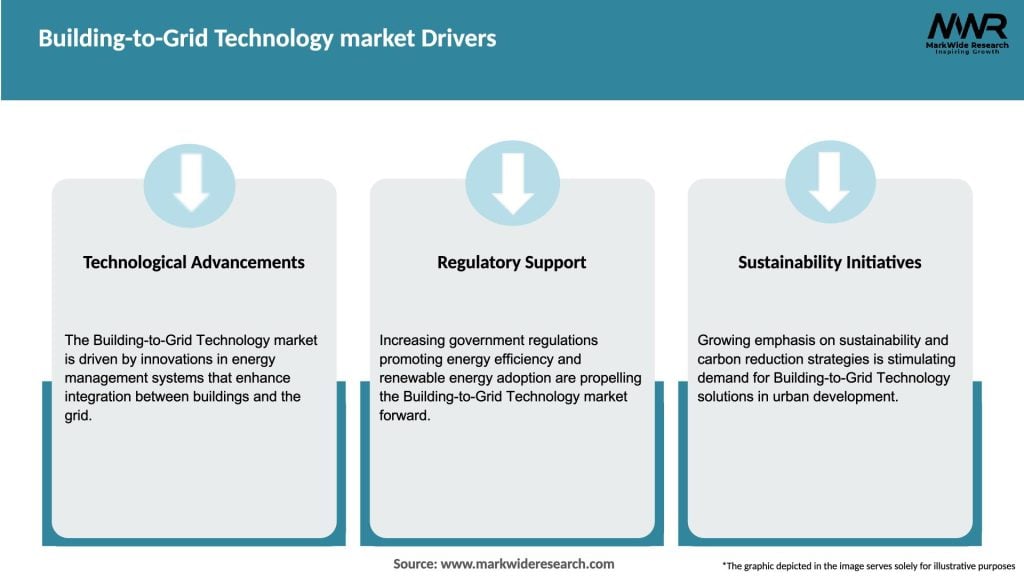
Market Drivers
Several market drivers contribute to the growth and adoption of Building-to-Grid Technology. Firstly, the rising demand for energy efficiency and sustainability drives building owners and operators to implement advanced energy management systems. Building-to-Grid Technology enables precise control and optimization of energy consumption, reducing costs and carbon emissions. Secondly, the increasing need for grid stability and reliability fosters the integration of buildings into the power grid. By actively participating in the grid’s demand response programs, buildings can contribute to grid balancing, load shifting, and peak demand reduction. This reduces strain on the grid during peak hours and enhances its overall stability. Thirdly, government initiatives and policies aimed at energy conservation and clean energy sources provide strong support for Building-to-Grid Technology adoption. Tax incentives, grants, and regulations incentivize building owners to invest in energy-efficient technologies and integrate their buildings with the grid. Moreover, the proliferation of smart buildings equipped with IoT sensors, automation systems, and data analytics platforms creates a conducive environment for Building-to-Grid Technology integration. Smart buildings enable real-time monitoring, analysis, and control of energy consumption, facilitating effective energy management and demand response.
Market Restraints
While the Building-to-Grid Technology market exhibits strong growth potential, it also faces certain restraints that may hinder its widespread adoption. The primary restraint is the high initial cost associated with implementing Building-to-Grid Technology. The installation of advanced energy management systems, smart meters, and communication infrastructure requires a substantial investment, especially for existing buildings. Building owners may hesitate to incur these costs, particularly if they perceive the return on investment to be unclear or long-term. Furthermore, interoperability issues between different building systems, energy management platforms, and grid infrastructure pose a challenge. Standardization efforts are underway to address these concerns, but compatibility issues may still arise during the integration process. Additionally, the lack of awareness and knowledge about Building-to-Grid Technology among building owners, operators, and utilities can impede adoption. Education and outreach programs are essential to showcase the benefits and long-term cost savings associated with this technology. Finally, cybersecurity and data privacy concerns also present challenges. Building-to-Grid Technology involves the exchange of sensitive information between buildings and the grid, requiring robust security measures to safeguard against potential cyber threats.
Market Opportunities
The Building-to-Grid Technology market presents significant opportunities for various industry participants, including technology providers, building owners, utilities, and policymakers. Firstly, technology providers have the opportunity to develop innovative solutions that address the specific needs of building owners and operators. Advanced energy management systems, data analytics platforms, and communication technologies can be further enhanced to optimize energy consumption, grid integration, and demand response. Secondly, building owners can benefit from reduced energy costs, enhanced sustainability, and improved grid reliability by adopting Building-to-Grid Technology. They have the opportunity to participate in demand response programs, earn incentives, and contribute to a greener and more efficient energy ecosystem. Thirdly, utilities can leverage Building-to-Grid Technology to enhance grid stability, load balancing, and peak demand management. By collaborating with building owners and integrating their energy consumption patterns into grid operations, utilities can optimize grid performance and avoid costly infrastructure upgrades. Lastly, policymakers have the opportunity to create a supportive regulatory environment for Building-to-Grid Technology. By incentivizing its adoption through grants, tax incentives, and regulations, policymakers can accelerate the transition towards a sustainable and resilient energy future.
