444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The 3D printing technology has revolutionized various industries, and the healthcare sector is no exception. 3D printing in healthcare refers to the use of additive manufacturing techniques to create customized medical devices, implants, prosthetics, and anatomical models. This technology has significantly impacted the healthcare industry by offering personalized solutions, enhancing patient care, and enabling medical professionals to perform complex procedures with greater precision.
Meaning
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process of creating three-dimensional objects by layering materials based on digital designs. In the context of healthcare, 3D printing involves the production of medical devices, implants, and anatomical models by depositing material layer by layer. This technology allows for the creation of complex geometries and customized designs, enabling healthcare providers to deliver personalized treatment options.
Executive Summary
The 3D printing in healthcare market has witnessed rapid growth in recent years, driven by advancements in technology, increasing demand for personalized healthcare solutions, and the rising prevalence of chronic diseases. This market offers significant opportunities for both established players and new entrants to develop innovative products and solutions. However, it also faces certain challenges, such as regulatory hurdles and high implementation costs. Despite these challenges, the market is expected to continue its upward trajectory in the coming years, fueled by ongoing research and development activities.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The 3D printing in healthcare market is characterized by rapid technological advancements, increasing adoption of the technology by healthcare providers, and strong competition among key players. The market dynamics are influenced by factors such as government regulations, reimbursement policies, and the ability of market participants to innovate and deliver cost-effective solutions. Continuous research and development activities are driving the market forward, with new materials, improved printing techniques, and novel applications being explored.
Regional Analysis
North America currently holds the largest share in the global 3D printing in healthcare market. The region is characterized by well-established healthcare infrastructure, significant investments in research and development, and a high level of awareness about the potential benefits of 3D printing technology. Europe follows closely, driven by strong support from government initiatives and a growing demand for personalized medical solutions. The Asia Pacific region is witnessing rapid growth, propelled by increasing healthcare expenditure, rising chronic disease burden, and the presence of a large patient population.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the 3D Printing in Healthcare Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
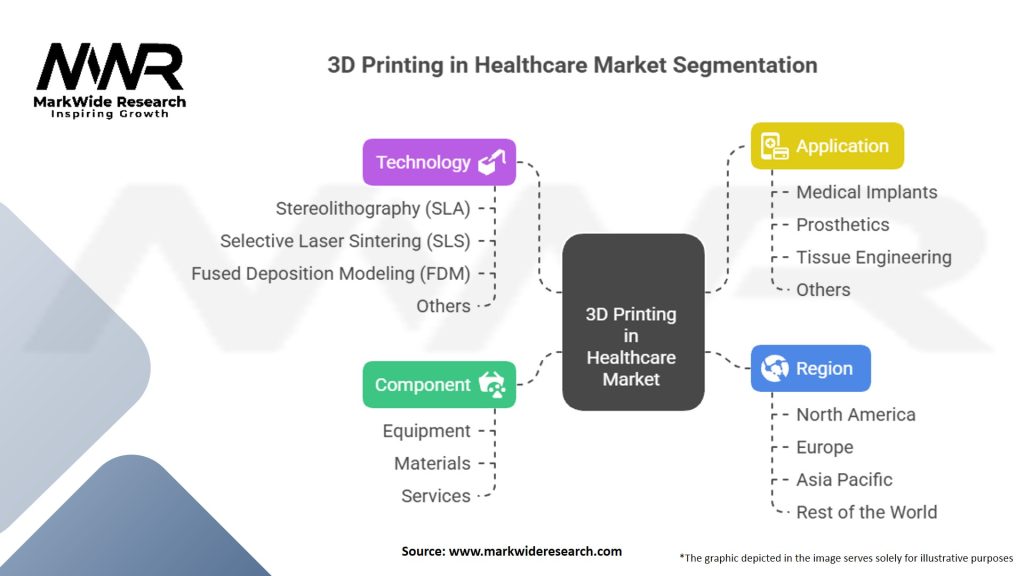
Segmentation
The 3D printing in healthcare market can be segmented based on product type, technology, material, application, and end-user.