Market Dynamics
The Building-to-Grid Technology market is driven by several dynamic factors that influence its growth and development. Firstly, technological advancements play a crucial role in shaping the market dynamics. Continuous innovations in energy management systems, IoT sensors, communication technologies, and data analytics platforms enhance the capabilities and functionalities of Building-to-Grid Technology. These advancements enable more precise control, real-time monitoring, and optimized energy consumption, fostering its adoption. Secondly, strategic collaborations between technology providers, building owners, and utilities are instrumental in driving market growth. Partnerships and joint ventures allow for the development of integrated solutions, interoperability standards, and seamless grid integration. Thirdly, regulatory frameworks and government policies significantly impact the market dynamics. Supportive policies, such as tax incentives, grants, and mandatory energy efficiency standards, incentivize building owners to invest in Building-to-Grid Technology. Moreover, the integration of renewable energy sources into the power grid requires regulatory frameworks that enable their seamless integration and balanced utilization. Finally, customer awareness and education programs play a vital role in driving market growth. Building owners and operators need to understand the benefits, cost savings, and long-term value proposition associated with Building-to-Grid Technology. Awareness campaigns, demonstrations, and case studies are essential to showcase successful implementations and encourage wider adoption.
Regional Analysis
The Building-to-Grid Technology market exhibits regional variations in terms of adoption, market size, and growth potential. North America, with its advanced infrastructure, supportive regulatory environment, and increasing focus on energy efficiency, represents a significant market for Building-to-Grid Technology. The region is witnessing a growing number of smart buildings, government initiatives promoting clean energy, and collaborations between technology providers and utilities. Europe is also a key market for Building-to-Grid Technology, driven by the region’s commitment to renewable energy, energy efficiency targets, and grid stability. The European Union’s Clean Energy Package and Energy Performance of Buildings Directive provide a favorable regulatory framework for market growth. Additionally, the Asia Pacific region is witnessing rapid urbanization, population growth, and increasing energy demand, making it a promising market for Building-to-Grid Technology. Governments in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea are implementing policies and initiatives to promote energy efficiency, grid integration, and sustainability. Other regions, such as Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa, are also witnessing gradual adoption of Building-to-Grid Technology, driven by growing awareness, supportive policies, and infrastructure development.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Building-to-Grid Technology Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
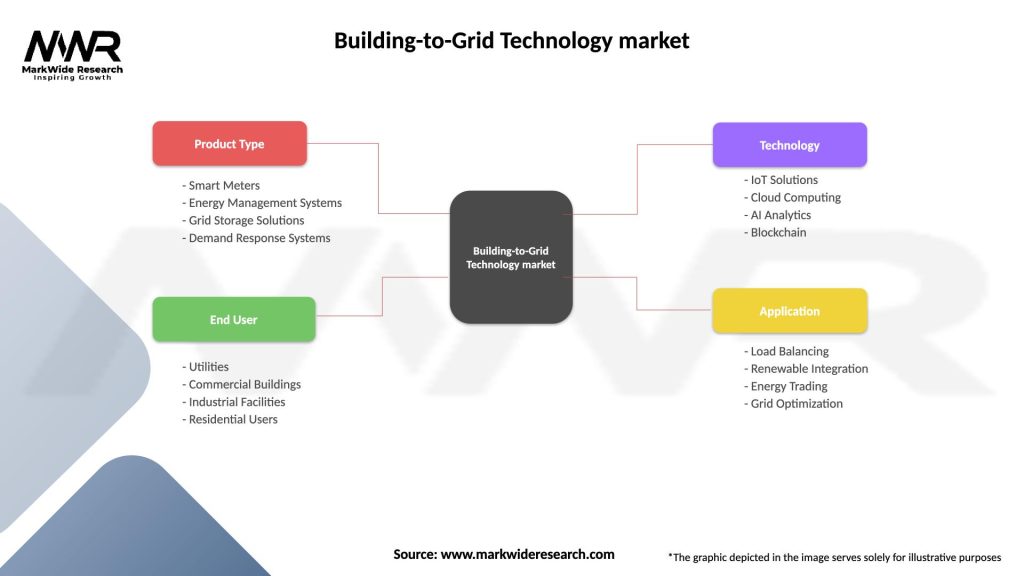
Segmentation
The Building-to-Grid Technology market can be segmented based on technology type, end-use sector, and geography.
Based on technology type, the market can be segmented into:
Based on the end-use sector, the market can be segmented into:
Based on geography, the market can be segmented into:
Category-wise Insights
The Building-to-Grid Technology market offers category-wise insights that provide a deeper understanding of its various aspects.
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
The adoption of Building-to-Grid Technology offers several key benefits for industry participants and stakeholders.
SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis of the Building-to-Grid Technology market provides insights into its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
Market Key Trends
Several key trends are shaping the Building-to-Grid Technology market and driving its growth:
Covid-19 Impact
The Covid-19 pandemic has had both short-term and long-term impacts on the Building-to-Grid Technology market. In the short term, the pandemic led to a slowdown in construction activities and building renovations, affecting the adoption of Building-to-Grid Technology. Building owners and operators focused on immediate cost-saving measures and operational efficiency rather than investing in long-term energy management solutions.