By product type:
By technology:
By material:
By application:
By end-user:
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic had a significant impact on the 3D printing in healthcare market. The technology played a crucial role in addressing the shortage of essential medical supplies, such as personal protective equipment (PPE), ventilator components, and nasopharyngeal swabs. 3D printing allowed for rapid production and distribution of these critical items, helping to alleviate supply chain disruptions.
The pandemic also highlighted the potential of 3D printing for decentralized manufacturing and personalized healthcare solutions. The ability to quickly produce medical devices and implants on-site reduced dependence on global supply chains and enabled healthcare providers to respond to patient needs effectively.
The increased adoption of telemedicine and remote healthcare during the pandemic further emphasized the importance of 3D printing in enabling virtual collaboration and providing remote access to medical solutions. The technology allowed for the creation of anatomical models and surgical guides that could be shared digitally, facilitating remote surgical planning and education.
Overall, the COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of 3D printing in healthcare and highlighted its potential in crisis situations, driving further innovation and investment in the market.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future of 3D printing in healthcare looks promising, with a growing demand for personalized medical solutions and ongoing technological advancements. The market is expected to witness substantial growth, driven by factors such as expanding applications, increasing healthcare expenditure, and the need for efficient healthcare delivery systems.
Bioprinting and tissue engineering hold significant potential for the future, with the aim of producing functional organs for transplantation and advancing regenerative medicine. The integration of 3D printing with other technologies, such as artificial intelligence and nanotechnology, will further enhance the capabilities of this field.
However, challenges related to regulations, reimbursement policies, and intellectual property rights need to be addressed for the market to reach its full potential. Continued collaboration between industry players, research institutions, and regulatory authorities will be crucial in shaping the future of 3D printing in healthcare.
Conclusion
3D printing in healthcare has emerged as a transformative technology, enabling the production of personalized medical devices, implants, and anatomical models. This technology offers numerous benefits, including improved patient care, enhanced surgical planning, and cost savings. Despite challenges related to regulations and implementation costs, the market continues to grow due to advancements in technology, increasing demand for personalized healthcare solutions, and collaboration between industry players and healthcare providers.
What is 3D printing in healthcare?
3D printing in healthcare refers to the use of additive manufacturing technologies to create medical devices, prosthetics, implants, and anatomical models. This innovative approach allows for customization and rapid prototyping, enhancing patient care and surgical planning.
Who are the key players in the 3D printing in healthcare market?
Key players in the 3D printing in healthcare market include Stratasys, Materialise, and 3D Systems, which are known for their advanced printing technologies and applications in medical devices and bioprinting, among others.
What are the main drivers of growth in the 3D printing in healthcare market?
The main drivers of growth in the 3D printing in healthcare market include the increasing demand for personalized medical solutions, advancements in bioprinting technologies, and the rising adoption of 3D printing for surgical planning and education.
What challenges does the 3D printing in healthcare market face?
Challenges in the 3D printing in healthcare market include regulatory hurdles, the need for standardization in materials and processes, and concerns regarding the long-term biocompatibility of printed products.
What future opportunities exist in the 3D printing in healthcare market?
Future opportunities in the 3D printing in healthcare market include the development of bio-printed organs, expansion into new therapeutic areas, and the integration of artificial intelligence to enhance design and manufacturing processes.
What are the current trends in the 3D printing in healthcare market?
Current trends in the 3D printing in healthcare market include the increasing use of patient-specific models for surgical preparation, the rise of on-demand manufacturing for medical supplies, and the exploration of new materials for enhanced functionality.
3D Printing in Healthcare Market
| Segmentation | Details in the Segmentation |
|---|---|
| Component | Equipment, Materials, Services |
| Technology | Stereolithography (SLA), Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Others |
| Application | Medical Implants, Prosthetics, Tissue Engineering, Others |
| Region | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Rest of the World |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the 3D Printing in Healthcare Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at