However, the pandemic also highlighted the importance of resilient and sustainable buildings. As businesses and organizations adapted to remote work and social distancing measures, the need for flexible and efficient building operations became evident. Building-to-Grid Technology offers solutions that enable remote monitoring, control, and optimization of energy consumption, making it an attractive option for building owners seeking operational resilience.
Moreover, the pandemic emphasized the significance of grid stability and demand response capabilities. Fluctuations in energy demand and supply due to changes in work patterns and economic activities required efficient demand response mechanisms to maintain grid stability. Building-to-Grid Technology can play a crucial role in enabling demand response and load management, ensuring grid reliability during unforeseen circumstances.
In the long term, the pandemic has increased awareness and accelerated the adoption of technologies that promote energy efficiency, sustainability, and remote management capabilities. Building owners and operators are expected to prioritize investments in advanced energy management systems, smart building solutions, and Building-to-Grid Technology to enhance operational resilience and cost savings.
Key Industry Developments
The Building-to-Grid Technology market has witnessed several key industry developments that shape its growth trajectory:
Analyst Suggestions
Based on the analysis of the Building-to-Grid Technology market, analysts provide the following suggestions:
Future Outlook
The future outlook for the Building-to-Grid Technology market is promising, with significant growth potential and increasing adoption expected. The market will be driven by factors such as the rising demand for energy efficiency, the integration of renewable energy sources, and supportive government policies. The continued advancement of technology, including IoT, data analytics, and artificial intelligence, will further enhance the capabilities of Building-to-Grid Technology. As building owners and operators become more aware of the benefits and cost savings associated with this technology, adoption rates are expected to increase. Furthermore, the increasing need for grid stability, resilience, and demand response capabilities will drive the integration of buildings into the power grid. The market will witness strategic partnerships, collaborations, and acquisitions as players strive to gain a competitive edge. Overall, the future of the Building-to-Grid Technology market looks promising, with sustainable and efficient energy management becoming a key priority for buildings and the power grid.
Conclusion
The Building-to-Grid Technology market is witnessing significant growth and holds immense potential for transforming the energy management landscape. This technology enables seamless integration between buildings and the power grid, facilitating optimized energy consumption, demand response, and grid stability. Building-to-Grid Technology offers numerous benefits, including cost savings, enhanced sustainability, and increased grid reliability. The market is driven by factors such as the rising demand for energy efficiency, supportive government policies, and the integration of renewable energy sources. However, challenges such as high implementation costs and interoperability issues need to be addressed. The market presents opportunities for technology providers, building owners, utilities, and policymakers. Continuous technological advancements, collaborations, and supportive regulatory frameworks will drive market growth. The future outlook for the Building-to-Grid Technology market is promising, with increasing adoption and a transition towards a more sustainable and resilient energy future.
What is Building-to-Grid Technology?
Building-to-Grid Technology refers to systems and solutions that enable buildings to interact with the electrical grid, allowing for energy efficiency, demand response, and integration of renewable energy sources. This technology facilitates the management of energy consumption and generation within buildings, contributing to a more sustainable energy ecosystem.
What are the key players in the Building-to-Grid Technology market?
Key players in the Building-to-Grid Technology market include Siemens, Schneider Electric, and Honeywell, which provide innovative solutions for energy management and grid integration. These companies focus on developing smart building technologies and energy storage systems, among others.
What are the main drivers of the Building-to-Grid Technology market?
The main drivers of the Building-to-Grid Technology market include the increasing demand for energy efficiency, the rise of renewable energy sources, and government initiatives promoting smart grid technologies. Additionally, advancements in IoT and automation are enhancing building energy management capabilities.
What challenges does the Building-to-Grid Technology market face?
Challenges in the Building-to-Grid Technology market include high initial investment costs, regulatory hurdles, and the need for interoperability among different systems. Additionally, the complexity of integrating various technologies can hinder widespread adoption.
What opportunities exist in the Building-to-Grid Technology market?
Opportunities in the Building-to-Grid Technology market include the growing trend of smart cities, advancements in energy storage solutions, and increasing consumer awareness of sustainability. These factors are driving innovation and investment in building energy management systems.
What trends are shaping the Building-to-Grid Technology market?
Trends shaping the Building-to-Grid Technology market include the integration of artificial intelligence for predictive energy management, the rise of decentralized energy systems, and the increasing use of blockchain for energy transactions. These innovations are enhancing the efficiency and reliability of energy distribution.
Building-to-Grid Technology market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Smart Meters, Energy Management Systems, Grid Storage Solutions, Demand Response Systems |
| End User | Utilities, Commercial Buildings, Industrial Facilities, Residential Users |
| Technology | IoT Solutions, Cloud Computing, AI Analytics, Blockchain |
| Application | Load Balancing, Renewable Integration, Energy Trading, Grid Optimization |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Building-to-Grid Technology Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at